Pivotal role of the non-hr origin of DNA replication in the genesis of defective interfering baculoviruses
- PMID: 11991989
- PMCID: PMC137048
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.11.5605-5611.2002
Pivotal role of the non-hr origin of DNA replication in the genesis of defective interfering baculoviruses
Abstract
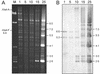
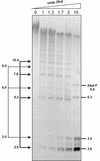
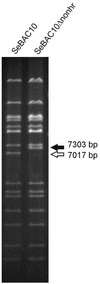
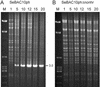
The generation of deletion mutants, including defective interfering viruses, upon serial passage of Spodoptera exigua multicapsid nucleopolyhedrovirus (SeMNPV) in insect cell culture has been studied. Sequences containing the non-homologous region origin of DNA replication (non-hr ori) became hypermolar in intracellular viral DNA within 10 passages in Se301 insect cells, concurrent with a dramatic drop in budded virus and polyhedron production. These predominant non-hr ori-containing sequences accumulated in larger concatenated forms and were generated de novo as demonstrated by their appearance and accumulation upon infection with a genetically homogeneous bacterial clone of SeMNPV (bacmid). Sequences were identified at the junctions of the non-hr ori units within the concatemers, which may be potentially involved in recombination events. Deletion of the SeMNPV non-hr ori using RecE/RecT-mediated homologous ET recombination in Escherichia coli resulted in a recombinant bacmid with strongly enhanced stability of virus and polyhedron production upon serial passage in insect cells. This suggests that the accumulation of non-hr oris upon passage is due to the replication advantage of these sequences. The non-hr ori deletion mutant SeMNPV bacmid can be exploited as a stable eukaryotic heterologous protein expression vector in insect cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Spontaneous excision of BAC vector sequences from bacmid-derived baculovirus expression vectors upon passage in insect cells.J Gen Virol. 2003 Oct;84(Pt 10):2669-2678. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.19438-0. J Gen Virol. 2003. PMID: 13679600
-
[Generation and analysis of a repeat DNA fragment of SeMNPV by serial undiluted passage in Se301 insect cells].Sheng Wu Hua Xue Yu Sheng Wu Wu Li Xue Bao (Shanghai). 2002 Sep;34(5):608-14. Sheng Wu Hua Xue Yu Sheng Wu Wu Li Xue Bao (Shanghai). 2002. PMID: 12198564 Chinese.
-
Cell line-specific accumulation of the baculovirus non-hr origin of DNA replication in infected insect cells.J Invertebr Pathol. 2003 Nov;84(3):214-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2003.10.005. J Invertebr Pathol. 2003. PMID: 14726243
-
Identification and functional analysis of a non-hr origin of DNA replication in the genome of Spodoptera exigua multicapsid nucleopolyhedrovirus.J Gen Virol. 1997 Jun;78 ( Pt 6):1497-506. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-78-6-1497. J Gen Virol. 1997. PMID: 9191948
-
Partial Alleviation of Homologous Superinfection Exclusion of SeMNPV Latently Infected Cells by G1 Phase Infection and G2/M Phase Arrest.Viruses. 2024 May 6;16(5):736. doi: 10.3390/v16050736. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38793618 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Baculovirus PTP2 Functions as a Pro-Apoptotic Protein.Viruses. 2018 Apr 7;10(4):181. doi: 10.3390/v10040181. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 29642442 Free PMC article.
-
Specificity of baculovirus P6.9 basic DNA-binding proteins and critical role of the C terminus in virion formation.J Virol. 2010 Sep;84(17):8821-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00072-10. Epub 2010 Jun 2. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20519380 Free PMC article.
-
Cryptophlebia peltastica Nucleopolyhedrovirus Is Highly Infectious to Codling Moth Larvae and Cells.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019 Aug 14;85(17):e00795-19. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00795-19. Print 2019 Sep 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31227557 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus orf74, a novel gene involved in virulence of virus.Virus Genes. 2009 Jun;38(3):487-94. doi: 10.1007/s11262-009-0350-5. Epub 2009 Apr 2. Virus Genes. 2009. PMID: 19340569
-
Identification of Multiple Replication Stages and Origins in the Nucleopolyhedrovirus of Anticarsia gemmatalis.Viruses. 2019 Jul 15;11(7):648. doi: 10.3390/v11070648. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31311127 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Black, B. C., L. A. Brennan, P. M. Dierks, and I. E. Gard. 1997. Commercialization of baculoviral insecticides, p. 341-387. In L. K. Miller (ed.), The baculoviruses. Plenum Press, New York, N.Y.
-
- Dai, X. J., J. P. Hajos, N. N. Joosten, M. M. van Oers, W. F. IJkel, D. Zuidema, Y. Pang, and J. M. Vlak. 2000. Isolation of a Spodoptera exigua baculovirus recombinant with a 10.6 kbp genome deletion that retains biological activity. J. Gen. Virol. 10:2545-2554. - PubMed
-
- DePamphilis, M. L. 1993. Eukaryotic DNA replication: anatomy of an origin. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 62:29-63. - PubMed
-
- Gelernter, W. D., and B. A. Federici. 1986. Isolation, identification, and determination of virulence of a nuclear polyhedrosis virus from the beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Environ. Entomol. 15:240-245.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

