Maize chromomethylase Zea methyltransferase2 is required for CpNpG methylation
- PMID: 11487702
- PMCID: PMC139128
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.010064
Maize chromomethylase Zea methyltransferase2 is required for CpNpG methylation
Abstract
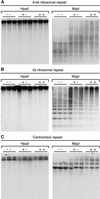
A cytosine DNA methyltransferase containing a chromodomain, Zea methyltransferase2 (Zmet2), was cloned from maize. The sequence of ZMET2 is similar to that of the Arabidopsis chromomethylases CMT1 and CMT3, with C-terminal motifs characteristic of eukaryotic and prokaryotic DNA methyltransferases. We used a reverse genetics approach to determine the function of the Zmet2 gene. Plants homozygous for a Mutator transposable element insertion into motif IX had a 13% reduction in methylated cytosines. DNA gel blot analysis of these plants with methylation-sensitive restriction enzymes and bisulfite sequencing of a 180-bp knob sequence showed reduced methylation only at CpNpG sites. No reductions in methylation were observed at CpG or asymmetric sites in heterozygous or homozygous mutant plants. Our research shows that chromomethylase Zmet2 is required for in vivo methylation of CpNpG sequences.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Natural variation for alleles under epigenetic control by the maize chromomethylase zmet2.Genetics. 2007 Oct;177(2):749-60. doi: 10.1534/genetics.107.072702. Epub 2007 Jul 29. Genetics. 2007. PMID: 17660570 Free PMC article.
-
Methylation of a different kind.Trends Plant Sci. 2001 Nov;6(11):503. doi: 10.1016/s1360-1385(01)02127-6. Trends Plant Sci. 2001. PMID: 11701357 No abstract available.
-
Natural polymorphisms in ZMET2 encoding a DNA methyltransferase modulate the number of husk layers in maize.Plant Physiol. 2024 Jun 28;195(3):2129-2142. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiae113. Plant Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38431291 Free PMC article.
-
Plant DNA methyltransferases.Plant Mol Biol. 2000 Jun;43(2-3):189-201. doi: 10.1023/a:1006427226972. Plant Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10999404 Review.
-
DNA methylation and activity of the maize Spm transposable element.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1995;197:143-64. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-79145-1_10. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1995. PMID: 7493489 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Natural variation for alleles under epigenetic control by the maize chromomethylase zmet2.Genetics. 2007 Oct;177(2):749-60. doi: 10.1534/genetics.107.072702. Epub 2007 Jul 29. Genetics. 2007. PMID: 17660570 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of two rice DNA methyltransferase genes and RNAi-mediated reactivation of a silenced transgene in rice callus.Planta. 2004 Jan;218(3):337-49. doi: 10.1007/s00425-003-1112-6. Epub 2003 Sep 25. Planta. 2004. PMID: 14513380
-
In Posidonia oceanica cadmium induces changes in DNA methylation and chromatin patterning.J Exp Bot. 2012 Jan;63(2):695-709. doi: 10.1093/jxb/err313. Epub 2011 Nov 4. J Exp Bot. 2012. PMID: 22058406 Free PMC article.
-
DNA METHYLTRANSFERASE 1 is involved in (m)CG and (m)CCG DNA methylation and is essential for sporophyte development in Physcomitrella patens.Plant Mol Biol. 2015 Jul;88(4-5):387-400. doi: 10.1007/s11103-015-0328-8. Epub 2015 May 6. Plant Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25944663
-
Comparative proteomic analysis of the shoot apical meristem in maize between a ZmCCT-associated near-isogenic line and its recurrent parent.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 29;6:30641. doi: 10.1038/srep30641. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27468931 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akhtar, A., Zink, D., and Becker, P.B. (2000). Chromodomains are protein–RNA interaction modules. Nature 407, 405–409. - PubMed
-
- Banks J.A., Masson, P., and Fedoroff, N. (1988). Molecular mechanisms in the developmental regulation of the Suppressor-mutator transposable element. Genes Dev. 2, 1364–1380. - PubMed
-
- Callebaut, I., Courvalin, J.C., and Mornon, J.P. (1999). The BAH (bromo-adjacent homology) domain: A link between DNA methylation, replication and transcriptional regulation. FEBS Lett. 446, 189–193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

