Inhibitory effects of small-molecule CCR5 antagonists on human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope-mediated membrane fusion and viral replication
- PMID: 11709336
- PMCID: PMC90865
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.45.12.3538-3543.2001
Inhibitory effects of small-molecule CCR5 antagonists on human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope-mediated membrane fusion and viral replication
Abstract
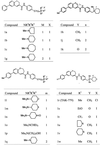
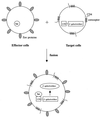
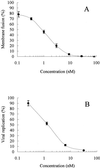
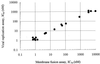
We established a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) envelope (Env)-mediated membrane fusion assay and examined the small-molecule CCR5 antagonist TAK-779 and its derivatives for their inhibitory effects on HIV-1 Env-mediated membrane fusion and viral replication. The membrane fusion assay is based on HIV-1 long terminal repeat-directed beta-D-galactosidase reporter gene expression in CD4- and CCR5-expressed HeLa (MAGI-CCR5) cells after cocultivation with effector 293T cells expressing HIV-1 Env. Inhibition of HIV-1 replication was also determined in MAGI-CCR5 cells infected with the corresponding cell-free HIV-1. TAK-779 effectively suppressed R5 HIV-1 (strain JR-FL) Env-mediated membrane fusion as well as viral replication. Its 50% inhibitory concentrations (IC(50)s) for membrane fusion and viral replication were 0.87 +/- 0.11 and 1.4 +/- 0.1 nM, respectively. These values corresponded well to the IC(50) for (125)I-RANTES (regulated on activation, T cell expressed, and secreted) binding to CCR5 (1.4 nM). The inhibitory effects of 18 TAK-779 derivatives on membrane fusion differed from one compound to another. However, there was a close correlation among their inhibitory effects on membrane fusion, viral replication, and RANTES binding. The correlation coefficient between their IC(50)s for membrane fusion and viral replication was 0.881. Furthermore, since this assay depends on Env expressed in the effector cells, it is also applicable to the evaluation of CXCR4 antagonists. These results indicate that the HIV-1 Env-mediated membrane fusion assay is a useful tool for the evaluation of entry inhibitors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Highly potent inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication by TAK-220, an orally bioavailable small-molecule CCR5 antagonist.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005 Aug;49(8):3474-82. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.8.3474-3482.2005. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005. PMID: 16048963 Free PMC article.
-
TAK-652 inhibits CCR5-mediated human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection in vitro and has favorable pharmacokinetics in humans.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005 Nov;49(11):4584-91. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.11.4584-4591.2005. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005. PMID: 16251299 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Generation and properties of a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolate resistant to the small molecule CCR5 inhibitor, SCH-417690 (SCH-D).Virology. 2005 Jul 20;338(1):182-99. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2005.04.035. Virology. 2005. PMID: 15935415
-
[Chemokine receptors and its importance in the replication cycle of human immunodeficiency virus: clinical and therapeutic implications].Acta Med Port. 2008 Sep-Oct;21(5):497-504. Epub 2009 Jan 16. Acta Med Port. 2008. PMID: 19187693 Review. Portuguese.
-
Prospects of HIV-1 entry inhibitors as novel therapeutics.Rev Med Virol. 2004 Jul-Aug;14(4):255-70. doi: 10.1002/rmv.435. Rev Med Virol. 2004. PMID: 15248253 Review.
Cited by
-
Highly potent inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication by TAK-220, an orally bioavailable small-molecule CCR5 antagonist.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005 Aug;49(8):3474-82. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.8.3474-3482.2005. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005. PMID: 16048963 Free PMC article.
-
Novel reporter T-cell line highly susceptible to both CCR5- and CXCR4-using human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and its application to drug susceptibility tests.J Clin Microbiol. 2003 Jun;41(6):2515-21. doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.6.2515-2521.2003. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12791875 Free PMC article.
-
Potential role for CD63 in CCR5-mediated human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection of macrophages.J Virol. 2003 Mar;77(6):3624-33. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.6.3624-3633.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12610138 Free PMC article.
-
TAK-652 inhibits CCR5-mediated human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection in vitro and has favorable pharmacokinetics in humans.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005 Nov;49(11):4584-91. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.11.4584-4591.2005. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005. PMID: 16251299 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Anti-human immunodeficiency virus type 1 activity and resistance profile of 2',3'-didehydro-3'-deoxy-4'-ethynylthymidine in vitro.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005 Aug;49(8):3355-60. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.8.3355-3360.2005. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005. PMID: 16048947 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alkhatib G, Ahuja S S, Light D, Mummidi S, Berger E A, Ahuja S K. CC chemokine receptor 5-mediated signaling and HIV-1 co-receptor activity share common structural determinants. Critical residues in the third extracellular loop support HIV-1 fusion. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:19771–19776. - PubMed
-
- Alkhatib G, Combadiere C, Broder C C, Feng Y, Kennedy P E, Murphy P M, Berger E A. CC CKR5: a RANTES, MIP-1α, MIP-1β receptor as a fusion cofactor for macrophage-tropic HIV-1. Science. 1996;272:1955–1958. - PubMed
-
- Baba M, Miyake H, Okamoto M, Iizawa Y, Okonogi K. Establishment of a CCR5-expressing T-lymphoblastoid cell line highly susceptible to R5 HIV Type 1. AIDS Res Hum Retrovir. 2000;16:935–941. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

