Glycosylation and the activation of proteinase-activated receptor 2 (PAR(2)) by human mast cell tryptase
- PMID: 11606310
- PMCID: PMC1572998
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704303
Glycosylation and the activation of proteinase-activated receptor 2 (PAR(2)) by human mast cell tryptase
Abstract
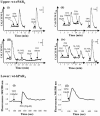
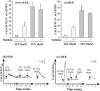
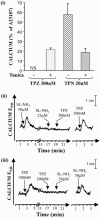
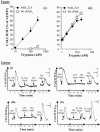
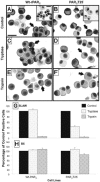
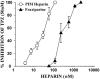
1. Human mast cell tryptase appears to display considerable variation in activating proteinase-activated receptor 2 (PAR(2)). We found tryptase to be an inefficient activator of wild-type rat-PAR(2) (wt-rPAR(2)) and therefore decided to explore the factors that may influence tryptase activation of PAR(2). 2. Using a 20 mer peptide (P20) corresponding to the cleavage/activation sequence of wt-rPAR(2), tryptase was as efficient as trypsin in releasing the receptor-activating sequence (SLIGRL.). However, in the presence of either human-PAR(2) or wt-r PAR(2) expressing cells, tryptase could only activate PAR(2) by releasing SLIGRL from the P20 peptide, suggesting that PAR(2) expressed on the cells was protected from tryptase activation. 3. Three approaches were employed to test the hypothesis that PAR(2) receptor glycosylation restricts tryptase activation. (a) pretreatment of wt-rPAR(2) expressing cells or human embryonic kidney cells (HEK293) with vibrio cholerae neuraminidase to remove oligosaccharide sialic acid, unmasked tryptase-mediated PAR(2) activation. (b) Inhibiting receptor glycosylation in HEK293 cells with tunicamycin enabled tryptase-mediated PAR(2) activation. (c) Wt-rPAR(2) devoid of the N-terminal glycosylation sequon (PAR(2)T25(-)), but not rPAR(2) devoid of the glycosylation sequon located on extracellular loop-2 (PAR(2)T224A), was selectively and substantially (>30 fold) more sensitive to tryptase compared with the wt-rPAR(2). 4. Immunocytochemistry using antisera that specifically recognized the N-terminal precleavage sequence of PAR(2) demonstrated that tryptase released the precleavage domain from PAR(2)T25(-) but not from wt-rPAR(2). 5. Heparin : tryptase molar ratios of greater than 2 : 1 abrogated tryptase activation of PAR(2)T25(-). 6. Our results indicate that glycosylation of PAR(2) and heparin-inhibition of PAR(2) activation by tryptase could provide novel mechanisms for regulating receptor activation by tryptase and possibly other proteases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glycosylation of human proteinase-activated receptor-2 (hPAR2): role in cell surface expression and signalling.Biochem J. 2002 Dec 1;368(Pt 2):495-505. doi: 10.1042/BJ20020706. Biochem J. 2002. PMID: 12171601 Free PMC article.
-
Restricted ability of human mast cell tryptase to activate proteinase-activated receptor-2 in rat aorta.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2002 Oct;80(10):987-92. doi: 10.1139/y02-125. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12450065
-
Reaction of mast cell proteases tryptase and chymase with protease activated receptors (PARs) on keratinocytes and fibroblasts.J Cell Physiol. 1998 Aug;176(2):365-73. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(199808)176:2<365::AID-JCP15>3.0.CO;2-2. J Cell Physiol. 1998. PMID: 9648924
-
Proteinase-activated receptors: a growing family of heptahelical receptors for thrombin, trypsin and tryptase.Biochem Soc Trans. 1999 Feb;27(2):246-54. doi: 10.1042/bst0270246. Biochem Soc Trans. 1999. PMID: 10093742 Review. No abstract available.
-
Targeting mast cells tryptase in tumor microenvironment: a potential antiangiogenetic strategy.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:154702. doi: 10.1155/2014/154702. Epub 2014 Sep 11. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25295247 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mast cells in vulnerable atherosclerotic plaques--a view to a kill.J Cell Mol Med. 2007 Jul-Aug;11(4):739-58. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2007.00052.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2007. PMID: 17760836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serratia marcescens serralysin induces inflammatory responses through protease-activated receptor 2.Infect Immun. 2007 Jan;75(1):164-74. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01239-06. Epub 2006 Oct 16. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17043106 Free PMC article.
-
Alveolar macrophages play a key role in cockroach-induced allergic inflammation via TNF-α pathway.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e47971. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047971. Epub 2012 Oct 19. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23094102 Free PMC article.
-
Pleiotropic actions of factor Xa inhibition in cardiovascular prevention: mechanistic insights and implications for anti-thrombotic treatment.Cardiovasc Res. 2021 Jul 27;117(9):2030-2044. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvaa263. Cardiovasc Res. 2021. PMID: 32931586 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kallikrein-related peptidase 4: a new activator of the aberrantly expressed protease-activated receptor 1 in colon cancer cells.Am J Pathol. 2010 Mar;176(3):1452-61. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.090523. Epub 2010 Jan 7. Am J Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20056842 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AL ANI B., SAIFEDDINE M., KAWABATA A., RENAUX B., MOKASHI S., HOLLENBERG M.D. Proteinase-activated receptor 2 (PAR(2)): development of a ligand- binding assay correlating with activation of PAR(2) by PAR(1)- and PAR(2)-derived peptide ligands. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999;290:753–760. - PubMed
-
- ALM A.K., GAGNEMO-PERSSON R., SORSA T., SUNDELIN J. Extrapancreatic trypsin-2 cleaves proteinase-activated receptor-2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000;275:77–83. - PubMed
-
- BROWN J.K., TYLER C.L., JONES C.A., RUOSS S.J., HARTMANN T., CAUGHEY G.H. Tryptase, the dominant secretory granular protein in human mast cells, is a potent mitogen for cultured dog tracheal smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1995;13:227–236. - PubMed
-
- CAIRNS J.A., WALLS A.F. Mast cell tryptase is a mitogen for epithelial cells. Stimulation of IL- 8 production and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression. J. Immunol. 1996;156:275–283. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

