C2A activates a cryptic Ca(2+)-triggered membrane penetration activity within the C2B domain of synaptotagmin I
- PMID: 11805296
- PMCID: PMC122248
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.032541099
C2A activates a cryptic Ca(2+)-triggered membrane penetration activity within the C2B domain of synaptotagmin I
Abstract
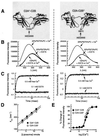
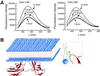
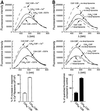
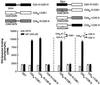
Synaptotagmin (syt) I, an integral membrane protein localized to secretory vesicles, is a putative Ca(2+) sensor for exocytosis. Its N terminus spans the membrane once, and its cytoplasmic domain contains two conserved C2 domains, designated C2A and C2B. The isolated C2A domain penetrates membranes in response to Ca(2+); isolated C2B does not. Here, we have addressed the function of each C2 domain, but in the context of the intact cytoplasmic domain (C2A-C2B), by using fluorescent reporters placed in the Ca(2+)-binding loops of either C2A or C2B. Surprisingly, these reporters revealed that, analogous to C2A, a Ca(2+)-binding loop in C2B directly penetrates into lipid bilayers. Penetration of each C2 domain was very rapid (k(on) approximately 10(10) M(-1) x s(-1)) and resulted in high affinity C2A-C2B-liposome complexes (K(d) approximately 13-14 nM). C2B-bilayer penetration strictly depended on the presence, but not the membrane binding activity, of an adjacent C2A domain, severing C2A from C2B after protein synthesis abolished the ability of C2B to dip into bilayers in response to Ca(2+). The activation of C2B by C2A was also displayed by the C2 domains of syt III but not the C2 domains of syt IV. A number of proteins contain more than one C2 domain; the findings reported here suggest these domains may harbor cryptic activities that are not detected when they are studied in isolation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Membrane-embedded synaptotagmin penetrates cis or trans target membranes and clusters via a novel mechanism.J Biol Chem. 2000 Aug 18;275(33):25427-35. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M906729199. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10840045
-
Mutations in the effector binding loops in the C2A and C2B domains of synaptotagmin I disrupt exocytosis in a nonadditive manner.J Biol Chem. 2003 Nov 21;278(47):47030-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M306728200. Epub 2003 Sep 8. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12963743
-
The C2B domain of synaptotagmin is a Ca(2+)-sensing module essential for exocytosis.J Cell Biol. 2000 Sep 4;150(5):1125-36. doi: 10.1083/jcb.150.5.1125. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10974000 Free PMC article.
-
The C2 domains of synaptotagmin--partners in exocytosis.Trends Biochem Sci. 2004 Mar;29(3):143-51. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2004.01.008. Trends Biochem Sci. 2004. PMID: 15003272 Review.
-
Role of synaptotagmin, a Ca2+ and inositol polyphosphate binding protein, in neurotransmitter release and neurite outgrowth.Chem Phys Lipids. 1999 Apr;98(1-2):59-67. doi: 10.1016/s0009-3084(99)00018-3. Chem Phys Lipids. 1999. PMID: 10358928 Review.
Cited by
-
High Functioning Autism with Missense Mutations in Synaptotagmin-Like Protein 4 (SYTL4) and Transmembrane Protein 187 (TMEM187) Genes: SYTL4- Protein Modeling, Protein-Protein Interaction, Expression Profiling and MicroRNA Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 9;20(13):3358. doi: 10.3390/ijms20133358. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31323913 Free PMC article.
-
DOC2B, C2 domains, and calcium: A tale of intricate interactions.Mol Neurobiol. 2010 Feb;41(1):42-51. doi: 10.1007/s12035-009-8094-8. Epub 2010 Jan 7. Mol Neurobiol. 2010. PMID: 20052564 Review.
-
Correlation between evoked neurotransmitter release and adaptive functions in SYT1-associated neurodevelopmental disorder.EBioMedicine. 2024 Nov;109:105416. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105416. Epub 2024 Oct 30. EBioMedicine. 2024. PMID: 39481209 Free PMC article.
-
Rat and Drosophila synaptotagmin 4 have opposite effects during SNARE-catalyzed membrane fusion.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 1;285(40):30759-66. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.137745. Epub 2010 Aug 5. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20688915 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the lipid binding properties of Otoferlin reveals specific interactions between PI(4,5)P2 and the C2C and C2F domains.Biochemistry. 2014 Aug 5;53(30):5023-33. doi: 10.1021/bi5004469. Epub 2014 Jul 23. Biochemistry. 2014. PMID: 24999532 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Augustine G J. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2001;11:320–326. - PubMed
-
- Brose N, Petrenko A G, Südhof T C, Jahn R. Science. 1992;256:1021–1025. - PubMed
-
- Fernandez-Chacon R, Konigstorfer A, Gerber S H, Garcia J, Matos M F, Stevens C F, Brose N, Rizo J, Rosenmund C, Südhof T C. Nature (London) 2001;410:41–49. - PubMed
-
- Perin M S, Fried V A, Mignery G A, Jahn R, Südhof T C. Nature (London) 1990;345:260–263. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

