Lytic replication-associated protein (RAP) encoded by Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus causes p21CIP-1-mediated G1 cell cycle arrest through CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-alpha
- PMID: 12145325
- PMCID: PMC125013
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.162352299
Lytic replication-associated protein (RAP) encoded by Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus causes p21CIP-1-mediated G1 cell cycle arrest through CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-alpha
Abstract
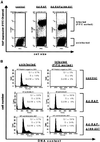
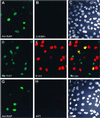
Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) is an oncogenic DNA virus that causes Kaposi sarcoma and AIDS-related primary effusion lymphoma (PEL). Here we show that KSHV lytic cycle replication in PEL cells induces G(1) cell cycle arrest, presumably to facilitate the progression of viral DNA replication. Expression of a KSHV-encoded early lytic protein referred to as RAP or K8 is induced within 12-24 h after the onset of lytic cycle induction in host PEL cells, and coincides with increased levels of both the endogenous C/EBPalpha and p21(CIP-1) proteins in the nucleus of the same cells. The KSHV RAP protein binds to C/EBPalpha in vitro and stimulates C/EBPalpha-induced expression from both the C/EBPalpha and p21 promoters in cotransfected cells. A recombinant adenovirus expressing the RAP protein induced the expression of both the C/EBPalpha and p21 proteins in primary human fibroblasts, and flow cytometric analysis revealed a dramatic inhibition of G(1) to S cell cycle progression in the same cells. All of these effects were abolished in cells that lack C/EBPalpha or by deletion of the basic/leucine zipper region in RAP that interacts with C/EBPalpha. Therefore, C/EBPalpha is essential for the p21-mediated inhibition of G(1) to S-phase progression by RAP in KSHV-infected host cells.
Figures
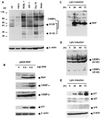
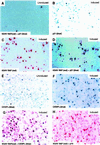
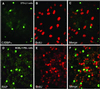
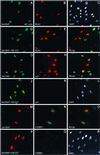
Similar articles
-
Cell cycle arrest by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus replication-associated protein is mediated at both the transcriptional and posttranslational levels by binding to CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha and p21(CIP-1).J Virol. 2003 Aug;77(16):8893-914. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.16.8893-8914.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12885907 Free PMC article.
-
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-alpha is induced during the early stages of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) lytic cycle reactivation and together with the KSHV replication and transcription activator (RTA) cooperatively stimulates the viral RTA, MTA, and PAN promoters.J Virol. 2003 Sep;77(17):9590-612. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.17.9590-9612.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12915572 Free PMC article.
-
Role of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (C/EBPalpha) in activation of the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) lytic-cycle replication-associated protein (RAP) promoter in cooperation with the KSHV replication and transcription activator (RTA) and RAP.J Virol. 2003 Jan;77(1):600-23. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.1.600-623.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12477864 Free PMC article.
-
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha interacts with ZTA and mediates ZTA-induced p21(CIP-1) accumulation and G(1) cell cycle arrest during the Epstein-Barr virus lytic cycle.J Virol. 2003 Jan;77(2):1481-500. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.2.1481-1500.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12502863 Free PMC article.
-
C/EBPalpha: a tumour suppressor in multiple tissues?Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 Aug;1766(1):88-103. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2006.02.003. Epub 2006 Mar 24. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 16616425 Review.
Cited by
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus immunoevasion and tumorigenesis: two sides of the same coin?Annu Rev Microbiol. 2003;57:609-39. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.57.030502.090824. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 14527293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus ORF57 functions as a viral splicing factor and promotes expression of intron-containing viral lytic genes in spliceosome-mediated RNA splicing.J Virol. 2008 Mar;82(6):2792-801. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01856-07. Epub 2008 Jan 9. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18184716 Free PMC article.
-
Disrupting galectin-1 interactions with N-glycans suppresses hypoxia-driven angiogenesis and tumorigenesis in Kaposi's sarcoma.J Exp Med. 2012 Oct 22;209(11):1985-2000. doi: 10.1084/jem.20111665. Epub 2012 Oct 1. J Exp Med. 2012. PMID: 23027923 Free PMC article.
-
Localization of Double-Strand Break Repair Proteins to Viral Replication Compartments following Lytic Reactivation of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus.J Virol. 2017 Oct 27;91(22):e00930-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00930-17. Print 2017 Nov 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28855246 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the Rta/Orf50 transactivator proteins of gamma-2-herpesviruses.J Virol. 2004 May;78(10):5491-9. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.10.5491-5499.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15113928 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chang Y., Cesarman, E., Pessin, M. S., Lee, F., Culpepper, J., Knowles, D. M. & Moore, P. S. (1994) Science 266, 1865-1869. - PubMed
-
- Whitby D., Howard, M. R., Tenant-Flowers, M., Brink, N. S., Copas, A., Boshoff, C., Hatzioannou, T., Suggett, F. E., Aldam, D. M., Denton, A. S., et al. (1995) Lancet 346, 799-802. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

