Inhibition of duck hepatitis B virus infection by a myristoylated pre-S peptide of the large viral surface protein
- PMID: 11799193
- PMCID: PMC135925
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.4.1986-1990.2002
Inhibition of duck hepatitis B virus infection by a myristoylated pre-S peptide of the large viral surface protein
Abstract
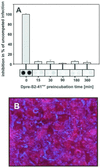
We have used the duck hepatitis B virus (DHBV) model to study the interference with infection by a myristoylated peptide representing an N-terminal pre-S subdomain of the large viral envelope protein. Although lacking the essential part of the carboxypeptidase D (formerly called gp180) receptor binding site, the peptide binds hepatocytes and subsequently blocks DHBV infection. Since its activity requires an amino acid sequence involved in host discrimination between DHBV and the related heron HBV (T. Ishikawa and D. Ganem, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92:6259-6263, 1995), we suggest that it is related to the postulated host-discriminating cofactor of infection.
Figures

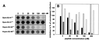
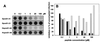
Similar articles
-
Viral and cellular determinants involved in hepadnaviral entry.World J Gastroenterol. 2007 Jan 7;13(1):22-38. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i1.22. World J Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 17206752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterologous replacement of the supposed host determining region of avihepadnaviruses: high in vivo infectivity despite low infectivity for hepatocytes.PLoS Pathog. 2008 Dec;4(12):e1000230. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000230. Epub 2008 Dec 5. PLoS Pathog. 2008. PMID: 19057662 Free PMC article.
-
Glycine decarboxylase mediates a postbinding step in duck hepatitis B virus infection.J Virol. 2004 Feb;78(4):1873-81. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.4.1873-1881.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 14747552 Free PMC article.
-
Avian hepatitis B virus infection is initiated by the interaction of a distinct pre-S subdomain with the cellular receptor gp180.J Virol. 1998 Oct;72(10):8089-97. doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.10.8089-8097.1998. J Virol. 1998. PMID: 9733849 Free PMC article.
-
[Research on the gene structure of duck hepatitis B virus and its encoding proteins].Bing Du Xue Bao. 2012 Nov;28(6):681-8. Bing Du Xue Bao. 2012. PMID: 23367570 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Fine mapping of pre-S sequence requirements for hepatitis B virus large envelope protein-mediated receptor interaction.J Virol. 2010 Feb;84(4):1989-2000. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01902-09. Epub 2009 Dec 9. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20007265 Free PMC article.
-
Viral and cellular determinants involved in hepadnaviral entry.World J Gastroenterol. 2007 Jan 7;13(1):22-38. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i1.22. World J Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 17206752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two potentially important elements of the hepatitis B virus large envelope protein are dispensable for the infectivity of hepatitis delta virus.J Virol. 2007 Apr;81(8):4343-7. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02478-06. Epub 2007 Jan 24. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17251287 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in HBV infection and replication systems in vitro.Virol J. 2021 May 29;18(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s12985-021-01580-6. Virol J. 2021. PMID: 34051803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Infection of a human hepatoma cell line by hepatitis B virus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Nov 26;99(24):15655-60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.232137699. Epub 2002 Nov 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12432097 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Borst, E. M. 1997. Untersuchungen zur Interaktion des Enten Hepatitis B Virus L-Proteins mit primären Entenhepatozyten. Ph.D. thesis. University of Ulm, Ulm, Germany.
-
- Chan, D. C., and P. S. Kim. 1998. HIV entry and its inhibition. Cell 93:681-684. - PubMed
-
- Gripon, P., J. Le Seyec, S. Rumin, and C. Guguen-Guillouzo. 1995. Myristylation of the hepatitis B virus large surface protein is essential for viral infectivity. Virology 213:292-299. - PubMed
-
- Ishikawa, T., K. Kuroki, R. Lenhoff, J. Summers, and D. Ganem. 1994. Analysis of the binding of a host cell surface glycoprotein to the pre-S protein of duck hepatitis B virus. Virology 202:1061-1064. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

