Identification and analysis of Arabidopsis expressed sequence tags characteristic of non-coding RNAs
- PMID: 11706161
- PMCID: PMC129250
Identification and analysis of Arabidopsis expressed sequence tags characteristic of non-coding RNAs
Abstract
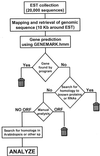
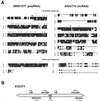
Sequencing of the Arabidopsis genome has led to the identification of thousands of new putative genes based on the predicted proteins they encode. Genes encoding tRNAs, ribosomal RNAs, and small nucleolar RNAs have also been annotated; however, a potentially important class of genes has largely escaped previous annotation efforts. These genes correspond to RNAs that lack significant open reading frames and encode RNA as their final product. Accumulating evidence indicates that such "non-coding RNAs" (ncRNAs) can play critical roles in a wide range of cellular processes, including chromosomal silencing, transcriptional regulation, developmental control, and responses to stress. Approximately 15 putative Arabidopsis ncRNAs have been reported in the literature or have been annotated. Although several have homologs in other plant species, all appear to be plant specific, with the exception of signal recognition particle RNA. Conversely, none of the ncRNAs reported from yeast or animal systems have homologs in Arabidopsis or other plants. To identify additional genes that are likely to encode ncRNAs, we used computational tools to filter protein-coding genes from genes corresponding to 20,000 expressed sequence tag clones. Using this strategy, we identified 19 clones with characteristics of ncRNAs, nine putative peptide-coding RNAs with open reading frames smaller than 100 amino acids, and 11 that could not be differentiated between the two categories. Again, none of these clones had homologs outside the plant kingdom, suggesting that most Arabidopsis ncRNAs are likely plant specific. These data indicate that ncRNAs represent a significant and underdeveloped aspect of Arabidopsis genomics that deserves further study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genomic features and regulatory roles of intermediate-sized non-coding RNAs in Arabidopsis.Mol Plant. 2014 Mar;7(3):514-27. doi: 10.1093/mp/sst177. Epub 2014 Jan 7. Mol Plant. 2014. PMID: 24398630
-
Identification of new small non-coding RNAs from tobacco and Arabidopsis.Biochimie. 2005 Sep-Oct;87(9-10):905-10. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2005.06.001. Biochimie. 2005. PMID: 16005138
-
Life without RNAi: noncoding RNAs and their functions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Biochem Cell Biol. 2009 Oct;87(5):767-79. doi: 10.1139/O09-043. Biochem Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19898526 Review.
-
Identification and expression analysis of putative mRNA-like non-coding RNA in Drosophila.Genes Cells. 2005 Dec;10(12):1163-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2005.00910.x. Genes Cells. 2005. PMID: 16324153
-
Dual RNAs in plants.Biochimie. 2011 Nov;93(11):1950-4. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2011.07.028. Epub 2011 Jul 31. Biochimie. 2011. PMID: 21824505 Review.
Cited by
-
Conserved and non-conserved RNA-target modules in plants: lessons for a better understanding of Marchantia development.Plant Mol Biol. 2023 Nov;113(4-5):121-142. doi: 10.1007/s11103-023-01392-y. Epub 2023 Nov 22. Plant Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37991688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond the proteome: non-coding regulatory RNAs.Genome Biol. 2002;3(5):reviews0005. doi: 10.1186/gb-2002-3-5-reviews0005. Epub 2002 Apr 15. Genome Biol. 2002. PMID: 12049667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The plant-specific database. Classification of Arabidopsis proteins based on their phylogenetic profile.Plant Physiol. 2004 Aug;135(4):1888-92. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.043687. Plant Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15326280 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Annotation of the Arabidopsis genome.Plant Physiol. 2003 Jun;132(2):461-8. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.022251. Plant Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12805579 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
An Overview of Methodologies in Studying lncRNAs in the High-Throughput Era: When Acronyms ATTACK!Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1933:1-30. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9045-0_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30945176 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akhtar A, Zink D, Becker PB. Chromodomains are protein-RNA interaction modules. Nature. 2000;407:405–409. - PubMed
-
- Altman S, Kirsebom L. Ribonuclease P. In: Gesteland RF, Cech T-R, Atkins JF, editors. The RNA World. Ed 2. Plainview, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1999. pp. 351–380.
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Amrein H, Axel R. Genes expressed in neurons of adult male Drosophila. Cell. 1997;88:459–469. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
