Neuronal loss and brain atrophy in mice lacking cathepsins B and L
- PMID: 12048238
- PMCID: PMC122989
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.112632299
Neuronal loss and brain atrophy in mice lacking cathepsins B and L
Abstract
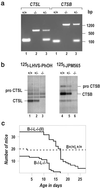
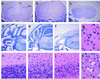
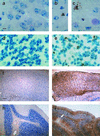
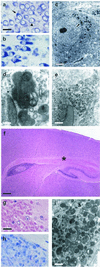
Cathepsins B and L are widely expressed cysteine proteases implicated in both intracellular proteolysis and extracellular matrix remodeling. However, specific roles remain to be validated in vivo. Here we show that combined deficiency of cathepsins B and L in mice is lethal during the second to fourth week of life. Cathepsin B(-/-)/L(-/-) mice reveal a degree of brain atrophy not previously seen in mice. This is because of massive apoptosis of select neurons in the cerebral cortex and the cerebellar Purkinje and granule cell layers. Neurodegeneration is accompanied by pronounced reactive astrocytosis and is preceded by an accumulation of ultrastructurally and biochemically unique lysosomal bodies in large cortical neurons and by axonal enlargements. Our data demonstrate a pivotal role for cathepsins B and L in maintenance of the central nervous system.
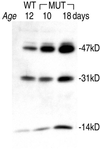
Figures
Similar articles
-
Age-related changes in activities and localizations of cathepsins D, E, B, and L in the rat brain tissues.Exp Neurol. 1994 Mar;126(1):119-28. doi: 10.1006/exnr.1994.1048. Exp Neurol. 1994. PMID: 8157122
-
Towards specific functions of lysosomal cysteine peptidases: phenotypes of mice deficient for cathepsin B or cathepsin L.Biol Chem. 2001 May;382(5):735-41. doi: 10.1515/BC.2001.089. Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11517926 Review.
-
Thyroid functions of mouse cathepsins B, K, and L.J Clin Invest. 2003 Jun;111(11):1733-45. doi: 10.1172/JCI15990. J Clin Invest. 2003. PMID: 12782676 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis of cathepsin B- and L-deficient mouse brain lysosomes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Oct;1774(10):1237-46. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2007.07.004. Epub 2007 Jul 19. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17765022 Free PMC article.
-
Cysteine Cathepsins in the secretory vesicle produce active peptides: Cathepsin L generates peptide neurotransmitters and cathepsin B produces beta-amyloid of Alzheimer's disease.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jan;1824(1):89-104. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2011.08.015. Epub 2011 Sep 8. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 21925292 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Running-Induced Systemic Cathepsin B Secretion Is Associated with Memory Function.Cell Metab. 2016 Aug 9;24(2):332-40. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.05.025. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Cell Metab. 2016. PMID: 27345423 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Ins and Outs of Cathepsins: Physiological Function and Role in Disease Management.Cells. 2020 Jul 13;9(7):1679. doi: 10.3390/cells9071679. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32668602 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Autophagy Modifier Screen Identifies Small Molecules Capable of Reducing Autophagosome Accumulation in a Model of CLN3-Mediated Neurodegeneration.Cells. 2019 Nov 27;8(12):1531. doi: 10.3390/cells8121531. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31783699 Free PMC article.
-
Cell death induced autophagy contributes to terminal differentiation of skin and skin appendages.Autophagy. 2020 May;16(5):932-945. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1646552. Epub 2019 Aug 4. Autophagy. 2020. PMID: 31379249 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated CTSL Gene Expression Correlated with Proinflammatory Cytokines in Omental Adipose Tissue of Patients with Obesity.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2022 Jul 30;15:2277-2285. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S373203. eCollection 2022. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2022. PMID: 35936052 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mort J S. In: Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes. Barrett A J, Rawlings N D, Woessner J F, editors. San Diego: Academic; 1998. pp. 609–617.
-
- Kirschke H. In: Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes. Barrett A J, Rawlings N D, Woessner J F, editors. San Diego: Academic; 1998. pp. 617–621.
-
- Bernstein H-G, Kirschke H, Wiederanders B, Pollak K-H, Zipress A, Rinne A. Mol Chem Neuropathol. 1996;27:225–247. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

