Histone-dependent association of Tup1-Ssn6 with repressed genes in vivo
- PMID: 11784848
- PMCID: PMC133554
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.3.693-703.2002
Histone-dependent association of Tup1-Ssn6 with repressed genes in vivo
Abstract
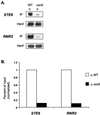
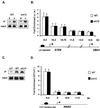
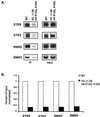
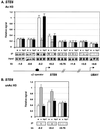
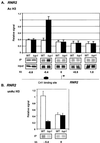
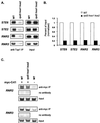
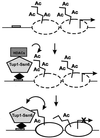
The Tup1-Ssn6 complex regulates diverse classes of genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and serves as a model for corepressor functions in many organisms. Tup1-Ssn6 does not directly bind DNA but is brought to target genes through interactions with sequence-specific DNA binding factors. Full repression by Tup1-Ssn6 appears to require interactions with both the histone tails and components of the general transcription machinery, although the relative contribution of these two pathways is not clear. Here, we map Tup1 locations on two classes of Tup1-Ssn6-regulated genes in vivo via chromatin immunoprecipitations. Distinct profiles of Tup1 are observed on a cell-specific genes and DNA damage-inducible genes, suggesting that alternate repressive architectures may be created on different classes of repressed genes. In both cases, decreases in acetylation of histone H3 colocalize with Tup1. Strikingly, although loss of the Srb10 mediator protein had no effect on Tup1 localization, both histone tail mutations and histone deacetylase mutations crippled the association of Tup1 with target loci. Together with previous findings that Tup1-Ssn6 physically associates with histone deacetylase activities, these results indicate that the repressor complex alters histone modification states to facilitate interactions with histones and that these interactions are required to maintain a stable repressive state.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Promoter-dependent roles for the Srb10 cyclin-dependent kinase and the Hda1 deacetylase in Tup1-mediated repression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Biol Cell. 2004 Sep;15(9):4191-202. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-05-0412. Epub 2004 Jul 7. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15240822 Free PMC article.
-
Ssn6-Tup1 interacts with class I histone deacetylases required for repression.Genes Dev. 2000 Nov 1;14(21):2737-44. doi: 10.1101/gad.829100. Genes Dev. 2000. PMID: 11069890 Free PMC article.
-
Redundant mechanisms are used by Ssn6-Tup1 in repressing chromosomal gene transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Biol Chem. 2004 Sep 17;279(38):39240-50. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M407159200. Epub 2004 Jul 14. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15254041
-
Transcriptional repression by Tup1-Ssn6.Biochem Cell Biol. 2006 Aug;84(4):437-43. doi: 10.1139/o06-073. Biochem Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16936817 Review.
-
Rox1 mediated repression. Oxygen dependent repression in yeast.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2000;475:185-95. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2000. PMID: 10849660 Review.
Cited by
-
Tup1-Ssn6 and Swi-Snf remodelling activities influence long-range chromatin organization upstream of the yeast SUC2 gene.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(16):5520-31. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm573. Epub 2007 Aug 17. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17704134 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Transcriptional Memory of GAL Genes Depends on Growth in Glucose and the Tup1 Transcription Factor in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2017 Aug;206(4):1895-1907. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.201632. Epub 2017 Jun 12. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 28607146 Free PMC article.
-
Promoter-dependent roles for the Srb10 cyclin-dependent kinase and the Hda1 deacetylase in Tup1-mediated repression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Biol Cell. 2004 Sep;15(9):4191-202. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-05-0412. Epub 2004 Jul 7. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15240822 Free PMC article.
-
SWI/SNF-dependent chromatin remodeling of RNR3 requires TAF(II)s and the general transcription machinery.Genes Dev. 2003 Feb 15;17(4):502-15. doi: 10.1101/gad.1039503. Genes Dev. 2003. PMID: 12600943 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of flocculation upon global gene transcription in a yeast CYC8 mutant.Microb Genom. 2024 Mar;10(3):001216. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.001216. Microb Genom. 2024. PMID: 38529898 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bannister, A. J., P. Zegerman, J. F. Partridge, E. A. Miska, J. O. Thomas, R. C. Allshire, and T. Kouzarides. 2001. Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature 410:120–124. - PubMed
-
- Bone, J. R., and S. Y. Roth. 2001. Recruitment of the yeast Tup1p-Ssn6p repressor is associated with localized decreases in histone acetylation. J. Biol. Chem. 276:1808–1813. - PubMed
-
- Burke, D., D. Dawson, and T. Stearns. 2000. Methods in yeast genetics. A Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory course manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
-
- Chen, G., and A. J. Courey. 2000. Groucho/TLE family proteins and transcriptional repression. Gene 249:1–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
