Therapeutic targeting of the MEK/MAPK signal transduction module in acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 11560954
- PMCID: PMC200930
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI12807
Therapeutic targeting of the MEK/MAPK signal transduction module in acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
The mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway regulates growth and survival of many cell types, and its constitutive activation has been implicated in the pathogenesis of a variety of malignancies. In this study we demonstrate that small-molecule MEK inhibitors (PD98059 and PD184352) profoundly impair cell growth and survival of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cell lines and primary samples with constitutive MAPK activation. These agents abrogate the clonogenicity of leukemic cells but have minimal effects on normal hematopoietic progenitors. MEK blockade also results in sensitization to spontaneous and drug-induced apoptosis. At a molecular level, these effects correlate with modulation of the expression of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors (p27(Kip1) and p21(Waf1/CIP1)) and antiapoptotic proteins of the inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAP) and Bcl-2 families. Interruption of constitutive MEK/MAPK signaling therefore represents a promising therapeutic strategy in AML.
Figures
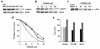
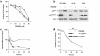


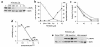
Similar articles
-
Pharmacological inhibitors of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase/MAPK cascade interact synergistically with UCN-01 to induce mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis in human leukemia cells.Cancer Res. 2001 Jul 1;61(13):5106-15. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11431348
-
Importance of MEK-1/-2 signaling in monocytic and granulocytic differentiation of myeloid cell lines.Leukemia. 2002 Apr;16(4):683-92. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2402400. Leukemia. 2002. PMID: 11960350
-
Pharmacologic mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase/mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors interact synergistically with STI571 to induce apoptosis in Bcr/Abl-expressing human leukemia cells.Cancer Res. 2002 Jan 1;62(1):188-99. Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 11782377
-
Beyond single pathway inhibition: MEK inhibitors as a platform for the development of pharmacological combinations with synergistic anti-leukemic effects.Curr Pharm Des. 2005;11(21):2779-95. doi: 10.2174/1381612054546842. Curr Pharm Des. 2005. PMID: 16101455 Review.
-
CI-1040 (PD184352), a targeted signal transduction inhibitor of MEK (MAPKK).Semin Oncol. 2003 Oct;30(5 Suppl 16):105-16. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2003.08.012. Semin Oncol. 2003. PMID: 14613031 Review.
Cited by
-
Ampelopsin Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis in HL60 and K562 Leukemia Cells by Downregulating AKT and NF-κB Signaling Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 20;22(8):4265. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084265. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33924032 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol induces apoptosis of human chronic myelogenous leukemia cells in vitro through p38 and JNK-regulated H2AX phosphorylation.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015 Mar;36(3):353-61. doi: 10.1038/aps.2014.132. Epub 2015 Jan 26. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015. PMID: 25619392 Free PMC article.
-
Susceptibility of myelomonocytic leukemia U937 cells to the induction of apoptosis by the non-peptidic Bcl-2 ligand HA14-1 is cell cycle phase-dependent.Cancer Lett. 2005 Apr 28;221(2):153-63. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2004.09.012. Cancer Lett. 2005. PMID: 15808401 Free PMC article.
-
Role of mitogen-activated protein kinase family in serum-induced leukaemia inhibitory factor and interleukin-6 secretion by bone marrow stromal cells.Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Aug;136(7):975-84. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704797. Br J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12145097 Free PMC article.
-
Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of the oral, small-molecule mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2 inhibitor AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) in patients with advanced cancers.J Clin Oncol. 2008 May 1;26(13):2139-46. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.14.4956. Epub 2008 Apr 7. J Clin Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18390968 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Lowenberg B, Downing JR, Burnett A. Acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:1051–1062. - PubMed
-
- Look AT. Oncogenic transcription factors in the human acute leukemias. Science. 1997;278:1059–1064. - PubMed
-
- Castilla LH, et al. The fusion gene Cbfb-MYH11 blocks myeloid differentiation and predisposes mice to acute myelomonocytic leukaemia. Nat Genet. 1999;23:144–146. - PubMed
-
- Rhoades KL, et al. Analysis of the role of AML1-ETO in leukemogenesis, using an inducible transgenic mouse model. Blood. 2000;96:2108–2115. - PubMed
-
- Dash A, Gilliland DG. Molecular genetics of acute myeloid leukaemia. Baillieres Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2001;14:49–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

