c-erbB-3: a nuclear protein in mammary epithelial cells
- PMID: 12045181
- PMCID: PMC2174048
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200109033
c-erbB-3: a nuclear protein in mammary epithelial cells
Abstract
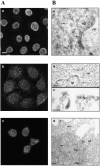
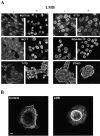
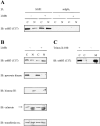
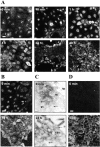
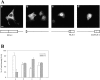
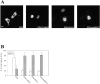
c-erbB receptors are usually located in cell membranes and are activated by extracellular binding of EGF-like growth factors. Unexpectedly, using immunofluorescence we found high levels of c-erbB-3 within the nuclei of MTSV1-7 immortalized nonmalignant human mammary epithelial cells. Nuclear localization was mediated by the COOH terminus of c-erbB-3, and a nuclear localization signal was identified by site-directed mutagenesis and by transfer of the signal to chicken pyruvate kinase. A nuclear export inhibitor caused accumulation of c-erbB-3 in the nuclei of other mammary epithelial cell lines as demonstrated by immunofluorescence and biochemical cell fractionation, suggesting that c-erbB-3 shuttles between nuclear and nonnuclear compartments in these cells. Growth of MTSV1-7 on permeable filters induced epithelial polarity and concentration of c-erbB-3 within the nucleoli. However, the c-erbB-3 ligand heregulin beta1 shifted c-erbB-3 from the nucleolus into the nucleoplasm and then into the cytoplasm. The subcellular localization of c-erbB-3 obviously depends on exogenous stimuli and on the stage of epithelial polarity and challenges the specific function of c-erbB-3 as a transmembrane receptor protein arguing for additional, as yet unidentified, roles of c-erbB-3 within the nucle(ol)us of mammary epithelial cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Functional interaction of the Ras effector RASSF5 with the tyrosine kinase Lck: critical role in nucleocytoplasmic transport and cell cycle regulation.J Mol Biol. 2010 Mar 19;397(1):89-109. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.01.005. Epub 2010 Jan 11. J Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20064523
-
Heregulin-beta is especially potent in activating phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in nontransformed human mammary epithelial cells.J Cell Physiol. 2000 Jun;183(3):301-13. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(200006)183:3<301::AID-JCP2>3.0.CO;2-W. J Cell Physiol. 2000. PMID: 10797304
-
Heregulin and retinoids synergistically induce branching morphogenesis of breast cancer cells cultivated in 3D collagen gels.J Cell Physiol. 2003 May;195(2):260-75. doi: 10.1002/jcp.10237. J Cell Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12652653
-
Mapping nucleolar and spliceosome localization sequences of neuregulin1-beta3.Exp Cell Res. 2004 Sep 10;299(1):110-8. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.05.028. Exp Cell Res. 2004. PMID: 15302578
-
The neuregulin-I/ErbB signaling system in development and disease.Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2007;190:1-65. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17432114 Review.
Cited by
-
Perhexiline promotes HER3 ablation through receptor internalization and inhibits tumor growth.Breast Cancer Res. 2015 Feb 15;17(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s13058-015-0528-9. Breast Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25849870 Free PMC article.
-
Syntaxin 6-mediated Golgi translocation plays an important role in nuclear functions of EGFR through microtubule-dependent trafficking.Oncogene. 2014 Feb 6;33(6):756-70. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.1. Epub 2013 Feb 4. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 23376851 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear localization and function of polypeptide ligands and their receptors: a new paradigm for hormone specificity within the mammary gland?Breast Cancer Res. 2003;5(4):181-7. doi: 10.1186/bcr601. Epub 2003 Apr 11. Breast Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12817988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Targeting Therapy against EGFR Family in Breast Cancer: Progress and Future Potentials.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Nov 20;11(12):1826. doi: 10.3390/cancers11121826. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31756933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An unusual function of RON receptor tyrosine kinase as a transcriptional regulator in cooperation with EGFR in human cancer cells.Carcinogenesis. 2010 Aug;31(8):1456-64. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgq100. Epub 2010 May 24. Carcinogenesis. 2010. PMID: 20498137 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguilar, Z., R.W. Akita, R.S. Finn, B.L. Ramos, M.D. Pegram, F.F. Kabbinavar, R.J. Pietras, P. Pisacane, M.X. Sliwkowski, and D.J. Slamon. 1999. Biologic effects of heregulin/neu differentiation factor on normal and malignant human breast and ovarian epithelial cells. Oncogene. 18:6050–6062. - PubMed
-
- Alimandi, M., A. Romano, M.C. Curia, R. Muraro, P. Fedi, S.A. Aaronson, P.P. Di-Fiore, and M.H. Kraus. 1995. Cooperative signaling of ErbB3 and ErbB2 in neoplastic transformation and human mammary carcinomas. Oncogene. 10:1813–1821. - PubMed
-
- Antoine, M., K. Reimers, C. Dickson, and P. Kiefer. 1997. Fibroblast growth factor 3, a protein with dual subcellular localization, is targeted to the nucleus and nucleolus by the concerted action of two nuclear localization signals and a nucleolar retention signal. J. Biol. Chem. 272:29475–29481. - PubMed
-
- Bartek, J., J. Bartkova, N. Kyprianou, E.N. Lalani, Z. Staskova, M. Shearer, S. Chang, and J. Taylor-Papadimitriou. 1991. Efficient immortalization of luminal epithelial cells from human mammary gland by introduction of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen with a recombinant retrovirus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 88:3520–3524. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bourguignon, L., K.-H. Lan, P. Singleton, S.-Y. Lin, D. Yu, and M.-C. Hung. 2002. Localizing the EGF receptor-Reply. Nat. Cell Biol. 4:E22–E23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

