Characterization of capsid genes, expressed in the baculovirus system, of three new genetically distinct strains of "Norwalk-like viruses"
- PMID: 11724834
- PMCID: PMC88538
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.39.12.4288-4295.2001
Characterization of capsid genes, expressed in the baculovirus system, of three new genetically distinct strains of "Norwalk-like viruses"
Abstract
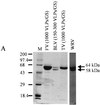
"Norwalk-like viruses" (NLVs), members of a newly defined genus of the family Caliciviridae, are the most common agents of outbreaks of gastroenteritis in the United States. Two features of NLVs have hindered the development of simple methods for detection and determination of serotype: their genetic diversity and their inability to grow in cell culture. To assess the immune responses of patients involved in outbreaks of gastroenteritis resulting from infection with NLVs, we previously used recombinant-expressed capsid antigens representing four different genetic clusters, but this panel proved insufficient for detection of an immune response in many patients. To extend and further refine this panel, we expressed in baculovirus the capsid genes of three additional genetically distinct viruses, Burwash Landing virus (BLV), White River virus (WRV), and Florida virus. All three expressed proteins assembled into virus-like particles (VLPs) that contained a full-length 64-kDa protein, but both the BLV and WRV VLPs also contained a 58-kDa protein that resulted from deletion of 39 amino acids at the amino terminus. The purified VLPs were used to measure the immune responses in 403 patients involved in 37 outbreaks of acute gastroenteritis. A majority of patients demonstrated a fourfold rise in the titer of immunoglobulin G to the antigen homologous to the outbreak strain, but most seroconverted in response to other genetically distinct antigens as well, suggesting no clear pattern of type-specific immune response. Further study of the antigenicity of the NLVs by use of VLPs should allow us to design new detection systems with either broader reactivity or better specificity and to define the optimum panel of antigens required for routine screening of patient sera.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Baculovirus expression and antigenic characterization of the capsid proteins of three Norwalk-like viruses.Arch Virol. 2002;147(1):119-30. doi: 10.1007/s705-002-8306-5. Arch Virol. 2002. PMID: 11855626
-
Molecular detection and sequence analysis of human caliciviruses from acute gastroenteritis outbreaks in Hungary.J Med Virol. 2002 Aug;67(4):567-73. doi: 10.1002/jmv.10140. J Med Virol. 2002. PMID: 12116006
-
Self-assembly of the recombinant capsid protein of a bovine norovirus (BoNV) into virus-like particles and evaluation of cross-reactivity of BoNV with human noroviruses.J Clin Microbiol. 2005 Feb;43(2):778-85. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.2.778-785.2005. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15695679 Free PMC article.
-
[Antibody-based diagnostic assays with recombinant virus-like particles].Nihon Rinsho. 2002 Jun;60(6):1194-201. Nihon Rinsho. 2002. PMID: 12078094 Review. Japanese.
-
Diagnosis of human caliciviruses by use of enzyme immunoassays.J Infect Dis. 2000 May;181 Suppl 2:S349-59. doi: 10.1086/315577. J Infect Dis. 2000. PMID: 10804148 Review.
Cited by
-
Mutational study of sapovirus expression in insect cells.Virol J. 2005 Feb 23;2:13. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-2-13. Virol J. 2005. PMID: 15727685 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for human norovirus infection of dogs in the United kingdom.J Clin Microbiol. 2015 Jun;53(6):1873-83. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02778-14. Epub 2015 Apr 1. J Clin Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25832298 Free PMC article.
-
Serological evidence for multiple strains of canine norovirus in the UK dog population.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 5;8(12):e81596. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081596. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24339947 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular analysis of noroviruses involved in acute gastroenteritis outbreaks in military units in Israel, 1999-2004.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2005 Oct;24(10):697-700. doi: 10.1007/s10096-005-0002-1. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2005. PMID: 16231127
-
Absolute Humidity Influences the Seasonal Persistence and Infectivity of Human Norovirus.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014 Dec;80(23):7196-205. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01871-14. Epub 2014 Sep 12. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25217015 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ando T, Jin Q, Gentsch J R, Monroe S S, Noel J S, Dowell S F, Cicirello H G, Kohn M A, Glass R I. Epidemiologic applications of novel molecular methods to detect and differentiate small round structured viruses (Norwalk-like viruses) J Med Virol. 1995;47:145–152. - PubMed
-
- Ando T, Monroe S S, Noel J S, Glass R I. A one-tube method of reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction to efficiently amplify a 3-kilobase region from the RNA polymerase gene to the poly(A) tail of small round-structured viruses (Norwalk virus-like viruses) J Clin Microbiol. 1997;35:570–577. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ando T, Noel J S, Fankhauser R L. Genetic classification of “Norwalk-like viruses.”. J Infect Dis. 2000;181(Suppl. 2):S336–S348. - PubMed
-
- Beller M, Ellis A, Lee S H, Drebot M A, Jenkerson S A, Funk E, Sobsey M D, Simmons O D, Monroe S S, Ando T, Noel J, Petric M, Middaugh J P, Spika J S. Outbreak of viral gastroenteritis due to a contaminated well. JAMA. 1997;278:563–568. - PubMed
-
- Dimitrov D H, Dashti S A H, Ball J M, Bishbishi E, Alsaeid K, Jiang X, Estes M K. Prevalence of antibodies to human caliciviruses (HuCVs) in Kuwait established by ELISA using baculovirus-expressed capsid antigens representing two genogroups of HuCVs. J Med Virol. 1997;51:115–118. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

