Salvinorin A: a potent naturally occurring nonnitrogenous kappa opioid selective agonist
- PMID: 12192085
- PMCID: PMC129372
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.182234399
Salvinorin A: a potent naturally occurring nonnitrogenous kappa opioid selective agonist
Abstract
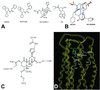
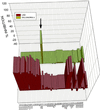
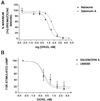
Salvia divinorum, whose main active ingredient is the neoclerodane diterpene Salvinorin A, is a hallucinogenic plant in the mint family that has been used in traditional spiritual practices for its psychoactive properties by the Mazatecs of Oaxaca, Mexico. More recently, S. divinorum extracts and Salvinorin A have become more widely used in the U.S. as legal hallucinogens. We discovered that Salvinorin A potently and selectively inhibited (3)H-bremazocine binding to cloned kappa opioid receptors. Salvinorin A had no significant activity against a battery of 50 receptors, transporters, and ion channels and showed a distinctive profile compared with the prototypic hallucinogen lysergic acid diethylamide. Functional studies demonstrated that Salvinorin A is a potent kappa opioid agonist at cloned kappa opioid receptors expressed in human embryonic kidney-293 cells and at native kappa opioid receptors expressed in guinea pig brain. Importantly, Salvinorin A had no actions at the 5-HT(2A) serotonin receptor, the principal molecular target responsible for the actions of classical hallucinogens. Salvinorin A thus represents, to our knowledge, the first naturally occurring nonnitrogenous opioid-receptor subtype-selective agonist. Because Salvinorin A is a psychotomimetic selective for kappa opioid receptors, kappa opioid-selective antagonists may represent novel psychotherapeutic compounds for diseases manifested by perceptual distortions (e.g., schizophrenia, dementia, and bipolar disorders). Additionally, these results suggest that kappa opioid receptors play a prominent role in the modulation of human perception.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Salvinorin A, an active component of the hallucinogenic sage salvia divinorum is a highly efficacious kappa-opioid receptor agonist: structural and functional considerations.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004 Mar;308(3):1197-203. doi: 10.1124/jpet.103.059394. Epub 2004 Jan 8. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004. PMID: 14718611
-
Salvinorin A: the "magic mint" hallucinogen finds a molecular target in the kappa opioid receptor.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2003 Mar;24(3):107-9. doi: 10.1016/S0165-6147(03)00027-0. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2003. PMID: 12628350 Review.
-
A unique natural selective kappa-opioid receptor agonist, salvinorin A, and its roles in human therapeutics.Phytochemistry. 2017 May;137:9-14. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2017.02.001. Epub 2017 Feb 10. Phytochemistry. 2017. PMID: 28190678
-
Kappa-opioid receptor-mediated effects of the plant-derived hallucinogen, salvinorin A, on inverted screen performance in the mouse.Behav Pharmacol. 2005 Dec;16(8):627-33. doi: 10.1097/00008877-200512000-00005. Behav Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16286814
-
Neuropharmacology of the naturally occurring kappa-opioid hallucinogen salvinorin A.Pharmacol Rev. 2011 Jun;63(2):316-47. doi: 10.1124/pr.110.003244. Epub 2011 Mar 28. Pharmacol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21444610 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clerodane diterpenes: sources, structures, and biological activities.Nat Prod Rep. 2016 Oct 28;33(10):1166-226. doi: 10.1039/c5np00137d. Epub 2016 Jul 18. Nat Prod Rep. 2016. PMID: 27433555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological and phosphoproteomic approaches to roles of protein kinase C in kappa opioid receptor-mediated effects in mice.Neuropharmacology. 2020 Dec 15;181:108324. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108324. Epub 2020 Sep 22. Neuropharmacology. 2020. PMID: 32976891 Free PMC article.
-
The kappa opioid receptor: from addiction to depression, and back.Front Psychiatry. 2014 Dec 8;5:170. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2014.00170. eCollection 2014. Front Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 25538632 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kappa-opioid receptor signaling in the striatum as a potential modulator of dopamine transmission in cocaine dependence.Front Psychiatry. 2013 Jun 3;4:44. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2013.00044. eCollection 2013. Front Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 23760592 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand/kappa-opioid receptor interactions: insights from the X-ray crystal structure.Eur J Med Chem. 2013 Aug;66:114-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2013.05.021. Epub 2013 May 30. Eur J Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23792349 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Valdes L J., III J Psychoactive Drugs. 1994;26:277–283. - PubMed
-
- Giroud C, Felber F, Augsburger M, Horisberger B, Rivier L, Mangin P. Forensic Sci Int. 2000;112:143–150. - PubMed
-
- Siebert D J. J Ethnopharmacol. 1994;43:53–56. - PubMed
-
- Koreeda, M., Brown, L. & Valdes, I. L. (1990) Chem. Lett. 2015–2018.
-
- Valdes L J, Butler W M, Hatfield G M, Paul A G, Koreeda M. J Org Chem. 1984;49:4716–7720.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Molecular Biology Databases

