Constitutive association of BRCA1 and c-Abl and its ATM-dependent disruption after irradiation
- PMID: 12024016
- PMCID: PMC133860
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.12.4020-4032.2002
Constitutive association of BRCA1 and c-Abl and its ATM-dependent disruption after irradiation
Abstract
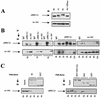
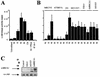
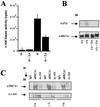
BRCA1 plays an important role in mechanisms of response to double-strand breaks, participating in genome surveillance, DNA repair, and cell cycle checkpoint arrests. Here, we identify a constitutive BRCA1-c-Abl complex and provide evidence for a direct interaction between the PXXP motif in the C terminus of BRCA1 and the SH3 domain of c-Abl. Following exposure to ionizing radiation (IR), the BRCA1-c-Abl complex is disrupted in an ATM-dependent manner, which correlates temporally with ATM-dependent phosphorylation of BRCA1 and ATM-dependent enhancement of the tyrosine kinase activity of c-Abl. The BRCA1-c-Abl interaction is affected by radiation-induced modification to both BRCA1 and c-Abl. We show that the C terminus of BRCA1 is phosphorylated by c-Abl in vitro. In vivo, BRCA1 is phosphorylated at tyrosine residues in an ATM-dependent, radiation-dependent manner. Tyrosine phosphorylation of BRCA1, however, is not required for the disruption of the BRCA1-c-Abl complex. BRCA1-mutated cells exhibit constitutively high c-Abl kinase activity that is not further increased on exposure to IR. We suggest a model in which BRCA1 acts in concert with ATM to regulate c-Abl tyrosine kinase activity.
Figures




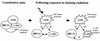
Similar articles
-
Ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) kinase and ATM and Rad3 related kinase mediate phosphorylation of Brca1 at distinct and overlapping sites. In vivo assessment using phospho-specific antibodies.J Biol Chem. 2001 May 18;276(20):17276-80. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M011681200. Epub 2001 Feb 13. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11278964
-
Regulation of DNA-dependent protein kinase activity by ionizing radiation-activated abl kinase is an ATM-dependent process.J Biol Chem. 2000 Sep 29;275(39):30163-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M004302200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10906134
-
c-Abl tyrosine kinase is not essential for ataxia telangiectasia mutated functions in chromosomal maintenance.J Biol Chem. 2000 Jan 14;275(2):725-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.2.725. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10625600
-
ATM: the protein encoded by the gene mutated in the radiosensitive syndrome ataxia-telangiectasia.Int J Radiat Biol. 1999 Oct;75(10):1201-14. doi: 10.1080/095530099139359. Int J Radiat Biol. 1999. PMID: 10549596 Review.
-
Determination of cell fate by c-Abl activation in the response to DNA damage.Oncogene. 1998 Dec 24;17(25):3309-18. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202571. Oncogene. 1998. PMID: 9916993 Review.
Cited by
-
BRCA Mutations-The Achilles Heel of Breast, Ovarian and Other Epithelial Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 5;24(5):4982. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054982. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
c-Abl tyrosine kinase in the DNA damage response: cell death and more.Cell Death Differ. 2011 Jan;18(1):2-4. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2010.132. Cell Death Differ. 2011. PMID: 21151157 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reversion of the ErbB malignant phenotype and the DNA damage response.Exp Mol Pathol. 2012 Dec;93(3):324-33. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2012.09.007. Epub 2012 Sep 27. Exp Mol Pathol. 2012. PMID: 23022358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tyrosine phosphorylation enhances RAD52-mediated annealing by modulating its DNA binding.EMBO J. 2011 Jul 29;30(16):3368-82. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.238. EMBO J. 2011. PMID: 21804533 Free PMC article.
-
miR-27b-3p a Negative Regulator of DSB-DNA Repair.Genes (Basel). 2021 Aug 27;12(9):1333. doi: 10.3390/genes12091333. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34573315 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barila, D., and G. Superti-Furga. 1998. An intermolecular SH3-domain interaction regulates c-Abl activity. Nat. Genet. 18:280-282. - PubMed
-
- Baskaran, R., L. D. Wood, L. L. Whitaker, C. E. Canman, S. E. Morgan, Y. Xu, C. Barlow, D. Baltimore, A. Wynshaw-Boris, M. B. Kastan, and J. Y. J. Wang. 1997. Ataxia telangiectasia mutant protein activates c-Abl tyrosine kinase in response to ionizing radiation. Nature 387:516-519. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
