Plasma levels of soluble CD27: a simple marker to monitor immune activation during potent antiretroviral therapy in HIV-1-infected subjects
- PMID: 11966765
- PMCID: PMC1906306
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2002.01786.x
Plasma levels of soluble CD27: a simple marker to monitor immune activation during potent antiretroviral therapy in HIV-1-infected subjects
Erratum in
- Clin Exp Immunol. 2003 Oct;134(1):167. D Fuchs [corrected to Fuchs D]
Abstract
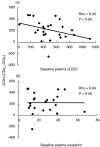
Plasma levels of soluble CD27 (sCD27) are elevated in diseases characterized by T cell activation and are used as a marker of immune activation. We assessed the usefulness of determining plasma sCD27 as a marker for monitoring immune activation in HIV-1-infected patients treated with highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART). A first cross-sectional examination of 68 HIV-1-infected and 18 normal subjects showed high levels of sCD27 in HIV-1 infection; plasma sCD27 was correlated to HIV-1 viraemia and inversely correlated to CD4+ T cell count. Twenty-six HIV-1-infected patients undergoing HAART were studied at baseline and after 6, 12, 18 and 24 months of therapy. Seven additional patients under HAART were analysed at baseline, during and after interruption of therapy. In the total population, HAART induced a significant and progressive reduction, but not a normalization, of plasma levels of sCD27 after 24 months. A full normalization of plasma sCD27 was observed in the virological responders (undetectable HIV-1 RNA at months 18 and 24) and also in patients with moderate immunodeficiency at baseline (CD4+ T cell count >200 cells/mm3). Changes in plasma neopterin paralleled the changes in sCD27 but only baseline sCD27 levels were predictive of a greater increase in CD4+ T cell count during the follow-up. Discontinuation of therapy resulted in a rapid increase of sCD27 plasma levels associated with viraemia rebound and drop in CD4+ T cell count. Our findings suggest that plasma sCD27 may represent an alternative and simple marker to monitor immune activation during potent antiretroviral therapy. HIV-1-induced immune activation can be normalized by HAART in successfully treated patients where the disease is not advanced.
Figures

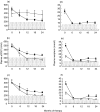
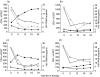
 ), CD4+ T cell count (cells/mm3, –•–), plasma sCD27 (U/ml,□) and plasma neopterin (nmol/l, ×) during therapy in four patients representative of the MOD group (a), SEV group (b), responders (c) and non-responders (d).
), CD4+ T cell count (cells/mm3, –•–), plasma sCD27 (U/ml,□) and plasma neopterin (nmol/l, ×) during therapy in four patients representative of the MOD group (a), SEV group (b), responders (c) and non-responders (d).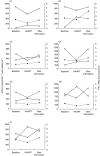
Similar articles
-
Plasma levels of viro-immunological markers in HIV-infected and non-infected Ethiopians: correlation with cell surface activation markers.Clin Immunol. 2001 Feb;98(2):212-9. doi: 10.1006/clim.2000.4958. Clin Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11161977
-
Residual viraemia in HIV-1-infected patients with plasma viral load <or=20 copies/ml is associated with increased blood levels of soluble immune activation markers.Scand J Immunol. 2008 Dec;68(6):652-60. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.2008.02184.x. Scand J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 19055701
-
Effects of potent antiretroviral therapy on the immune activation marker soluble CD27 in patients infected with HIV-1 subtypes A-D.J Med Virol. 2004 Mar;72(3):345-51. doi: 10.1002/jmv.20006. J Med Virol. 2004. PMID: 14748056
-
Study of the impact of HIV genotypic drug resistance testing on therapy efficacy.Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 2001;63(5):447-73. Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 2001. PMID: 11813503 Review.
-
Failure to reconstitute CD4+ T-cells despite suppression of HIV replication under HAART.AIDS Rev. 2006 Apr-Jun;8(2):88-97. AIDS Rev. 2006. PMID: 16848276 Review.
Cited by
-
Soluble levels of CD27 and CD30 are associated with risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in three Chinese prospective cohorts.Int J Cancer. 2015 Dec 1;137(11):2688-95. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29637. Epub 2015 Jun 26. Int J Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26095604 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocyte activation and apoptosis: their roles in the neuropathology of HIV infection.Brain Pathol. 2003 Jan;13(1):84-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2003.tb00009.x. Brain Pathol. 2003. PMID: 12580548 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Longitudinal microarray analysis of cell surface antigens on peripheral blood mononuclear cells from HIV+ individuals on highly active antiretroviral therapy.Retrovirology. 2008 Mar 4;5:24. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-5-24. Retrovirology. 2008. PMID: 18315888 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of memory B-cell populations in blood, lymph nodes, and bone marrow during antiretroviral therapy and envelope boosting in simian immunodeficiency virus SIVmac251-infected rhesus macaques.J Virol. 2012 Dec;86(23):12591-604. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00298-12. Epub 2012 Sep 12. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22973034 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-associated memory B cell perturbations.Vaccine. 2015 May 21;33(22):2524-9. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.04.008. Epub 2015 Apr 14. Vaccine. 2015. PMID: 25887082 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lens SMA, Tesselaar K, van Oers MHJ, van Lier RAW. Control of lymphocyte function through CD27–CD70 interactions. Semin Immunol. 1998;10:491–9. - PubMed
-
- van Lier RAW, Borst J, Vroom TM, et al. Tissue distribution and biochemical and functional properties of Tp55 (CD27), a novel T cell differentiation antigen. J Immunol. 1987;139:1589–96. - PubMed
-
- Bigler RD, Bushkin Y, Chiorazzi N. S152 (CD27). A modulating disulfide-linked T cell activation antigen. J Immunol. 1988;141:21–8. - PubMed
-
- Hintzen RQ, de Jong R, Hack CE, et al. A soluble form of the human T cell differentiation antigen CD27 is released after triggering of the TCR/CD3 complex. J Immunol. 1991;147:29–35. - PubMed
-
- Loenen WAM, de Vries E, Gravestein LA, et al. The CD27 membrane receptor, a lymphocytic-specific member of the nerve growth factor family, gives rise to a soluble form by protein processing that does not involve receptor endocytosis. Eur J Immunol. 1992;22:447–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

