Small-molecule antagonists of Myc/Max dimerization inhibit Myc-induced transformation of chicken embryo fibroblasts
- PMID: 11891322
- PMCID: PMC122609
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.062036999
Small-molecule antagonists of Myc/Max dimerization inhibit Myc-induced transformation of chicken embryo fibroblasts
Abstract
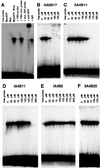
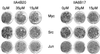
Myc is a transcriptional regulator of the basic helix-loop-helix leucine zipper protein family. It has strong oncogenic potential, mutated or virally transduced forms of Myc induce lymphoid tumors in animals, and deregulated expression of Myc is associated with numerous types of human cancers. For its oncogenic activity, Myc must dimerize with the ubiquitously expressed basic helix-loop-helix leucine zipper protein Max. This requirement for dimerization may allow control of Myc activity with small molecules that interfere with Myc/Max dimerization. We have measured Myc/Max dimerization with fluorescence resonance energy transfer and have screened combinatorial chemical libraries for inhibitors of dimerization. Candidate inhibitors were isolated from a peptidomimetics library. Inhibition of Myc/Max interaction was validated by ELISA and electrophoretic mobility-shift assay. Two of the candidate inhibitors also interfere with Myc-induced oncogenic transformation in chicken embryo fibroblast cultures. Our work provides proof of principle for the identification of small molecule inhibitors of protein-protein interactions by using high-throughput screens of combinatorial chemical libraries.
Figures
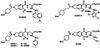

Similar articles
-
Low molecular weight inhibitors of Myc-Max interaction and function.Oncogene. 2003 Sep 18;22(40):6151-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206641. Oncogene. 2003. PMID: 13679853
-
Structure, function, and dynamics of the dimerization and DNA-binding domain of oncogenic transcription factor v-Myc.J Mol Biol. 2001 Apr 13;307(5):1395-410. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.4537. J Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11292350
-
A credit-card library approach for disrupting protein-protein interactions.Bioorg Med Chem. 2006 Apr 15;14(8):2660-73. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2005.11.052. Epub 2005 Dec 27. Bioorg Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 16384710
-
Function of the c-Myc oncogenic transcription factor.Exp Cell Res. 1999 Nov 25;253(1):63-77. doi: 10.1006/excr.1999.4686. Exp Cell Res. 1999. PMID: 10579912 Review.
-
Small-molecule modulators of c-Myc/Max and Max/Max interactions.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2011;348:139-49. doi: 10.1007/82_2010_90. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2011. PMID: 20680803 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacophore identification of c-Myc inhibitor 10074-G5.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013 Jan 1;23(1):370-4. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.10.013. Epub 2012 Oct 17. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013. PMID: 23177256 Free PMC article.
-
Demystifying the Druggability of the MYC Family of Oncogenes.J Am Chem Soc. 2023 Feb 15;145(6):3259-3269. doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c12732. Epub 2023 Feb 3. J Am Chem Soc. 2023. PMID: 36734615 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thermodynamics of protein-protein interactions of cMyc, Max, and Mad: effect of polyions on protein dimerization.Biochemistry. 2006 Feb 21;45(7):2333-8. doi: 10.1021/bi0522551. Biochemistry. 2006. PMID: 16475822 Free PMC article.
-
Small-molecule inhibitors of the Myc oncoprotein.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 May;1849(5):525-43. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.03.005. Epub 2014 Mar 19. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 24657798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting of the MYCN protein with small molecule c-MYC inhibitors.PLoS One. 2014 May 23;9(5):e97285. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097285. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24859015 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

