A plant gene up-regulated at rust infection sites
- PMID: 12011348
- PMCID: PMC155881
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.010940
A plant gene up-regulated at rust infection sites
Abstract
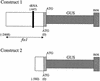
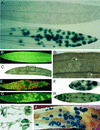
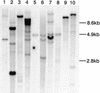
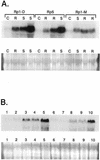
Expression of the fis1 gene from flax (Linum usitatissimum) is induced by a compatible rust (Melampsora lini) infection. Infection of transgenic plants containing a beta-glucuronidase (GUS) reporter gene under the control of the fis1 promoter showed that induction is highly localized to those leaf mesophyll cells within and immediately surrounding rust infection sites. The level of induction reflects the extent of fungal growth. In a strong resistance reaction, such as the hypersensitive fleck mediated by the L6 resistance gene, there is very little fungal growth and a microscopic level of GUS expression. Partially resistant flax leaves show levels of GUS expression that were intermediate to the level observed in the fully susceptible infection. Sequence and deletion analysis using both transient Agrobacterium tumefaciens expression and stable transformation assays have shown that the rust-inducible fis1 promoter is contained within a 580-bp fragment. Homologs of fis1 were identified in expressed sequence tag databases of a range of plant species including dicots, monocots, and a gymnosperm. Homologous genes isolated from maize (Zea mays; mis1), barley (Hordeum vulgare; bis1), wheat (Triticum aestivum; wis1), and Arabidopsis encode proteins that are highly similar (76%-82%) to the FIS1 protein. The Arabidopsis homologue has been reported to encode a delta1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase that is involved in the catabolism of proline to glutamate. RNA-blot analysis showed that mis1 in maize and the bis1 homolog in barley are both up-regulated by a compatible infection with the corresponding species-specific rust. The rust-induced genes homologous to fis1 are present in many plants. The promoters of these genes have potential roles for the engineering of synthetic rust resistance genes by targeting transgene expression to the sites of rust infection.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A rust-inducible gene from flax (fis1) is involved in proline catabolism.Planta. 2006 Jan;223(2):213-22. doi: 10.1007/s00425-005-0079-x. Epub 2005 Aug 4. Planta. 2006. PMID: 16079997
-
Autoactive alleles of the flax L6 rust resistance gene induce non-race-specific rust resistance associated with the hypersensitive response.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2005 Jun;18(6):570-82. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-18-0570. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2005. PMID: 15986927
-
Isolation of a flax (Linum usitatissimum) gene induced during susceptible infection by flax rust (Melampsora lini).Plant J. 1995 Jul;8(1):1-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1995.08010001.x. Plant J. 1995. PMID: 7655501
-
Co-evolutionary interactions between host resistance and pathogen effector genes in flax rust disease.Mol Plant Pathol. 2011 Jan;12(1):93-102. doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2010.00657.x. Epub 2010 Aug 29. Mol Plant Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21118351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular farming of industrial proteins from transgenic maize.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1999;464:127-47. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-4729-7_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1999. PMID: 10335391 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential Contribution of P5CS Isoforms to Stress Tolerance in Arabidopsis.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Sep 25;11:565134. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.565134. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 33101333 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous siRNAs derived from a pair of natural cis-antisense transcripts regulate salt tolerance in Arabidopsis.Cell. 2005 Dec 29;123(7):1279-91. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.11.035. Cell. 2005. PMID: 16377568 Free PMC article.
-
Context of action of proline dehydrogenase (ProDH) in the Hypersensitive Response of Arabidopsis.BMC Plant Biol. 2014 Jan 13;14:21. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-14-21. BMC Plant Biol. 2014. PMID: 24410747 Free PMC article.
-
Proline metabolism and its implications for plant-environment interaction.Arabidopsis Book. 2010;8:e0140. doi: 10.1199/tab.0140. Epub 2010 Nov 3. Arabidopsis Book. 2010. PMID: 22303265 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis in cereals of a key proline catabolism gene.Mol Genet Genomics. 2005 Dec;274(5):494-505. doi: 10.1007/s00438-005-0048-x. Epub 2005 Sep 23. Mol Genet Genomics. 2005. PMID: 16179990
References
-
- Ayliffe MA, Frost DV, Finnegan EJ, Lawrence GJ, Anderson PA, Ellis JG. Analysis of alternative transcripts of the flax L6rust resistance gene. Plant J. 1999;17:287–292. - PubMed
-
- Chou H-M, Bundock N, Rolfe SA, Scholes JD. Infection of Arabidopsis thaliana with Albugo candida(white blister rust) causes a reprogramming of host metabolism. Mol Plant Pathol. 2000;1:99–113. - PubMed
-
- Clancy FG, Coffey MD. Patterns of translocation, changes in invertase activity, and polyol formation in susceptible and resistant flax infected with the rust fungus Melampsora lini. Physiol Plant Pathol. 1980;17:41–52.
-
- Deuschle K, Funck D, Hellman H, Daschner K, Binder S, Frommer WB. A nuclear gene encoding mitochondrial Δ1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase and its potential role in protection from proline toxicity. Plant J. 2001;27:345–355. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

