Toxoplasma gondii myosin A and its light chain: a fast, single-headed, plus-end-directed motor
- PMID: 11980712
- PMCID: PMC125985
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/21.9.2149
Toxoplasma gondii myosin A and its light chain: a fast, single-headed, plus-end-directed motor
Abstract
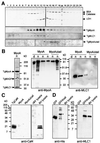
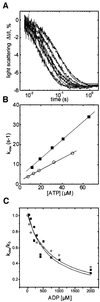
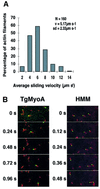
Successful host cell invasion is a prerequisite for survival of the obligate intracellular apicomplexan parasites and establishment of infection. Toxoplasma gondii penetrates host cells by an active process involving its own actomyosin system and which is distinct from induced phagocytosis. Toxoplasma gondii myosin A (TgMyoA) is presumed to achieve power gliding motion and host cell penetration by the capping of apically released adhesins towards the rear of the parasite. We report here an extensive biochemical characterization of the functional TgMyoA motor complex. TgMyoA is anchored at the plasma membrane and binds a novel type of myosin light chain (TgMLC1). Despite some unusual features, the kinetic and mechanical properties of TgMyoA are unexpectedly similar to those of fast skeletal muscle myosins. Microneedle-laser trap and sliding velocity assays established that TgMyoA moves in unitary steps of 5.3 nm with a velocity of 5.2 microm/s towards the plus end of actin filaments. TgMyoA is the first fast, single-headed myosin and fulfils all the requirements for power parasite gliding.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Blocking Palmitoylation of Toxoplasma gondii Myosin Light Chain 1 Disrupts Glideosome Composition but Has Little Impact on Parasite Motility.mSphere. 2021 May 19;6(3):e00823-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00823-20. mSphere. 2021. PMID: 34011689 Free PMC article.
-
A Toxoplasma gondii class XIV myosin, expressed in Sf9 cells with a parasite co-chaperone, requires two light chains for fast motility.J Biol Chem. 2014 Oct 31;289(44):30832-30841. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.572453. Epub 2014 Sep 17. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25231988 Free PMC article.
-
A small-molecule inhibitor of T. gondii motility induces the posttranslational modification of myosin light chain-1 and inhibits myosin motor activity.PLoS Pathog. 2010 Jan 15;6(1):e1000720. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000720. PLoS Pathog. 2010. PMID: 20084115 Free PMC article.
-
Microneme proteins: structural and functional requirements to promote adhesion and invasion by the apicomplexan parasite Toxoplasma gondii.Int J Parasitol. 2001 Oct;31(12):1293-302. doi: 10.1016/s0020-7519(01)00257-0. Int J Parasitol. 2001. PMID: 11566297 Review.
-
The role of the cytoskeleton in host cell invasion by Toxoplasma gondii.Behring Inst Mitt. 1997 Mar;(99):90-6. Behring Inst Mitt. 1997. PMID: 9303207 Review.
Cited by
-
Whole transcriptome analysis of HCT-8 cells infected by Cryptosporidium parvum.Parasit Vectors. 2022 Nov 24;15(1):441. doi: 10.1186/s13071-022-05565-4. Parasit Vectors. 2022. PMID: 36434735 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a new rhoptry neck complex RON9/RON10 in the Apicomplexa parasite Toxoplasma gondii.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e32457. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032457. Epub 2012 Mar 12. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22427839 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of T. gondii myosin light chain-1 as a direct target of TachypleginA-2, a small-molecule inhibitor of parasite motility and invasion.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 3;9(6):e98056. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098056. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24892871 Free PMC article.
-
Post-translational modifications as key regulators of apicomplexan biology: insights from proteome-wide studies.Mol Microbiol. 2018 Jan;107(1):1-23. doi: 10.1111/mmi.13867. Epub 2017 Nov 28. Mol Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29052917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphorylation of a Myosin Motor by TgCDPK3 Facilitates Rapid Initiation of Motility during Toxoplasma gondii egress.PLoS Pathog. 2015 Nov 6;11(11):e1005268. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005268. eCollection 2015. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 26544049 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen M.L., Dobrowolski,J.M., Muller,H., Sibley,L.D. and Mansour,T.E. (1997) Cloning and characterization of actin depolymerizing factor from Toxoplasma gondii. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol., 88, 43–52. - PubMed
-
- Anson M. (1992) Temperature dependence and Arrhenius activation energy of F-actin velocity generated in vitro by skeletal myosin. J. Mol. Biol., 224, 1029–1038. - PubMed
-
- Batra R. and Manstein,D.J. (1999) Functional characterisation of Dictyostelium myosin II with conserved tryptophanyl residue 501 mutated to tyrosine. Biol. Chem., 380, 1017–1023. - PubMed
-
- Batra R., Geeves,M.A. and Manstein,D.J. (1999) Kinetic analysis of Dictyostelium discoideum myosin motor domains with glycine-to-alanine mutations in the reactive thiol region. Biochemistry, 38, 6126–6134. - PubMed
-
- Bement W.M. and Mooseker,M.S. (1995) TEDS rule: a molecular rationale for differential regulation of myosins by phosphorylation of the heavy chain head. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton, 31, 87–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

