G2-phase radiation response in lymphoblastoid cell lines from Nijmegen breakage syndrome
- PMID: 11952644
- PMCID: PMC6495264
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2184.2002.00234.x
G2-phase radiation response in lymphoblastoid cell lines from Nijmegen breakage syndrome
Abstract
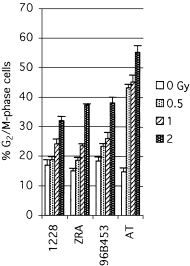
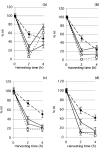
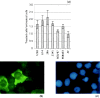
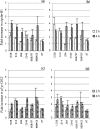
The relationship between G2-phase checkpoint activation, cytoplasmic cyclin-B1 accumulation and nuclear phosphorylation of p34CDC2 was studied in Nijmegen breakage syndrome cells treated with DNA damaging agents. Experiments were performed on lymphoblastoid cell lines from four Nijmegen breakage syndrome patients with different mutations, as well as on cells from an ataxia telangiectasia patient. Lymphoblastoid cell lines were irradiated with 0.50-2 Gy X-rays and the percentage of G2-phase accumulated cells was evaluated by means of flow cytometry in samples that were harvested 24 h later. The G2-checkpoint activation was analysed by scoring the mitotic index at 2 and 4 h after treatment with 0.5 and 1 Gy X-rays and treatment with the DNA double-strand break inducer calicheamicin-gamma1. Cytoplasmic accumulation of cyclin-B1 was evaluated by means of fluorescence immunostaining or Western blotting, in cells harvested shortly after irradiation with 1 and 2 Gy. The extent of tyrosine 15-phosphorylated p34CDC2 was assessed in the nuclear fractions. Nijmegen breakage syndrome cells showed suboptimal G2-phase checkpoint activation respect to normal cells and were greatly different from ataxia telangiectasia cells. Increased cytoplasmic cyclin-B1 accumulation was detected by both immunofluorescence and immunoblot in normal as well as in Nijmegen breakage syndrome cells. Furthermore, nuclear p34CDC2. phosphorylation was detected at a higher level in Nijmegen breakage syndrome than in ataxia telangiectasia cells. In conclusion, our data do not suggest that failure to activate checkpoints plays a major role in the radiosensitivity of Nijmegen breakage syndrome cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Chromosomal sensitivity to clastogenic agents and cell cycle perturbations in Nijmegen breakage syndrome lymphoblastoid cell lines.Int J Radiat Biol. 1997 Jan;71(1):41-9. doi: 10.1080/095530097144409. Int J Radiat Biol. 1997. PMID: 9020962
-
UCN-01: a potent abrogator of G2 checkpoint function in cancer cells with disrupted p53.J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996 Jul 17;88(14):956-65. doi: 10.1093/jnci/88.14.956. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996. PMID: 8667426
-
Dissociation between cell cycle arrest and apoptosis can occur in Li-Fraumeni cells heterozygous for p53 gene mutations.Oncogene. 1997 May 8;14(18):2137-47. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201050. Oncogene. 1997. PMID: 9174049
-
Influence of the G2 cell cycle block abrogator pentoxifylline on the expression and subcellular location of cyclin B1 and p34cdc2 in HeLa cervical carcinoma cells.Cell Prolif. 2000 Feb;33(1):39-50. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2184.2000.00160.x. Cell Prolif. 2000. PMID: 10741643 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation and the G2 phase of the cell cycle.Radiat Res. 1998 Nov;150(5 Suppl):S52-9. Radiat Res. 1998. PMID: 9806609 Review.
References
-
- Antoccia A, Ricordy R., Maraschio P, Prudente S, Tanzarella C (1997) Chromosomal radiosensitivity to clastogenic agents and cell cycle perturbations in Nijmegen Breakage Syndrome lymphoblastoid cell lines. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 35, 41. - PubMed
-
- Antoccia A, Stumm M, Saar K, Ricordy R., Maraschio P, Tanzarella C (1999) Impaired p53 mediated DNA damage response, cell cycle disturbances and chromosome aberrations in Nijmegen Breakage Syndrome lymphoblastoid cell lines. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 35, 583. - PubMed
-
- Barbi G, Scheres JM, Schindler D, Taalman RD, Rodens K, Mehnert K, Muller M, Seyschab H (1991) Chromosome instability and X‐ray hypersensitivity in a microcephalic and growth‐retarded child. Am. J. Med. Genet. 35, 44. - PubMed
-
- Beamish H, Lavin MF (1994) Radiosensitivity in ataxia telangiectasia: anomalies in radiation‐induced cell cycle delay. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 35, 175. - PubMed
-
- Carney JP, Maser RS, Olivares H, Davis EM, Le Beau M, Yates JR III, Hayes L, Morgan WF, Petrini JHJ (1998) The hMMre11/hRad50 protein complex and Nijmegen breakage syndrome: linkage of double‐strand break repair to the cellular DNA damage response. Cell 35, 477. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

