Domains in human splicing factors SF3a60 and SF3a66 required for binding to SF3a120, assembly of the 17S U2 snRNP, and prespliceosome formation
- PMID: 11533230
- PMCID: PMC99788
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.19.6406-6417.2001
Domains in human splicing factors SF3a60 and SF3a66 required for binding to SF3a120, assembly of the 17S U2 snRNP, and prespliceosome formation
Abstract
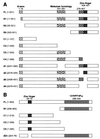
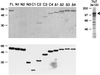
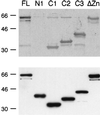
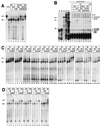
The active 17S U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle (snRNP), which binds to the intron branch site during the formation of the prespliceosome, is assembled in vitro by sequential interactions of the essential splicing factors SF3b and SF3a with the 12S U2 snRNP. We have analyzed the function of individual subunits of human SF3a (SF3a60, SF3a66, and SF3a120) by testing recombinant proteins, expressed in insect cells, in various in vitro assays. The recombinant subunits readily form the SF3a heterotrimer, where SF3a60 and SF3a66 interact with SF3a120, but not with each other. All SF3a subunits are essential for the formation of the mature 17S U2 snRNP and the prespliceosome. Single subunits engage in interactions with the 15S U2 snRNP (consisting of the 12S U2 snRNP and SF3b), and SF3a60 appears to play a major role in recruiting SF3a120 into the U2 particle. Analysis of functional domains in SF3a60 and SF3a66 identified interaction sites for SF3a120 in their N-terminal portions. C(2)H(2)-type zinc finger domains mediate the integration of SF3a60 and SF3a66 into the U2 snRNP, and we propose a model in which protein-protein interactions between the zinc finger domains and the Sm proteins, common to all spliceosomal snRNPs, contribute to the assembly of the 17S U2 snRNP. Finally, we demonstrate that all domains required for interactions within the SF3a heterotrimer and the formation of the 17S U2 snRNP are also necessary to assemble the prespliceosome.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A role for Cajal bodies in the final steps of U2 snRNP biogenesis.J Cell Sci. 2004 Sep 1;117(Pt 19):4423-33. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01308. Epub 2004 Aug 17. J Cell Sci. 2004. PMID: 15316075
-
Interaction of mammalian splicing factor SF3a with U2 snRNP and relation of its 60-kD subunit to yeast PRP9.Science. 1993 Oct 1;262(5130):102-5. doi: 10.1126/science.8211112. Science. 1993. PMID: 8211112
-
Interaction domains and nuclear targeting signals in subunits of the U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle-associated splicing factor SF3a.J Biol Chem. 2011 Apr 15;286(15):13106-14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.201491. Epub 2011 Feb 24. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21349847 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-function analysis of the U2 snRNP-associated splicing factor SF3a.Biochem Soc Trans. 2005 Jun;33(Pt 3):439-42. doi: 10.1042/BST0330439. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005. PMID: 15916536 Review.
-
Structural and functional modularity of the U2 snRNP in pre-mRNA splicing.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2019 Oct;54(5):443-465. doi: 10.1080/10409238.2019.1691497. Epub 2019 Nov 20. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31744343 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structural insights into branch site proofreading by human spliceosome.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024 May;31(5):835-845. doi: 10.1038/s41594-023-01188-0. Epub 2024 Jan 9. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38196034
-
The Cajal body: a meeting place for spliceosomal snRNPs in the nuclear maze.Chromosoma. 2006 Oct;115(5):343-54. doi: 10.1007/s00412-006-0056-6. Epub 2006 Mar 31. Chromosoma. 2006. PMID: 16575476 Review.
-
The Sm-core mediates the retention of partially-assembled spliceosomal snRNPs in Cajal bodies until their full maturation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Apr 20;46(7):3774-3790. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky070. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29415178 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian splicing factor SF1 interacts with SURP domains of U2 snRNP-associated proteins.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Dec 2;43(21):10456-73. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv952. Epub 2015 Sep 29. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 26420826 Free PMC article.
-
Protein interaction network of alternatively spliced NudCD1 isoforms.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 11;7(1):12987. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-13441-w. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29021621 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams M D, et al. The genome sequence of Drosophila melanogaster. Science. 2000;287:2185–2195. - PubMed
-
- Behrens S-E, Galisson F, Legrain P, Lührmann R. Evidence that the 60-kDa protein of 17S U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein is immunologically and functionally related to the yeast PRP9 splicing factor and is required for the efficient formation of prespliceosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90:8229–8233. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bennett M, Michaud S, Kingston J, Reed R. Protein components specifically associated with prespliceosome and spliceosome complexes. Genes Dev. 1992;6:1986–2000. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
