Requirement of Ras for the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase by calcium influx, cAMP, and neurotrophin in hippocampal neurons
- PMID: 11517234
- PMCID: PMC6763070
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-17-06459.2001
Requirement of Ras for the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase by calcium influx, cAMP, and neurotrophin in hippocampal neurons
Abstract
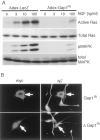
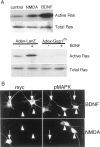
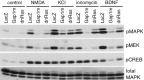
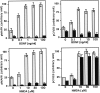
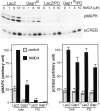
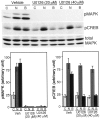
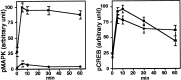
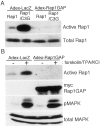
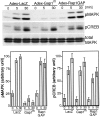
Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase plays important roles in the establishment of long-term potentiation both in vitro and in living animals. MAP kinase is activated in response to a broad range of stimuli, including calcium influx through NMDA receptor and L-type calcium channel, cAMP, and neurotrophins. To investigate the role of Ras in the activation of MAP kinase and cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) in hippocampal neurons, we inhibited Ras function by overexpressing a Ras GTPase-activating protein, Gap1(m), or dominant negative Ras by means of adenovirus vectors. Gap1(m) expression almost completely suppressed MAP kinase activation in response to NMDA, calcium ionophore, membrane depolarization, forskolin, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Dominant negative Ras also showed similar effects. On the other hand, Rap1GAP did not significantly inhibit the forskolin-induced activation of MAP kinase. In contrast to MAP kinase activation, the inactivation of Ras activity did not inhibit significantly NMDA-induced CREB phosphorylation, whereas BDNF-induced CREB phosphorylation was inhibited almost completely. These results demonstrate that Ras transduces signals elicited by a broad range of stimuli to MAP kinase in hippocampal neurons and further suggest that CREB phosphorylation depends on multiple pathways.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Developmentally regulated NMDA receptor-dependent dephosphorylation of cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) in hippocampal neurons.J Neurosci. 2000 May 15;20(10):3529-36. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-10-03529.2000. J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 10804193 Free PMC article.
-
Differential regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinases ERK1/2 and ERK5 by neurotrophins, neuronal activity, and cAMP in neurons.J Neurosci. 2001 Jan 15;21(2):434-43. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-02-00434.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11160424 Free PMC article.
-
Activated cAMP-response element-binding protein regulates neuronal expression of presenilin-1.J Biol Chem. 2001 Mar 30;276(13):9688-98. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M006153200. Epub 2000 Dec 14. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11116137
-
Rit subfamily small GTPases: regulators in neuronal differentiation and survival.Cell Signal. 2013 Oct;25(10):2060-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.06.002. Epub 2013 Jun 11. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23770287 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of CREB and its associated upstream signaling pathways in pesticide-induced neurotoxicity.Mol Cell Biochem. 2022 Nov;477(11):2581-2593. doi: 10.1007/s11010-022-04472-7. Epub 2022 May 21. Mol Cell Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35596844 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Modulation of presynaptic plasticity and learning by the H-ras/extracellular signal-regulated kinase/synapsin I signaling pathway.J Neurosci. 2005 Oct 19;25(42):9721-34. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2836-05.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16237176 Free PMC article.
-
Ras protein activation is a key event in activity-dependent survival of cerebellar granule neurons.J Biol Chem. 2014 Mar 21;289(12):8462-72. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.536375. Epub 2014 Feb 12. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24523415 Free PMC article.
-
DISC1 regulates neurotrophin-induced axon elongation via interaction with Grb2.J Neurosci. 2007 Jan 3;27(1):4-14. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3825-06.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17202467 Free PMC article.
-
Beta-amyloid peptide at sublethal concentrations downregulates brain-derived neurotrophic factor functions in cultured cortical neurons.J Neurosci. 2004 Jul 28;24(30):6799-809. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5463-03.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15282285 Free PMC article.
-
Patterned vision causes CRE-mediated gene expression in the visual cortex through PKA and ERK.J Neurosci. 2003 Aug 6;23(18):7012-20. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-18-07012.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12904462 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambrosini A, Tininini S, Barassi A, Racagni G, Sturani E, Zippel R. cAMP cascade leads to Ras activation in cortical neurons. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2000;75:54–60. - PubMed
-
- Atkins CM, Selcher JC, Petraitis JJ, Trzaskos JM, Sweatt JD. The MAPK cascade is required for mammalian associative learning. Nat Neurosci. 1998;1:602–609. - PubMed
-
- Bading H, Greenberg ME. Stimulation of protein tyrosine phosphorylation by NMDA receptor activation. Science. 1991;253:912–914. - PubMed
-
- Bading H, Hardingham GE, Johnson CM, Chawla S. Gene regulation by nuclear and cytoplasmic calcium signals. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997;236:541–543. - PubMed
-
- Brambilla R, Gnesutta N, Minichiello L, White G, Roylance AJ, Herron CE, Ramsey M, Wolfer DP, Cestari V, Rossi-Arnaud C, Grant SG, Chapman PF, Lipp HP, Sturani E, Klein R. A role for the Ras signalling pathway in synaptic transmission and long-term memory. Nature. 1997;390:281–286. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
