Critical but distinct roles for the pleckstrin homology and cysteine-rich domains as positive modulators of Vav2 signaling and transformation
- PMID: 11909943
- PMCID: PMC133724
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.8.2487-2497.2002
Critical but distinct roles for the pleckstrin homology and cysteine-rich domains as positive modulators of Vav2 signaling and transformation
Abstract
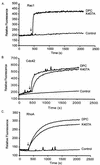
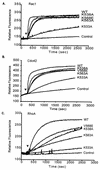
Vav2, like all Dbl family proteins, possesses tandem Dbl homology (DH) and pleckstrin homology (PH) domains and functions as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Rho family GTPases. Whereas the PH domain is a critical positive regulator of DH domain function for a majority of Dbl family proteins, the PH domains of the related Vav and Vav3 proteins are dispensable for DH domain activity. Instead, Vav proteins contain a cysteine-rich domain (CRD) critical for DH domain function. We evaluated the contribution of the PH domain and the CRD to Vav2 guanine nucleotide exchange, signaling, and transforming activity. Unexpectedly, we found that mutations of the PH domain impaired Vav2 signaling, transforming activity, and membrane association. However, these mutations do not influence exchange activity on Rac and only slightly affect exchange on RhoA and Cdc42. We also found that the CRD was critical for the exchange activity in vitro and contributed to Vav2 membrane localization. Finally, we found that phosphoinositol 3-kinase activation synergistically enhanced Vav2 transforming and signaling activity by stimulating exchange activity but not membrane association. In conclusion, the PH domain and CRD are mechanistically distinct, positive modulators of Vav2 DH domain function in vivo.
Figures

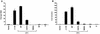

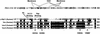
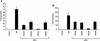

Similar articles
-
Recognition and activation of Rho GTPases by Vav1 and Vav2 guanine nucleotide exchange factors.Biochemistry. 2005 May 3;44(17):6573-85. doi: 10.1021/bi047443q. Biochemistry. 2005. PMID: 15850391
-
Critical role of the pleckstrin homology and cysteine-rich domains in Vav signaling and transforming activity.J Biol Chem. 2002 Oct 18;277(42):39350-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M202641200. Epub 2002 Aug 12. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12177050
-
Vav2 is required for cell spreading.J Cell Biol. 2001 Jul 9;154(1):177-86. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200103134. J Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11448999 Free PMC article.
-
Vav proteins, masters of the world of cytoskeleton organization.Cell Signal. 2004 Jan;16(1):1-11. doi: 10.1016/s0898-6568(03)00110-4. Cell Signal. 2004. PMID: 14607270 Review.
-
Signaling to the Rho GTPases: networking with the DH domain.FEBS Lett. 2002 Feb 20;513(1):85-91. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(01)03310-5. FEBS Lett. 2002. PMID: 11911885 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural basis of guanine nucleotide exchange mediated by the T-cell essential Vav1.J Mol Biol. 2008 Jul 25;380(5):828-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.05.024. Epub 2008 May 17. J Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18589439 Free PMC article.
-
LOVTRAP: an optogenetic system for photoinduced protein dissociation.Nat Methods. 2016 Sep;13(9):755-8. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3926. Epub 2016 Jul 18. Nat Methods. 2016. PMID: 27427858 Free PMC article.
-
An active form of Vav1 induces migration of mammary epithelial cells by stimulating secretion of an epidermal growth factor receptor ligand.Cell Commun Signal. 2006 May 18;4:5. doi: 10.1186/1478-811X-4-5. Cell Commun Signal. 2006. PMID: 16709244 Free PMC article.
-
Diacylglycerol-dependent binding recruits PKCtheta and RasGRP1 C1 domains to specific subcellular localizations in living T lymphocytes.Mol Biol Cell. 2004 Jun;15(6):2932-42. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e03-11-0844. Epub 2004 Apr 2. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15064353 Free PMC article.
-
Vav family exchange factors: an integrated regulatory and functional view.Small GTPases. 2014;5(2):9. doi: 10.4161/21541248.2014.973757. Small GTPases. 2014. PMID: 25483299 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abe, K., K. L. Rossman, B. Liu, K. D. Ritola, D. Chiang, S. L. Campbell, K. Burridge, and C. J. Der. 2000. Vav2 is an activator of Cdc42, Rac1, and RhoA. J. Biol. Chem. 275:10141-10149. - PubMed
-
- Abe, K., I. P. Whitehead, J. P. O'Bryan, and C. J. Der. 1999. Involvement of N-terminal sequences in the negative regulation of vav signaling and transforming activity. J. Biol. Chem. 274:30410-30418. - PubMed
-
- Brtva, T. R., J. K. Drugan, S. Ghosh, R. S. Terrell, S. Campbell-Burk, R. M. Bell, and C. J. Der. 1995. Two distinct Raf domains mediate interaction with Ras. J. Biol. Chem. 270:9809-9812. - PubMed
-
- Buss, J. E., P. A. Solski, J. P. Schaeffer, M. J. MacDonald, and C. J. Der. 1989. Activation of the cellular proto-oncogene product p21Ras by addition of a myristylation signal. Science 243:1600-1603. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
