The amino-terminal half of Sendai virus C protein is not responsible for either counteracting the antiviral action of interferons or down-regulating viral RNA synthesis
- PMID: 12072511
- PMCID: PMC136303
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.14.7114-7124.2002
The amino-terminal half of Sendai virus C protein is not responsible for either counteracting the antiviral action of interferons or down-regulating viral RNA synthesis
Abstract
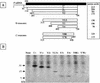
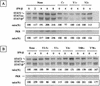
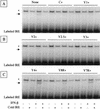
The Sendai virus C proteins, C', C, Y1, and Y2, are a nested set of independently initiated carboxy-coterminal proteins translated from a reading frame overlapping the P frame on the P mRNA. The C proteins are extremely versatile and have been shown to counteract the antiviral action of interferons (IFNs), to down-regulate viral RNA synthesis, and to promote virus assembly. Using the stable cell lines expressing the C, Y1, Y2, or truncated C protein, we investigated the region responsible for anti-IFN action and for down-regulating viral RNA synthesis. Truncation from the amino terminus to the middle of the C protein maintained the inhibition of the signal transduction of IFNs, the formation of IFN-stimulated gene factor 3 (ISGF3) complex, the generation of the anti-vesicular stomatitis virus state, and the synthesis of viral RNA, but further truncation resulted in the simultaneous loss of all of these inhibitory activities. A relatively small truncation from the carboxy terminus also abolished all of these inhibitory activities. These data indicated that the activities of the C protein to counteract the antiviral action of IFNs and to down-regulate viral RNA synthesis were not encoded within a region of at least 98 amino acids in its amino-terminal half.
Figures

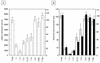
Similar articles
-
Y2, the smallest of the Sendai virus C proteins, is fully capable of both counteracting the antiviral action of interferons and inhibiting viral RNA synthesis.J Virol. 2001 Apr;75(8):3802-10. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.8.3802-3810.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11264369 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the amino acid residues of sendai virus C protein that are critically involved in its interferon antagonism and RNA synthesis down-regulation.J Virol. 2004 Jul;78(14):7443-54. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.14.7443-7454.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15220418 Free PMC article.
-
Longer and shorter forms of Sendai virus C proteins play different roles in modulating the cellular antiviral response.J Virol. 2001 Aug;75(15):6800-7. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.15.6800-6807.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11435558 Free PMC article.
-
[Interferons: between structure and function].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2014 May 6;68:428-40. doi: 10.5604/17322693.1101229. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2014. PMID: 24864095 Review. Polish.
-
Paramyxovirus accessory proteins as interferon antagonists.Microbiol Immunol. 2001;45(12):787-800. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.2001.tb01315.x. Microbiol Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11838896 Review.
Cited by
-
C Proteins: Controllers of Orderly Paramyxovirus Replication and of the Innate Immune Response.Viruses. 2022 Jan 12;14(1):137. doi: 10.3390/v14010137. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35062341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conserved charged amino acids within Sendai virus C protein play multiple roles in the evasion of innate immune responses.PLoS One. 2010 May 19;5(5):e10719. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010719. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20502666 Free PMC article.
-
Domain within the C protein of human parainfluenza virus type 3 that regulates interferon signaling.Gene Expr. 2010;15(1):43-50. doi: 10.3727/105221610x12819686555132. Gene Expr. 2010. PMID: 21061916 Free PMC article.
-
C Protein is Essential for Canine Distemper Virus Virulence and Pathogenicity in Ferrets.J Virol. 2021 Feb 15;95(4):e01840-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01840-20. Epub 2020 Nov 25. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33239455 Free PMC article.
-
Trafficking of Sendai virus nucleocapsids is mediated by intracellular vesicles.PLoS One. 2010 Jun 7;5(6):e10994. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010994. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20543880 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Curran, J., J.-B. Marq, and D. Kolakofsky. 1992. The Sendai virus nonstructural C proteins specifically inhibit viral mRNA synthesis. Virology 189:647-656. - PubMed
-
- Delenda, C., S. Hausmann, D. Garcin, and D. Kolakofsky. 1997. Normal cellular replication of Sendai virus without the trans-frame, nonstructural V protein. Virology 228:55-62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

