The Drosophila homolog of NTF-2, the nuclear transport factor-2, is essential for immune response
- PMID: 11943764
- PMCID: PMC1084060
- DOI: 10.1093/embo-reports/kvf072
The Drosophila homolog of NTF-2, the nuclear transport factor-2, is essential for immune response
Abstract
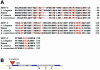
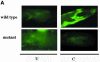
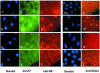
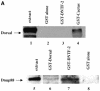
Nuclear transport factor-2 (NTF-2) functions in yeast and mammalian cell culture in targeting proteins into the nucleus. The Drosophila homolog, DNTF-2, is an essential component of the nuclear import machinery, since ntf mutants are lethal. Interestingly, hypomorphic alleles show specific phenotypes. Some are viable, but the number of omatidia in the eye is severely reduced. The immune response in the Drosophila larval fat body is also affected; the three NF-kappaB/Rel proteins Dorsal, Dif and Relish do not target to the nucleus after infection, and, consequently, the expression of the anti-microbial peptide genes drosomycin, attacin and drosocin is severely impaired. Hence, in spite of its general requirement in many developmental processes, DNTF-2 has a higher specific requirement in the development of the eye and in the immune response. We also found that DNTF-2 interacts directly with Mbo/DNup88, which does not contain phenylalanine-glycine-rich repeats, but has been shown to function in the import of Rel proteins.
Figures




Similar articles
-
members only encodes a Drosophila nucleoporin required for rel protein import and immune response activation.Genes Dev. 2000 Aug 1;14(15):1945-57. Genes Dev. 2000. PMID: 10921908 Free PMC article.
-
Regulated nuclear import of Rel proteins in the Drosophila immune response.Nature. 1998 Mar 5;392(6671):93-7. doi: 10.1038/32195. Nature. 1998. PMID: 9510254
-
Tamo selectively modulates nuclear import in Drosophila.Genes Cells. 2003 Apr;8(4):299-310. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2443.2002.00634.x. Genes Cells. 2003. PMID: 12653959
-
An in vitro study of NF-κB factors cooperatively in regulation of Drosophila melanogaster antimicrobial peptide genes.Dev Comp Immunol. 2019 Jun;95:50-58. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2019.01.017. Epub 2019 Feb 6. Dev Comp Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30735676
-
Control of development and immunity by rel transcription factors in Drosophila.Oncogene. 1999 Nov 22;18(49):6875-87. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203223. Oncogene. 1999. PMID: 10602463 Review.
Cited by
-
Learning Retention Mechanisms and Evolutionary Parameters of Duplicate Genes from Their Expression Data.Mol Biol Evol. 2021 Mar 9;38(3):1209-1224. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msaa267. Mol Biol Evol. 2021. PMID: 33045078 Free PMC article.
-
NXT2 is required for embryonic heart development in zebrafish.BMC Dev Biol. 2005 Mar 24;5:7. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-5-7. BMC Dev Biol. 2005. PMID: 15790397 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of genes differentially expressed during larval molting and metamorphosis of Helicoverpa armigera.BMC Dev Biol. 2007 Jun 25;7:73. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-7-73. BMC Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17588272 Free PMC article.
-
The non-dosage compensated Lsp1alpha gene of Drosophila melanogaster escapes acetylation by MOF in larval fat body nuclei, but is flanked by two dosage compensated genes.BMC Mol Biol. 2007 May 19;8:35. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-8-35. BMC Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17511883 Free PMC article.
-
Sexual Dimorphisms in Innate Immunity and Responses to Infection in Drosophila melanogaster.Front Immunol. 2020 Jan 31;10:3075. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.03075. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32076419 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arai Y., Hosoda, F., Kobayashi, H., Arai, K., Hayashi, Y., Kamada, N., Kaneko, Y. and Okhi, M. (1997) The inv(11)(p15q22) chromosome translocation of de novo and therapy-related myeloid malignancies result in fusion of the nucleoporin gene, NUP98, with the putative RNA helicase gene DDX10. Blood, 89, 3936–3944. - PubMed
-
- Bayliss R., Ribbeck, K., Akin, D., Kent, H.M., Feldherr, C., Görlich, D. and Stewart, M. (1999) Interaction between NTF2 and xFxFG-containing nucleoporins is required to mediate nuclear import of RanGDP. J. Mol. Biol., 293, 579–593. - PubMed
-
- Clarkson W.D., Kent, H.M. and Stewart, M. (1996) Separate binding sites on nuclear transport factor 2 for GDP–Ran and the phenylalanine-rich repeat regions of nucleoporins p62 and Nsp1p. J. Mol. Biol., 263, 517–524. - PubMed
-
- Corbett A.H. and Silver, P.A. (1996) The NTF2 gene encodes an essential, highly conserved protein that functions in nuclear transport in vivo. J. Biol. Chem., 271, 18477–18484. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

