5-fluorouracil-induced cardiotoxicity mimicking myocardial infarction: a case report
- PMID: 11734065
- PMCID: PMC60652
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2261-1-3
5-fluorouracil-induced cardiotoxicity mimicking myocardial infarction: a case report
Abstract
Background: Severe cardiotoxicity is a documented, but very unusual side-effect of intravenous 5-fluorouracil therapy. The mechanism producing cardiotoxicity is poorly understood.
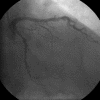
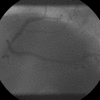
Case presentation: A case of 5-fluorouracil-induced cardiotoxicity, possibly due to coronary artery spasm, and mimicking acute anterolateral myocardial infarction is presented and discussed. Electrocardiographs highlighting the severity of the presentation are included in the report along with coronary angiograms demonstrating the absence of significant coronary atherosclerosis.
Conclusion: Severe 5-fluorouracil-induced cardiotoxicity is rare, but can be severe and may mimic acute myocardial infarction, leading to diagnostic and therapeutic dilemmas. Readministration of 5-fluorouracil is not advised following an episode of cardiotoxicity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A case of 5-fluorouracil cardiotoxicity simulating acute myocardial infarction.Jpn Circ J. 1995 May;59(5):303-7. doi: 10.1253/jcj.59.303. Jpn Circ J. 1995. PMID: 7596036
-
A case of coronary spasm induced by 5-fluorouracil.Acta Cardiol. 2002 Oct;57(5):381-3. doi: 10.2143/AC.57.5.2005458. Acta Cardiol. 2002. PMID: 12405579
-
Management of patients with persistent chest pain and ST-segment elevation during 5-fluorouracil treatment: report about two cases.Ital Heart J. 2003 Dec;4(12):895-9. Ital Heart J. 2003. PMID: 14976858
-
Cardiotoxicity of 5-fluorouracil.Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2006 Jan;4(1):1-5. doi: 10.2174/187152506775268785. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 16529545 Review.
-
Paradoxical effect of capecitabine in 5-fluorouracil-induced cardiotoxicity: A case vignette and literature review.J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2016 Jun;22(3):552-5. doi: 10.1177/1078155215579303. Epub 2015 Apr 6. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2016. PMID: 25852107 Review.
Cited by
-
Atherosclerosis, Ischemia, and Anticancer Drugs.Heart Views. 2021 Apr-Jun;22(2):127-133. doi: 10.4103/HEARTVIEWS.HEARTVIEWS_45_20. Epub 2021 Aug 19. Heart Views. 2021. PMID: 34584624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute coronary syndrome associated with continuous 5-Fluorouracil infusion in a patient with metastatic colorectal cancer-a case report with a discussion on this clinical dilemma.J Gastrointest Cancer. 2009;40(3-4):133-7. doi: 10.1007/s12029-009-9101-z. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19936641
-
Myocardial infarction caused by pharmacological substances - case description and literature review.Postepy Kardiol Interwencyjnej. 2013;9(3):250-5. doi: 10.5114/pwki.2013.37504. Epub 2013 Sep 16. Postepy Kardiol Interwencyjnej. 2013. PMID: 24570727 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of the pathophysiology of 5-fluorouracil-induced cardiotoxicity.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2014 Sep 4;15:47. doi: 10.1186/2050-6511-15-47. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 25186061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coronary Artery Vasospasm Induced by 5-fluorouracil: Proposed Mechanisms, Existing Management Options and Future Directions.Interv Cardiol. 2019 May 21;14(2):89-94. doi: 10.15420/icr.2019.12. eCollection 2019 May. Interv Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31178935 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical