Differential activation of innate immune responses by adenovirus and adeno-associated virus vectors
- PMID: 11932423
- PMCID: PMC155101
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.9.4580-4590.2002
Differential activation of innate immune responses by adenovirus and adeno-associated virus vectors
Abstract
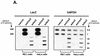
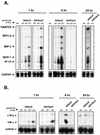
Adenovirus vectors induce acute inflammation of infected tissues due to activation of the innate immune system and expression of numerous chemokines and cytokines in transduced target cells. In contrast, adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors are not associated with significant inflammation experimentally or clinically. We tested the ability of AAV vectors to induce the expression of chemokines in vitro and to activate the innate immune system in vivo. In human HeLa cells and murine renal epithelium-derived cells (REC cells) the adenovirus vector AdlacZ induced the expression of multiple inflammatory chemokines including RANTES, interferon-inducible protein 10 (IP-10), interleukin-8 (IL-8), MIP-1beta, and MIP-2 in a dose-dependent manner. The use of AAVlacZ did not induce the expression of these chemokines above baseline levels despite 40-fold-greater titers than AdlacZ and greater amounts of intracellular AAVlacZ genomes according to Southern and slot blot analysis. This finding confirmed that the lack of AAVlacZ induction of chemokine was not due to reduced transduction. In DBA/2 mice, the intravenous administration of 2.5 x 10(11) particles of AAVlacZ resulted in the rapid induction of liver tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), RANTES, IP-10, MIP-1beta, MCP-1, and MIP-2 mRNAs. However, 6 h following injection, chemokine mRNA levels returned to baseline. As expected, administration of 10-fold less AdlacZ caused an induction of liver TNF-alpha and chemokine mRNAs that persisted for more than 24 h posttransduction. Whereas intravenous administration of 2.5 x 10(11) particles of AAVlacZ triggered a transient infiltration of neutrophils and CD11b(+) cells into liver, this response stood in contrast to widespread inflammation and toxicity induced by AdlacZ. Kupffer cell depletion abolished AAVlacZ but not AdlacZ-induced chemokine expression and neutrophil infiltration. In summary, these results show that AAV vectors activate the innate immune system to a lesser extent than do adenovirus vectors and offer a possible explanation for the reduced inflammatory properties of AAV compared to adenovirus vectors.
Figures
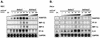

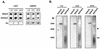



Similar articles
-
Adenoviral gene therapy leads to rapid induction of multiple chemokines and acute neutrophil-dependent hepatic injury in vivo.Hum Gene Ther. 1999 Apr 10;10(6):965-76. doi: 10.1089/10430349950018364. Hum Gene Ther. 1999. PMID: 10223730
-
The role of capsid-endothelial interactions in the innate immune response to adenovirus vectors.Hum Gene Ther. 2003 May 1;14(7):627-43. doi: 10.1089/104303403321618146. Hum Gene Ther. 2003. PMID: 12804145
-
Helper-dependent adenovirus vectors elicit intact innate but attenuated adaptive host immune responses in vivo.J Virol. 2004 Jun;78(11):5966-72. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.11.5966-5972.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15140994 Free PMC article.
-
Innate Immune Sensing of Adeno-Associated Virus Vectors.Hum Gene Ther. 2024 Jul;35(13-14):451-463. doi: 10.1089/hum.2024.040. Epub 2024 Jul 5. Hum Gene Ther. 2024. PMID: 38887999 Review.
-
Immune responses to adeno-associated virus vectors.Curr Gene Ther. 2005 Jun;5(3):323-31. doi: 10.2174/1566523054065039. Curr Gene Ther. 2005. PMID: 15975009 Review.
Cited by
-
AAV8 induces tolerance in murine muscle as a result of poor APC transduction, T cell exhaustion, and minimal MHCI upregulation on target cells.Mol Ther. 2014 Jan;22(1):28-41. doi: 10.1038/mt.2013.134. Epub 2013 Jun 19. Mol Ther. 2014. PMID: 23778424 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factor-based gene therapy to treat glioblastoma through direct neuronal conversion.Cancer Biol Med. 2021 Mar 23;18(3):860-74. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2020.0499. Online ahead of print. Cancer Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 33755378 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo reduction or blockade of interleukin-1β in primary osteoarthritis influences expression of mediators implicated in pathogenesis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012 Dec;20(12):1610-8. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2012.08.011. Epub 2012 Aug 27. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012. PMID: 22935786 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges for gene therapy for muscular dystrophy.Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2006 Jan;6(1):47-56. doi: 10.1007/s11910-996-0009-8. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2006. PMID: 16469271 Review.
-
Circulating anti-wild-type adeno-associated virus type 2 (AAV2) antibodies inhibit recombinant AAV2 (rAAV2)-mediated, but not rAAV5-mediated, gene transfer in the brain.J Virol. 2004 Jun;78(12):6344-59. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.12.6344-6359.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15163728 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amin, R., R. Wilmott, Y. Schwarz, B. Trapnell, and J. Stark. 1995. Replication-deficient adenovirus induces expression of interleukin-8 by airway epithelial cells in vitro. Hum. Gene Ther. 6:145-153. - PubMed
-
- Becker, T. C., H. BeltrandelRio, R. J. Noel, J. H. Johnson, and C. B. Newgard. 1994. Overexpression of hexokinase I in isolated islets of Langerhans via recombinant adenovirus. Enhancement of glucose metabolism and insulin secretion at basal but not stimulatory glucose levels. J. Biol. Chem. 269:21234-21238. - PubMed
-
- Becker, T. C., R. J. Noel, W. S. Coats, A. M. Gomez-Foix, T. Alam, R. D. Gerard, and C. B. Newgard. 1994. Use of recombinant adenovirus for metabolic engineering of mammalian cells. Methods Cell Biol. 43:161-189. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

