Highly productive infection with pseudotyped human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) indicates no intracellular restrictions to HIV-1 replication in primary human astrocytes
- PMID: 11483737
- PMCID: PMC115036
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.75.17.7925-7933.2001
Highly productive infection with pseudotyped human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) indicates no intracellular restrictions to HIV-1 replication in primary human astrocytes
Abstract
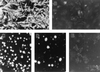
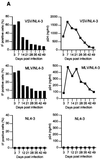
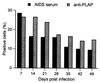
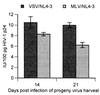
Human astrocytes can be infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) in vitro and in vivo, but, in contrast to T lymphocytes and macrophages, virus expression is inefficient. To investigate the HIV-1 life cycle in human fetal astrocytes, we infected cells with HIV-1 pseudotyped with envelope glycoproteins of either amphotropic murine leukemia virus or vesicular stomatitis virus. Infection by both pseudotypes was productive and long lasting and reached a peak of 68% infected cells and 1.7 microg of viral p24 per ml of culture supernatant 7 days after virus inoculation and then continued with gradually declining levels of virus expression through 7 weeks of follow-up. This contrasted with less than 0.1% HIV-1 antigen-positive cells and 400 pg of extracellular p24 per ml at the peak of astrocyte infection with native HIV-1. Cell viability and growth kinetics were similar in infected and control cells. Northern blot analysis revealed the presence of major HIV-1 RNA species of 9, 4, and 2 kb in astrocytes exposed to pseudotyped (but not wild-type) HIV-1 at 2, 14, and 28 days after infection. Consistent with productive infection, the 9- and 4-kb viral transcripts in astrocytes infected by pseudotyped HIV-1 were as abundant as the 2-kb mRNA during 4 weeks of follow-up, and both structural and regulatory viral proteins were detected in infected cells by immunoblotting or cell staining. The progeny virus released by these cells was infectious. These results indicate that the major barrier to HIV-1 infection of primary astrocytes is at virus entry and that astrocytes have no intrinsic intracellular restriction to efficient HIV-1 replication.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Productive infection of primary murine astrocytes, lymphocytes, and macrophages by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in culture.J Neurovirol. 2004 Dec;10(6):400-8. doi: 10.1080/13550280490890097. J Neurovirol. 2004. PMID: 15765811
-
The B-oligomer of pertussis toxin inhibits human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication at multiple stages.J Virol. 2000 Sep;74(18):8767-70. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.18.8767-8770.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10954581 Free PMC article.
-
Production of high-titer human immunodeficiency virus type 1 pseudotyped with vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein.Methods. 1997 Aug;12(4):337-42. doi: 10.1006/meth.1997.0487. Methods. 1997. PMID: 9245614
-
Astrocyte infection by HIV-1: mechanisms of restricted virus replication, and role in the pathogenesis of HIV-1-associated dementia.Curr HIV Res. 2003 Oct;1(4):463-73. doi: 10.2174/1570162033485122. Curr HIV Res. 2003. PMID: 15049431 Review.
-
Effects of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 on astrocyte gene expression and function: potential role in neuropathogenesis.J Neurovirol. 2004;10 Suppl 1:25-32. doi: 10.1080/753312749. J Neurovirol. 2004. PMID: 14982736 Review.
Cited by
-
Human synaptic plasticity gene expression profile and dendritic spine density changes in HIV-infected human CNS cells: role in HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders (HAND).PLoS One. 2013 Apr 19;8(4):e61399. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061399. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23620748 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocytes as an HIV Reservoir: Mechanism of HIV Infection.Curr HIV Res. 2016;14(5):373-381. doi: 10.2174/1570162x14666161006121455. Curr HIV Res. 2016. PMID: 27719663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The brain-specific factor FEZ1 is a determinant of neuronal susceptibility to HIV-1 infection.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Aug 18;106(33):14040-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0900502106. Epub 2009 Aug 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19667186 Free PMC article.
-
Human immunodeficiency virus-restricted replication in astrocytes and the ability of gamma interferon to modulate this restriction are regulated by a downstream effector of the Wnt signaling pathway.J Virol. 2007 Jun;81(11):5864-71. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02234-06. Epub 2007 Mar 28. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17392368 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of gene products suppressed by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection or gp120 exposure of primary human astrocytes by rapid subtraction hybridization.J Neurovirol. 2003 Jun;9(3):372-89. doi: 10.1080/13550280390201263. J Neurovirol. 2003. PMID: 12775420
References
-
- Ausubel M F, Brent R, Kingston E R, Moore D D, Seidman G J, Smith A J, Struhl K, editors. Current protocols in molecular biology. New York, N.Y: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 1995.
-
- Bagasra O, Lavi E, Bobroski L, Khalili K, Pestaner J P, Tawadros R, Pomerantz R J. Cellular reservoirs of HIV-1 in the central nervous system of infected individuals: identification by the combination of in situ polymerase chain reaction and immunohistochemistry. AIDS. 1996;10:573–585. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

