Histone H1 represses estrogen receptor alpha transcriptional activity by selectively inhibiting receptor-mediated transcription initiation
- PMID: 11909941
- PMCID: PMC133703
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.8.2463-2471.2002
Histone H1 represses estrogen receptor alpha transcriptional activity by selectively inhibiting receptor-mediated transcription initiation
Abstract
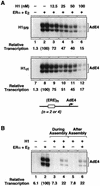
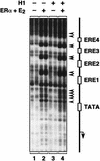
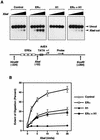
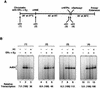
Chromatin is the physiological template for many nuclear processes in eukaryotes, including transcription by RNA polymerase II. In vivo, chromatin is assembled from genomic DNA, core histones, linker histones such as histone H1, and nonhistone chromatin-associated proteins. Histone H1 is thought to act as a general repressor of transcription by promoting the compaction of chromatin into higher-order structures. We have used a biochemical approach, including an in vitro chromatin assembly and transcription system, to examine the effects of histone H1 on estrogen receptor alpha (ER alpha)-mediated transcription with chromatin templates. We show that histone H1 acts as a potent repressor of ligand- and coactivator-regulated transcription by ER alpha. Histone H1 exerts its repressive effect without inhibiting the sequence-specific binding of ER alpha to chromatin or the overall extent of targeted acetylation of nucleosomal histones by the coactivator p300. Instead, histone H1 acts by blocking a specific step in the ER alpha-dependent transcription process, namely, transcription initiation, without affecting transcription reinitiation. Together, our data indicate that histone H1 acts selectively to reduce the overall level of productive transcription initiation by restricting promoter accessibility and preventing the ER alpha-dependent formation of a stable transcription pre-initiation complex.
Figures

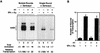
Similar articles
-
Mediator and p300/CBP-steroid receptor coactivator complexes have distinct roles, but function synergistically, during estrogen receptor alpha-dependent transcription with chromatin templates.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Jan;23(1):335-48. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.1.335-348.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12482985 Free PMC article.
-
A role for coactivators and histone acetylation in estrogen receptor alpha-mediated transcription initiation.EMBO J. 2001 Nov 1;20(21):6084-94. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.21.6084. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11689448 Free PMC article.
-
pRb2/p130-E2F4/5-HDAC1-SUV39H1-p300 and pRb2/p130-E2F4/5-HDAC1-SUV39H1-DNMT1 multimolecular complexes mediate the transcription of estrogen receptor-alpha in breast cancer.Oncogene. 2003 Jun 5;22(23):3511-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206578. Oncogene. 2003. PMID: 12789259
-
Nuclear matrix, dynamic histone acetylation and transcriptionally active chromatin.Mol Biol Rep. 1997 Aug;24(3):197-207. doi: 10.1023/a:1006811817247. Mol Biol Rep. 1997. PMID: 9291093 Review.
-
Influence of linker histone H1 on chromatin remodeling.Biochem Cell Biol. 2001;79(3):317-24. Biochem Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11467745 Review.
Cited by
-
Biochemical analyses of transcriptional regulatory mechanisms in a chromatin context.Methods. 2007 Mar;41(3):259-70. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2006.11.004. Methods. 2007. PMID: 17309835 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative proteomics and transcriptomics addressing the estrogen receptor subtype-mediated effects in T47D breast cancer cells exposed to the phytoestrogen genistein.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011 Jan;10(1):M110.002170. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M110.002170. Epub 2010 Sep 30. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011. PMID: 20884965 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin exposes intrinsic differences in the transcriptional activities of estrogen receptors alpha and beta.EMBO J. 2003 Feb 3;22(3):600-11. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg037. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12554660 Free PMC article.
-
Competition between histone H1 and HMGN proteins for chromatin binding sites.EMBO Rep. 2002 Aug;3(8):760-6. doi: 10.1093/embo-reports/kvf156. Epub 2002 Jul 15. EMBO Rep. 2002. PMID: 12151335 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin remodeling by nuclear receptors.Chromosoma. 2003 May;111(8):495-504. doi: 10.1007/s00412-003-0232-x. Epub 2003 Feb 26. Chromosoma. 2003. PMID: 12743713 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
