The effect of external divalent cations on spontaneous non-selective cation channel currents in rabbit portal vein myocytes
- PMID: 11600676
- PMCID: PMC2278865
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.0409c.xd
The effect of external divalent cations on spontaneous non-selective cation channel currents in rabbit portal vein myocytes
Abstract
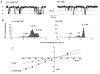
1. The effects of external divalent cations on spontaneous single non-selective cation channel currents were studied in outside-out patches from rabbit portal vein smooth muscle cells in K+-free conditions. 2. In an external medium containing 1.5 mM Ca2+ (Ca2+o) the majority of spontaneous channel currents had a unitary conductance of 23 pS, reversal potential (Vr) of +10 mV and a low open probability (Po) at negative patch potentials. Some channels opened to a lower conductance state of about 13 pS suggesting that the cation channels have two conductance states. Open time and burst duration distributions could both be described by two exponentials with time constants of about of 1 ms and 7 ms for open times and 3 ms and 16 ms for burst durations. 3. In 0 Ca2+o the majority of spontaneous cation channels had a unitary conductance of 13 pS and Vr was shifted to +4 mV. Moreover the longer open time and longer burst duration time constants were both reduced to approximately half the values in 1.5 mM Ca2+o. 4. Compared to 0 Ca2+o the single channel currents in 3 microM and 100 microM Ca2+o had a 5- to 6-fold increase in Po which was accompanied by increases in both open times and burst durations. In 3 microM and 100 microM Ca2+o the unitary conductance of the single channel currents was between 22 and 26 pS. 5. At positive membrane potentials the single channel currents had an increased Po compared to negative potentials which was associated with increased open times and burst durations but these values were similar in 3 microM, 100 microM and 1.5 mM Ca2+o. 6. In 1.5 mM Sr2+o and 1.5 mM Ba2+o channels opened to the higher conductance state of about 22-25 pS and had a 3- to 7-fold greater Po than in 0 Ca2+o. 7. In conclusion, external divalent cations have marked effects on the unitary conductance and kinetic behaviour of non-selective cation channels in rabbit portal vein smooth muscle cells.
Figures




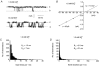

Similar articles
-
Properties of a constitutively active Ca2+-permeable non-selective cation channel in rabbit ear artery myocytes.J Physiol. 2003 May 15;549(Pt 1):143-56. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.038190. Epub 2003 Apr 4. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12679370 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of spontaneous and noradrenaline-evoked non-selective cation channels in rabbit portal vein myocytes.J Physiol. 2001 Feb 1;530(Pt 3):457-68. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.0457k.x. J Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11158276 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the effects of divalent cations on the noradrenaline-evoked cation current in rabbit portal vein smooth muscle cells.J Physiol. 1999 Nov 1;520 Pt 3(Pt 3):771-82. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.00771.x. J Physiol. 1999. PMID: 10545143 Free PMC article.
-
A Ca2+-permeable non-selective cation channel activated by depletion of internal Ca2+ stores in single rabbit portal vein myocytes.J Physiol. 2002 Feb 1;538(Pt 3):717-28. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2001.013101. J Physiol. 2002. PMID: 11826160 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of calciseptine on unitary barium channel currents in guinea-pig portal vein.Pflugers Arch. 1996 Jul;432(3):462-70. doi: 10.1007/s004240050158. Pflugers Arch. 1996. PMID: 8766006
Cited by
-
Inhibitory regulation of constitutive transient receptor potential-like cation channels in rabbit ear artery myocytes.J Physiol. 2004 Oct 1;560(Pt 1):169-80. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.071738. Epub 2004 Aug 5. J Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15297579 Free PMC article.
-
Store-operated calcium entry in vascular smooth muscle.Br J Pharmacol. 2008 Mar;153(5):846-57. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707455. Epub 2007 Sep 17. Br J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 17876304 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Properties of a constitutively active Ca2+-permeable non-selective cation channel in rabbit ear artery myocytes.J Physiol. 2003 May 15;549(Pt 1):143-56. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.038190. Epub 2003 Apr 4. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12679370 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of store-operated channels by noradrenaline via protein kinase C in rabbit portal vein myocytes.J Physiol. 2002 Oct 1;544(Pt 1):113-25. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.022574. J Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12356885 Free PMC article.
-
Non-selective cation channels mediate chloroquine-induced relaxation in precontracted mouse airway smooth muscle.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 3;9(7):e101578. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101578. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24992312 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

