Analysis of DNA microarrays using algorithms that employ rule-based expert knowledge
- PMID: 11854507
- PMCID: PMC122328
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.251687398
Analysis of DNA microarrays using algorithms that employ rule-based expert knowledge
Abstract
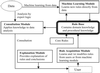
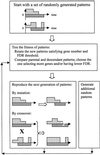
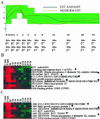
The ability to investigate the transcription of thousands of genes concurrently by using DNA microarrays offers both major scientific opportunities and significant analytical challenges. Here we describe GABRIEL, a rule-based system of computer programs designed to apply domain-specific and procedural knowledge systematically and uniformly for the analysis and interpretation of data from DNA microarrays. GABRIEL'S problem-solving rules direct stereotypical tasks, whereas domain-specific knowledge pertains to gene functions and relationships or to experimental conditions. Additionally, GABRIEL can learn novel rules through genetic algorithms, which define patterns that best match the data being analyzed and can identify groupings in gene expression profiles preordered by chromosomal position or by a nonsupervised algorithm such as hierarchical clustering. GABRIEL subsystems explain the logic that underlies conclusions and provide a graphical interface and interactive platform for the acquisition of new knowledge. The present report compares GABRIEL'S output with published findings in which expert knowledge has been applied post hoc to microarray groupings generated by hierarchical clustering.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Transcriptomes for serial analysis of gene expression].J Soc Biol. 2002;196(4):303-7. J Soc Biol. 2002. PMID: 12645300 Review. French.
-
A method for clustering gene expression data based on graph structure.Genome Inform. 2004;15(2):151-60. Genome Inform. 2004. PMID: 15706501
-
Clustering short time series gene expression data.Bioinformatics. 2005 Jun;21 Suppl 1:i159-68. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti1022. Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 15961453
-
goCluster integrates statistical analysis and functional interpretation of microarray expression data.Bioinformatics. 2005 Sep 1;21(17):3575-7. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti574. Epub 2005 Jul 14. Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 16020468
-
Data Analysis Strategies for Protein Microarrays.Microarrays (Basel). 2012 Aug 6;1(2):64-83. doi: 10.3390/microarrays1020064. Microarrays (Basel). 2012. PMID: 27605336 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analytical Validation and Application of a Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing Mutation-Detection Assay for Use in Treatment Assignment in the NCI-MPACT Trial.J Mol Diagn. 2016 Jan;18(1):51-67. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2015.07.006. Epub 2015 Nov 18. J Mol Diagn. 2016. PMID: 26602013 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Phenotype-based identification of host genes required for replication of African swine fever virus.J Virol. 2006 Sep;80(17):8705-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00475-06. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16912318 Free PMC article.
-
A parallel genetic algorithm for single class pattern classification and its application for gene expression profiling in Streptomyces coelicolor.BMC Genomics. 2007 Feb 13;8:49. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-49. BMC Genomics. 2007. PMID: 17298664 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular analyses of disease pathogenesis: application of bovine microarrays.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2005 May 15;105(3-4):277-87. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2005.02.015. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2005. PMID: 15808306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic expression profiling of TNF-alpha-treated BDC2.5 diabetogenic CD4+ T cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Jul 22;105(29):10107-12. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0803336105. Epub 2008 Jul 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18632574 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

