Complement C4 monitoring in the follow-up of chronic hepatitis C treatment
- PMID: 11882043
- PMCID: PMC1906298
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2002.01729.x
Complement C4 monitoring in the follow-up of chronic hepatitis C treatment
Abstract
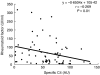
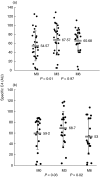
The overall role of complement in the host--pathogen relationship is now well understood. However, its involvement at a chronic stage of infection, such as chronic hepatitis C, is less well documented. Here, results are reported which point to the use of specific C4 monitoring in the follow-up of HCV patients. This study concerns 66 patients with chronic HCV infection, treated with interferon alpha 2b alone or with interferon alpha 2b + ribavirin, and 50 healthy adults as controls. Complement blood tests were performed to measure C1q, C3, C4, mannan binding lectin (MBL), C1s-C1 inhibitor complexes, total (CH50) and C4 (C4H) haemolytic activity; specific C4 activity was taken as the C4H/C4 protein ratio. Rheumatoid factor (RF) levels were also measured. A significant reduction in CH50 and specific C4 activity in HCV patients, compared with the healthy controls, was observed before the onset of treatment; the other parameters were not affected and no C1s-C1 inhibitor complexes were detected. At the same time, a significant reduction in specific C4 activity was observed in relapsers compared with sustained responders. These results point to a potential predictive function of C4 specific activity to monitor the response to therapy. Restoration of specific C4 activity at 6 months was better in responders than in non-responders. Complement activation in chronic hepatitis C does not seem to involve the C1 stage of the classical pathway. A negative correlation between specific C4 activity and RF titres suggests a possible involvement of RF in C4 activation, via the lectin pathway. Specific C4 monitoring appears to be a valuable tool for the follow-up of chronic hepatitis C treatment, together with the other conventional investigations.
Figures
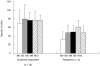
Similar articles
-
Serum complements C3 and C4 in chronic HCV infection and their correlation with response to pegylated interferon and ribavirin treatment.Arab J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jun;15(2):58-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ajg.2014.04.005. Epub 2014 Jun 2. Arab J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25097047
-
Effect of IFN-alpha on total haemolytic activity of CH50 complement system and C3, C4 levels in children with chronic hepatitis C.Med Sci Monit. 2001 May;7 Suppl 1:202-6. Med Sci Monit. 2001. PMID: 12211720
-
Early HCV RNA changes in patients with chronic hepatitis C treated with peginterferon alfa 2b and ribavirin.Rev Invest Clin. 2003 Mar-Apr;55(2):138-42. Rev Invest Clin. 2003. PMID: 12827916
-
Interferon-alpha-2b plus ribavirin: a review of its use in the management of chronic hepatitis C.Drugs. 2002;62(3):507-56. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200262030-00009. Drugs. 2002. PMID: 11827565 Review.
-
A comparison of peginterferon α-2a and α-2b for treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis C virus: A meta-analysis of randomized trials.Clin Ther. 2010 Aug;32(9):1565-77. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2010.08.009. Clin Ther. 2010. PMID: 20974315 Review.
Cited by
-
Phospholipase A2 Receptor-Related Membranous Nephropathy and Mannan-Binding Lectin Deficiency.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016 Dec;27(12):3539-3544. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2015101155. Epub 2016 May 6. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27153925 Free PMC article.
-
Complement complex 1 subunit q-mediated hepatic stellate cell activation with connective tissue growth factor elevation is a prognostic factor for survival in rat and human chronic liver diseases.Hepatol Commun. 2022 Dec;6(12):3515-3527. doi: 10.1002/hep4.2097. Epub 2022 Oct 5. Hepatol Commun. 2022. PMID: 36199236 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody-dependent enhancement of hepatitis C virus infection.J Virol. 2008 Mar;82(5):2140-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01867-07. Epub 2007 Dec 19. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18094180 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of plasma biomarkers in HIV-1/HCV mono- and coinfected individuals by multiplex iTRAQ quantitative proteomics.OMICS. 2011 Oct;15(10):705-17. doi: 10.1089/omi.2011.0004. OMICS. 2011. PMID: 21978398 Free PMC article.
-
Serum complement C4a and its relation to liver fibrosis in children with chronic hepatitis C.World J Hepatol. 2013 Aug 27;5(8):445-51. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v5.i8.445. World J Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 24023984 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Choo QL, Kuo G, Wriner AJ, Overby LR, Bradley DW, Houghton M. Isolation of a cDNA clone derived from a blood-borne non-A, non-B viral hepatitis genome. Science. 1989;244:359–62. - PubMed
-
- Gales MJ, Korth MJ, Tang NM, et al. Evidence that hepatitis C resistance to interferon is mediated through repression of the PKR protein kinase by the non structural 5A protein. Virology. 1997;230:217–27. - PubMed
-
- Morgan BP, Harris CL. Complement regulators and micro-organisms. In: Morgan BP, Harris CL, editors. Complement regulatory proteins. San Diego: Academic Press; 1999. pp. 207–25.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

