Antibody protects macaques against vaginal challenge with a pathogenic R5 simian/human immunodeficiency virus at serum levels giving complete neutralization in vitro
- PMID: 11483779
- PMCID: PMC115078
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.75.17.8340-8347.2001
Antibody protects macaques against vaginal challenge with a pathogenic R5 simian/human immunodeficiency virus at serum levels giving complete neutralization in vitro
Abstract
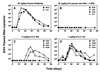
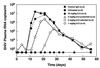
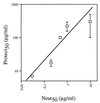
A major unknown in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) vaccine design is the efficacy of antibodies in preventing mucosal transmission of R5 viruses. These viruses, which use CCR5 as a coreceptor, appear to have a selective advantage in transmission of HIV-1 in humans. Hence R5 viruses predominate during primary infection and persist throughout the course of disease in most infected people. Vaginal challenge of macaques with chimeric simian/human immunodeficiency viruses (SHIV) is perhaps one of the best available animal models for human HIV-1 infection. Passive transfer studies are widely used to establish the conditions for antibody protection against viral challenge. Here we show that passive intravenous transfer of the human neutralizing monoclonal antibody b12 provides dose-dependent protection to macaques vaginally challenged with the R5 virus SHIV(162P4). Four of four monkeys given 25 mg of b12 per kg of body weight 6 h prior to challenge showed no evidence of viral infection (sterile protection). Two of four monkeys given 5 mg of b12/kg were similarly protected, whereas the other two showed significantly reduced and delayed plasma viremia compared to control animals. In contrast, all four monkeys treated with a dose of 1 mg/kg became infected with viremia levels close to those for control animals. Antibody b12 serum concentrations at the time of virus challenge corresponded to approximately 400 (25 mg/kg), 80 (5 mg/kg), and 16 (1 mg/kg) times the in vitro (90%) neutralization titers. Therefore, complete protection against mucosal challenge with an R5 SHIV required essentially complete neutralization of the infecting virus. This suggests that a vaccine based on antibody alone would need to sustain serum neutralizing antibody titers (90%) of the order of 1:400 to achieve sterile protection but that lower titers, around 1:100, could provide a significant benefit. The significance of such substerilizing neutralizing antibody titers in the context of a potent cellular immune response is an important area for further study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Broadly neutralizing human anti-HIV antibody 2G12 is effective in protection against mucosal SHIV challenge even at low serum neutralizing titers.PLoS Pathog. 2009 May;5(5):e1000433. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000433. Epub 2009 May 15. PLoS Pathog. 2009. PMID: 19436712 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Efficacy of Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies with Incomplete Neutralization Activity against Simian-Human Immunodeficiency Virus in Rhesus Monkeys.J Virol. 2017 Sep 27;91(20):e01187-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01187-17. Print 2017 Oct 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28768869 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of a statistically valid neutralization titer in plasma that confers protection against simian-human immunodeficiency virus challenge following passive transfer of high-titered neutralizing antibodies.J Virol. 2002 Mar;76(5):2123-30. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.5.2123-2130.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11836389 Free PMC article.
-
Protection of neonatal macaques against experimental SHIV infection by human neutralizing monoclonal antibodies.Transfus Clin Biol. 2001 Aug;8(4):350-8. doi: 10.1016/s1246-7820(01)00187-2. Transfus Clin Biol. 2001. PMID: 11642027 Review.
-
Passive transfer studies to elucidate the role of antibody-mediated protection against HIV-1.Vaccine. 2002 May 6;20(15):1922-5. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(02)00068-3. Vaccine. 2002. PMID: 11983246 Review.
Cited by
-
Superinfection by discordant subtypes of HIV-1 does not enhance the neutralizing antibody response against autologous virus.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e38989. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038989. Epub 2012 Jun 14. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22720009 Free PMC article.
-
A broadly neutralizing macaque monoclonal antibody against the HIV-1 V3-Glycan patch.Elife. 2020 Oct 21;9:e61991. doi: 10.7554/eLife.61991. Elife. 2020. PMID: 33084569 Free PMC article.
-
Current advances in HIV vaccines.Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2004 Apr;1(1):18-24. doi: 10.1007/s11904-004-0003-1. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2004. PMID: 16091219 Review.
-
Specificity of the autologous neutralizing antibody response.Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2009 Sep;4(5):358-63. doi: 10.1097/COH.0b013e32832ea7e8. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2009. PMID: 20048698 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibody-mediated prevention and treatment of HIV-1 infection.Retrovirology. 2018 Nov 16;15(1):73. doi: 10.1186/s12977-018-0455-9. Retrovirology. 2018. PMID: 30445968 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baba T W, Liska V, Hofmann-Lehmann R, Vlasak J, Xu W, Ayehunie S, Cavacini L A, Posner M R, Katinger H, Stiegler G, Bernacky B J, Rizvi T A, Schmidt R, Hill L R, Keeling M E, Lu Y, Wright J E, Chou T C, Ruprecht R M. Human neutralizing monoclonal antibodies of the IgG1 subtype protect against mucosal simian-human immunodeficiency virus infection. Nat Med. 2000;6:200–206. - PubMed
-
- Barouch D H, Santra S, Schmitz J E, Kuroda M J, Fu T M, Wagner W, Bilska M, Craiu A, Zheng X X, Krivulka G R, Beaudry K, Lifton M A, Nickerson C E, Trigona W L, Punt K, Freed D C, Guan L, Dubey S, Casimiro D, Simon A, Davies M E, Chastain M, Strom T B, Gelman R S, Montefiori D C, Lewis M G, Emini E A, Shiver J W, Letvin N L. Control of viremia and prevention of clinical AIDS in rhesus monkeys by cytokine-augmented DNA vaccination. Science. 2000;290:486–492. - PubMed
-
- Burton D R, Pyati J, Koduri R, Sharp S J, Thornton G B, Parren P W H I, Sawyer L S W, Hendry R M, Dunlop N, Nara P L, Lamacchia M, Garratty E, Stiehm E R, Bryson Y J, Cao Y, Moore J P, Ho D D, Barbas C F. Efficient neutralization of primary isolates of HIV-1 by a recombinant human monoclonal antibody. Science. 1994;266:1024–1027. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

