Mad2 binding to Mad1 and Cdc20, rather than oligomerization, is required for the spindle checkpoint
- PMID: 11707408
- PMCID: PMC125308
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.22.6371
Mad2 binding to Mad1 and Cdc20, rather than oligomerization, is required for the spindle checkpoint
Abstract
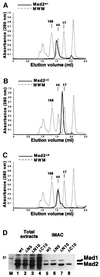
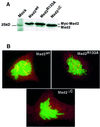
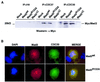
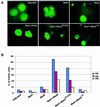
Mad2 is a key component of the spindle checkpoint, a device that controls the fidelity of chromosome segregation in mitosis. The ability of Mad2 to form oligomers in vitro has been correlated with its ability to block the cell cycle upon injection into Xenopus embryos. Here we show that Mad2 forms incompatible complexes with Mad1 and Cdc20, neither of which requires Mad2 oligomerization. A monomeric point mutant of Mad2 can sustain a cell cycle arrest of comparable strength to that of the wild-type protein. We show that the interaction of Mad2 with Mad1 is crucial for the localization of Mad2 to kinetochores, where Mad2 interacts with Cdc20. We propose a model that features the kinetochore as a 'folding factory' for the formation of a Mad2-Cdc20 complex endowed with inhibitory activity on the anaphase promoting complex.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification of an overlapping binding domain on Cdc20 for Mad2 and anaphase-promoting complex: model for spindle checkpoint regulation.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Aug;21(15):5190-9. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.15.5190-5199.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11438673 Free PMC article.
-
Bub3 interaction with Mad2, Mad3 and Cdc20 is mediated by WD40 repeats and does not require intact kinetochores.EMBO J. 2001 Dec 3;20(23):6648-59. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.23.6648. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11726501 Free PMC article.
-
Human CENP-I specifies localization of CENP-F, MAD1 and MAD2 to kinetochores and is essential for mitosis.Nat Cell Biol. 2003 Apr;5(4):341-5. doi: 10.1038/ncb953. Nat Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12640463
-
Checkpoint signalling: Mad2 conformers and signal propagation.Curr Biol. 2005 Feb 22;15(4):R122-4. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.02.008. Curr Biol. 2005. PMID: 15723780 Review.
-
Structural activation of Mad2 in the mitotic spindle checkpoint: the two-state Mad2 model versus the Mad2 template model.J Cell Biol. 2006 Apr 24;173(2):153-7. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200601172. J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16636141 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Aneuploid abortion correlates positively with MAD1 overexpression and miR-125b down-regulation.Mol Cytogenet. 2021 Apr 26;14(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s13039-021-00538-1. Mol Cytogenet. 2021. PMID: 33902659 Free PMC article.
-
The conserved AAA-ATPase PCH-2 TRIP13 regulates spindle checkpoint strength.Mol Biol Cell. 2020 Sep 15;31(20):2219-2233. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E20-05-0310. Epub 2020 Jul 22. Mol Biol Cell. 2020. PMID: 32697629 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitivity to sodium arsenite in human melanoma cells depends upon susceptibility to arsenite-induced mitotic arrest.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2008 Jun 1;229(2):252-61. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2008.01.020. Epub 2008 Feb 5. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18328521 Free PMC article.
-
HAT cofactor Trrap regulates the mitotic checkpoint by modulation of Mad1 and Mad2 expression.EMBO J. 2004 Dec 8;23(24):4824-34. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600479. Epub 2004 Nov 18. EMBO J. 2004. PMID: 15549134 Free PMC article.
-
Replicated associations of FADS1, MAD1L1, and a rare variant at 10q26.13 with bipolar disorder in Chinese population.Transl Psychiatry. 2018 Dec 7;8(1):270. doi: 10.1038/s41398-018-0337-x. Transl Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 30531795 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amon A. (1999) The spindle checkpoint. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 9, 69–75. - PubMed
-
- Aravind L. and Koonin,E.V. (1998) The HORMA domain: a common structural denominator in mitotic checkpoints, chromosome synapsis and DNA repair. Trends Biochem. Sci., 23, 284–286. - PubMed
-
- Chen R.H., Waters,J.C., Salmon,E.D. and Murray,A.W. (1996) Association of spindle assembly checkpoint component XMAD2 with unattached kinetochores. Science, 274, 242–246. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

