Human monocytic cell lines transformed in vitro by Epstein-Barr virus display a type II latency and LMP-1-dependent proliferation
- PMID: 12050358
- PMCID: PMC136267
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.13.6460-6472.2002
Human monocytic cell lines transformed in vitro by Epstein-Barr virus display a type II latency and LMP-1-dependent proliferation
Abstract
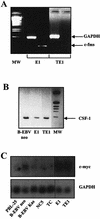
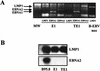
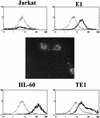
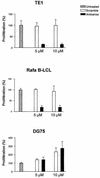
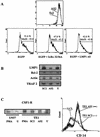
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) classically infects and transforms B lymphocytes in vitro, yielding lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs). In contrast to other herpesviruses, EBV is not described as an infectious agent for monocytes. However, recent papers described in vitro infection of monocytes leading to abortive or transient viral expression. In the present study, we report the characterization of E1, a monocytic cell line infected and transformed by EBV. This cell line was derived from an LCL by a drastic electroporation and selection of neomycin-resistant cells, unfavorable to B-cell outgrowth. E1 expressed surface molecules of monocytic lineage (CD14, major histocompatibility complex class II, and CD80) and the c-fms gene, a highly specific marker for the monocytic lineage. This cell line is able to phagocytose and secrete proinflammatory monokines tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin-6 (IL-6), and IL-8. E1 cells are tumorigenic after injection in nude mice, and a monocytic cell line obtained from one of these tumors (TE1) displayed immunophenotype and functional properties similar to those of E1. We detected the presence of the EBV genome in both cell lines, as well as expression of the EBNA-1 and LMP-1, but not EBNA-2, viral genes, characteristic of a type II latency. LMP-1 influences the phenotype of these monocytic cell lines, as demonstrated by down-regulation of cell proliferation and membrane intercellular adhesion molecule 1 expression due to an LMP-1 antisense strategy. This is the first description of a latently infected human monocytic cell line and the first direct demonstration of an instrumental role for LMP-1 in the proliferation of EBV-transformed cell lines expressing a type II latency.
Figures

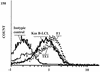
Similar articles
-
Simultaneous detection of the two main proliferation driving EBV encoded proteins, EBNA-2 and LMP-1 in single B cells.J Immunol Methods. 2012 Nov 30;385(1-2):60-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2012.08.008. Epub 2012 Aug 18. J Immunol Methods. 2012. PMID: 22921685
-
Expression of the simian Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein-1 in malignant lymphomas of SIV-infected rhesus macaques.J Med Virol. 2001 Sep;65(1):114-20. J Med Virol. 2001. PMID: 11505452
-
The role of methylation in the phenotype-dependent modulation of Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 2 and latent membrane protein genes in cells latently infected with Epstein-Barr virus.J Gen Virol. 1989 Nov;70 ( Pt 11):2989-3002. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-11-2989. J Gen Virol. 1989. PMID: 2479717
-
Cytokine mediated induction of the major Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-encoded transforming protein, LMP-1.Immunol Lett. 2006 Apr 15;104(1-2):83-8. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2005.11.003. Epub 2005 Dec 1. Immunol Lett. 2006. PMID: 16386314 Review.
-
Epstein-Barr virus latent genes.Exp Mol Med. 2015 Jan 23;47(1):e131. doi: 10.1038/emm.2014.84. Exp Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25613728 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
17-Beta estradiol enhances prostaglandin E2 production in human U937-derived macrophages.Mol Cell Biochem. 2004 Jul;262(1-2):101-10. doi: 10.1023/b:mcbi.0000038222.08915.84. Mol Cell Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15532714
-
Autoactivation of the Epstein-Barr virus oncogenic protein LMP1 during type II latency through opposite roles of the NF-kappaB and JNK signaling pathways.J Virol. 2006 Aug;80(15):7382-93. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02052-05. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16840319 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-infected monocytes facilitate dissemination of EBV within the oral mucosal epithelium.J Virol. 2007 Jun;81(11):5484-96. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00171-07. Epub 2007 Mar 21. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17376918 Free PMC article.
-
The Epstein-Barr virus BMRF-2 protein facilitates virus attachment to oral epithelial cells.Virology. 2008 Jan 20;370(2):430-42. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2007.09.012. Epub 2007 Oct 22. Virology. 2008. PMID: 17945327 Free PMC article.
-
Monocyte and Macrophage Functions in Oncogenic Viral Infections.Viruses. 2024 Oct 15;16(10):1612. doi: 10.3390/v16101612. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39459945 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baer, R., A. T. Bankier, M. D. Biggin, P. L. Deininger, P. J. Farrell, T. J. Gibson, G. Hatfull, G. S. Hudson, S. C. Satchwell, C. Seguin, et al. 1984. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature 310:207-211. - PubMed
-
- Baichwal, V. R., and B. Sudgen. 1988. Transformation of Balb/3T3 cells by the BNLF-1 gene of Epstein-Barr virus. Oncogene 12:1-9. - PubMed
-
- Brousset, P., F. Meggetto, S. Chittal, F. Bibeau, J. Arnaud, B. Rubin, and G. Delsol. 1993. Assessment of the methods for the detection of Epstein-Barr nucleic acids and related gene products in Hodgkin's disease. Lab. Investig. 69:483-490. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

