RNA polymerase II complexes in the very early phase of transcription are not susceptible to TFIIS-induced exonucleolytic cleavage
- PMID: 12034815
- PMCID: PMC117193
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/30.11.2290
RNA polymerase II complexes in the very early phase of transcription are not susceptible to TFIIS-induced exonucleolytic cleavage
Abstract
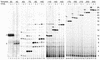
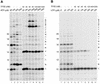
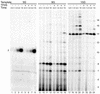
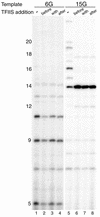
TFIIS is a transcription elongation factor for RNA polymerase II (pol II), which can suppress ribonucleotide misincorporation. We reconstituted transcription complexes in a highly purified pol II system on adenovirus Major-Late promoter constructs. We noted that these complexes have a high propensity for read-through upon GTP omission. Read-through occurred during the early stages at all registers analyzed. Addition of TFIIS reversed read-through of productive elongation complexes, which indicated that it was due to misincorporation. However, before register 13 transcription complexes were insensitive to TFIIS. These findings are discussed with respect to the structural models for pol II and we propose that TFIIS action is linked to the RNA:DNA hybrid.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Analysis of the open region of RNA polymerase II transcription complexes in the early phase of elongation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2001 Jul 1;29(13):2706-14. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.13.2706. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001. PMID: 11433015 Free PMC article.
-
Cleavage of the nascent transcript induced by TFIIS is insufficient to promote read-through of intrinsic blocks to elongation by RNA polymerase II.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 16;91(17):8087-91. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.17.8087. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994. PMID: 8058762 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription elongation through DNA arrest sites. A multistep process involving both RNA polymerase II subunit RPB9 and TFIIS.J Biol Chem. 1997 Jun 6;272(23):14747-54. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.23.14747. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9169440
-
RNA polymerase II structure: from core to functional complexes.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2004 Apr;14(2):218-26. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2004.01.003. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2004. PMID: 15196470 Review.
-
Architecture of the RNA polymerase II elongation complex: new insights into Spt4/5 and Elf1.Transcription. 2018;9(5):286-291. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2018.1454817. Epub 2018 May 7. Transcription. 2018. PMID: 29624124 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ARMC Subfamily: Structures, Functions, Evolutions, Interactions, and Diseases.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Nov 29;8:791597. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.791597. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34912852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The initiation-elongation transition: lateral mobility of RNA in RNA polymerase II complexes is greatly reduced at +8/+9 and absent by +23.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 May 13;100(10):5700-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1037057100. Epub 2003 Apr 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12719526 Free PMC article.
-
RNA polymerase II transcription elongation control.Chem Rev. 2013 Nov 13;113(11):8583-603. doi: 10.1021/cr400105n. Epub 2013 Aug 6. Chem Rev. 2013. PMID: 23919563 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Roeder R.G. (1996) The role of general initiation factors in transcription by RNA polymerase II. Trends Biochem. Sci., 21, 327–335. - PubMed
-
- Orphanides G., Lagrange,T. and Reinberg,D. (1996) The general transcription factors of RNA polymerase II. Genes Dev., 10, 2657–2683. - PubMed
-
- Dvir A., Conaway,J.W. and Conaway,R.C. (2001) Mechanism of transcription initiation and promoter escape by RNA polymerase II. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 11, 209–214. - PubMed
-
- Conaway R.C. and Conaway,J.W. (1988) ATP activates transcription initiation from promoters by RNA polymerase II in a reversible step prior to RNA synthesis. J. Biol. Chem., 263, 2962–2968. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

