Stimulation of bone formation and prevention of bone loss by prostaglandin E EP4 receptor activation
- PMID: 11917107
- PMCID: PMC123690
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.062053399
Stimulation of bone formation and prevention of bone loss by prostaglandin E EP4 receptor activation
Abstract
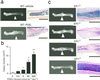
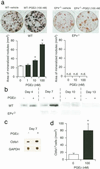
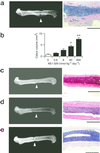
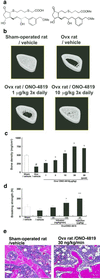
Bone remodeling, comprising resorption of existing bone and de novo bone formation, is required for the maintenance of a constant bone mass. Prostaglandin (PG)E2 promotes both bone resorption and bone formation. By infusing PGE2 to mice lacking each of four PGE receptor (EP) subtypes, we have identified EP4 as the receptor that mediates bone formation in response to this agent. Consistently, bone formation was induced in wild-type mice by infusion of an EP4-selective agonist and not agonists specific for other EP subtypes. In culture of bone marrow cells from wild-type mice, PGE2 induced expression of core-binding factor alpha1 (Runx2/Cbfa1) and enhanced formation of mineralized nodules, both of which were absent in the culture of cells from EP4-deficient mice. Furthermore, administration of the EP4 agonist restored bone mass and strength normally lost in rats subjected to ovariectomy or immobilization. Histomorphometric analysis revealed that the EP4 agonist induced significant increases in the volume of cancellous bone, osteoid formation, and the number of osteoblasts in the affected bone of immobilized rats, indicating that activation of EP4 induces de novo bone formation. In addition, osteoclasts were found on the increased bone surface at a density comparable to that found in the bone of control animals. These results suggest that activation of EP4 induces bone remodeling in vivo and that EP4-selective drugs may be beneficial in humans with osteoporosis.
Figures
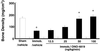
Similar articles
-
EP2 and EP4 receptors differentially mediate MAPK pathways underlying anabolic actions of prostaglandin E2 on bone formation in rat calvaria cell cultures.Bone. 2009 Jun;44(6):1177-85. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2009.02.010. Epub 2009 Feb 21. Bone. 2009. PMID: 19233324
-
Crucial involvement of the EP4 subtype of prostaglandin E receptor in osteoclast formation by proinflammatory cytokines and lipopolysaccharide.J Bone Miner Res. 2000 Feb;15(2):218-27. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.2000.15.2.218. J Bone Miner Res. 2000. PMID: 10703923
-
Effects of basic fibroblast growth factor and a prostaglandin E2 receptor subtype 4 agonist on osteoblastogenesis and adipogenesis in aged ovariectomized rats.J Bone Miner Res. 2007 Jun;22(6):877-88. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.070313. J Bone Miner Res. 2007. PMID: 17352655
-
[Role of EP4 receptor in bone resorption induced by PGE].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2001 Apr;117(4):293-7. doi: 10.1254/fpj.117.293. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2001. PMID: 11338379 Review. Japanese.
-
Prostaglandin EP2 and EP4 receptor agonists in bone formation and bone healing: In vivo and in vitro evidence.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2009 Jun;18(6):746-66. doi: 10.1517/13543780902893051. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19426119 Review.
Cited by
-
E-type prostanoid receptor 4 (EP4) in disease and therapy.Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Jun;138(3):485-502. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.03.006. Epub 2013 Mar 21. Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23523686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prostaglandin E(2) receptors in bone formation.Int Orthop. 2007 Dec;31(6):767-72. doi: 10.1007/s00264-007-0406-x. Epub 2007 Jun 26. Int Orthop. 2007. PMID: 17593365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prostaglandins in bone: bad cop, good cop?Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2010 May;21(5):294-301. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2009.12.004. Epub 2010 Jan 14. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2010. PMID: 20079660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single hormone or synthetic agonist induces Gs/Gi coupling selectivity of EP receptors via distinct binding modes and propagating paths.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Jul 25;120(30):e2216329120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2216329120. Epub 2023 Jul 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37478163 Free PMC article.
-
Ca2+-independent phospholipase A2β-derived PGE2 contributes to osteogenesis.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2022 Feb;158:106605. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2021.106605. Epub 2021 Dec 16. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2022. PMID: 34923151 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Manolagas S C. Endocr Rev. 2000;21:115–137. - PubMed
-
- NIH Consensus Development Panel on Osteoporosis Prevention, Diagnosis and Therapy. J Am Med Assoc. 2001;285:785–795. - PubMed
-
- Rodan G A, Martin T J. Science. 2000;289:1508–1514. - PubMed
-
- Karsenty G. Genes Dev. 1999;13:3037–3051. - PubMed
-
- Narumiya S, Sugimoto Y, Ushikubi F. Physiol Rev. 1999;79:1193–1226. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

