Role of Bcl-2 family members in caspase-independent apoptosis during Chlamydia infection
- PMID: 11748163
- PMCID: PMC127616
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.1.55-61.2002
Role of Bcl-2 family members in caspase-independent apoptosis during Chlamydia infection
Abstract
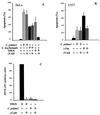
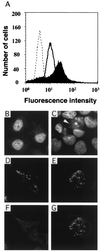
Infection with an obligate intracellular bacterium, the Chlamydia trachomatis lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV/L2) strain or the guinea pig inclusion conjunctivitis serovar of Chlamydia psittaci, leads to apoptosis of host cells. The apoptosis is not affected by a broad-spectrum caspase inhibitor, and caspase-3 is not activated in infected cells, suggesting that apoptosis mediated by these two strains of Chlamydia is independent of known caspases. Overexpression of the proapoptotic Bcl-2 family member, Bax, was previously shown to induce caspase-independent apoptosis, and we find that Bax is activated and translocates from the cytosol to the mitochondria in C. psittaci-infected cells. C. psittaci-induced apoptosis is inhibited in host cells overexpressing Bax inhibitor-1 and is inhibited through overexpression of Bcl-2, which blocks both caspase-dependent and -independent apoptosis. As Bax and mitochondria are ideally located to sense stress-related metabolic changes emanating from the interior of an infected cell, it is likely that Bax-dependent apoptosis may also be observed in cells infected with other intracellular pathogens.
Figures
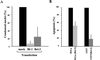
Similar articles
-
Cell death, BAX activation, and HMGB1 release during infection with Chlamydia.Microbes Infect. 2004 Nov;6(13):1145-55. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2004.07.004. Microbes Infect. 2004. PMID: 15488733
-
The histone deacetylase inhibitor suberic bishydroxamate regulates the expression of multiple apoptotic mediators and induces mitochondria-dependent apoptosis of melanoma cells.Mol Cancer Ther. 2004 Apr;3(4):425-35. Mol Cancer Ther. 2004. PMID: 15078986
-
Bax membrane insertion during Fas(CD95)-induced apoptosis precedes cytochrome c release and is inhibited by Bcl-2.Oncogene. 1999 Oct 28;18(44):5991-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203001. Oncogene. 1999. PMID: 10557088
-
Bcl-X(L) and calyculin A prevent translocation of Bax to mitochondria during apoptosis.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002 Mar 15;291(5):1258-64. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2002.6584. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002. PMID: 11883953
-
Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization is a critical step of lysosome-initiated apoptosis induced by hydroxychloroquine.Oncogene. 2003 Jun 19;22(25):3927-36. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206622. Oncogene. 2003. PMID: 12813466
Cited by
-
Role of high-mobility group box 1 protein and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 degradation in Chlamydia trachomatis-induced cytopathicity.Infect Immun. 2010 Jul;78(7):3288-97. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01404-09. Epub 2010 Apr 26. Infect Immun. 2010. PMID: 20421386 Free PMC article.
-
Neisseria gonorrhoeae Limits Chlamydia trachomatis Inclusion Development and Infectivity in a Novel In Vitro Co-Infection Model.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Jul 7;12:911818. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.911818. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35873141 Free PMC article.
-
Chlamydia pneumoniae augments the oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced death of mouse macrophages by a caspase-independent pathway.Infect Immun. 2005 Jul;73(7):4315-22. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.7.4315-4322.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 15972525 Free PMC article.
-
Chlamydia trachomatis infection inhibits both Bax and Bak activation induced by staurosporine.Infect Immun. 2004 Sep;72(9):5470-4. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.9.5470-5474.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15322047 Free PMC article.
-
Absence of Specific Chlamydia trachomatis Inclusion Membrane Proteins Triggers Premature Inclusion Membrane Lysis and Host Cell Death.Cell Rep. 2017 May 16;19(7):1406-1417. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.04.058. Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 28514660 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams, J. M., and S. Cory. 1998. The Bcl-2 protein family: arbiters of cell survival. Science 281: 1322–1326. - PubMed
-
- Aillet, F., H. Masutani, C. Elbim, H. Raoul, L. Chêne, M.-T. Nugeyre, C. Paya, F. Barré-Sinoussi, M.-A. Gougerot-Pocidalo, and N. Israël. 1998. Human immunodeficiency virus induces a dual regulation of Bcl-2, resulting in persistent infection of CD4+ T or monocytic cell lines. J. Virol. 72: 9698–9705. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amarante-Mendes, G. P., D. M. Finucane, S. J. Martin, T. G. Cotter, G. S. Salvesen, and D. R. Green. 1998. Anti-apoptotic oncogenes prevent caspase-dependent and independent commitment for cell death. Cell Death Differ. 5: 298–306. - PubMed
-
- Ameisen, J. C., J. Estaquier, and T. Idziorek. 1994. From AIDS to parasite infection: pathogen-mediated subversion of programmed cell death as a mechanism for immune dysregulation. Immunol. Rev. 142: 9–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

