Hematopoietic colony-forming cells derived from human embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 11535826
- PMCID: PMC58532
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.191362598
Hematopoietic colony-forming cells derived from human embryonic stem cells
Abstract
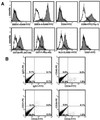
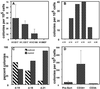
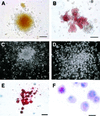
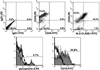
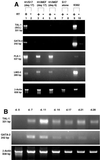
Human embryonic stem (ES) cells are undifferentiated, pluripotent cells that can be maintained indefinitely in culture. Here we demonstrate that human ES cells differentiate to hematopoietic precursor cells when cocultured with the murine bone marrow cell line S17 or the yolk sac endothelial cell line C166. This hematopoietic differentiation requires fetal bovine serum, but no other exogenous cytokines. ES cell-derived hematopoietic precursor cells express the cell surface antigen CD34 and the hematopoietic transcription factors TAL-1, LMO-2, and GATA-2. When cultured on semisolid media with hematopoietic growth factors, these hematopoietic precursor cells form characteristic myeloid, erythroid, and megakaryocyte colonies. Selection for CD34(+) cells derived from human ES cells enriches for hematopoietic colony-forming cells, similar to CD34 selection of primary hematopoietic tissue (bone marrow, umbilical cord blood). More terminally differentiated hematopoietic cells derived from human ES cells under these conditions also express normal surface antigens: glycophorin A on erythroid cells, CD15 on myeloid cells, and CD41 on megakaryocytes. The in vitro differentiation of human ES cells provides an opportunity to better understand human hematopoiesis and could lead to a novel source of cells for transfusion and transplantation therapies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[The investigation of hematopoietic capacity of HPP-CFC derived from murine embryonic stem cells in vitro and in vivo].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2003 May;19(3):312-6. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2003. PMID: 15969013 Chinese.
-
CD34+ endothelial cell lines derived from murine yolk sac induce the proliferation and differentiation of yolk sac CD34+ hematopoietic progenitors.Blood. 1995 Dec 15;86(12):4454-67. Blood. 1995. PMID: 8541534
-
Human embryonic stem cell-derived CD34+ cells: efficient production in the coculture with OP9 stromal cells and analysis of lymphohematopoietic potential.Blood. 2005 Jan 15;105(2):617-26. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-04-1649. Epub 2004 Sep 16. Blood. 2005. PMID: 15374881
-
Regulation of hemangioblast development.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001 Jun;938:96-107; discussion 108. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2001.tb03578.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001. PMID: 11458531 Review.
-
Human ES cells--haematopoiesis and transplantation strategies.J Anat. 2002 Mar;200(Pt 3):243-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-7580.2002.00028.x. J Anat. 2002. PMID: 12033728 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel, high-yield red blood cell production methods from CD34-positive cells derived from human embryonic stem, yolk sac, fetal liver, cord blood, and peripheral blood.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2012 Aug;1(8):604-14. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2012-0059. Epub 2012 Aug 2. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2012. PMID: 23197866 Free PMC article.
-
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs) in Vascular Research: from Two- to Three-Dimensional Organoids.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021 Oct;17(5):1741-1753. doi: 10.1007/s12015-021-10149-3. Epub 2021 Mar 18. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021. PMID: 33738695 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characteristics of myeloid differentiation and maturation pathway derived from human hematopoietic stem cells exposed to different linear energy transfer radiation types.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e59385. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059385. Epub 2013 Mar 12. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23555027 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-species transcriptional profiles establish a functional portrait of embryonic stem cells.Genomics. 2007 Jan;89(1):22-35. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2006.09.010. Epub 2006 Oct 19. Genomics. 2007. PMID: 17055697 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombopoietin knock-in augments platelet generation from human embryonic stem cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018 Jul 17;9(1):194. doi: 10.1186/s13287-018-0926-x. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 30016991 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

