Influenza virus ns1 protein induces apoptosis in cultured cells
- PMID: 11483732
- PMCID: PMC115031
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.75.17.7875-7881.2001
Influenza virus ns1 protein induces apoptosis in cultured cells
Abstract
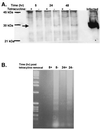
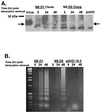
The importance of influenza viruses as worldwide pathogens in humans, domestic animals, and poultry is well recognized. Discerning how influenza viruses interact with the host at a cellular level is crucial for a better understanding of viral pathogenesis. Influenza viruses induce apoptosis through mechanisms involving the interplay of cellular and viral factors that may depend on the cell type. However, it is unclear which viral genes induce apoptosis. In these studies, we show that the expression of the nonstructural (NS) gene of influenza A virus is sufficient to induce apoptosis in MDCK and HeLa cells. Further studies showed that the multimerization domain of the NS1 protein but not the effector domain is required for apoptosis. However, this mutation is not sufficient to inhibit apoptosis using whole virus.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The NS1 gene from bat-derived influenza-like virus H17N10 can be rescued in influenza A PR8 backbone.J Gen Virol. 2016 Aug;97(8):1797-1806. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.000509. Epub 2016 May 23. J Gen Virol. 2016. PMID: 27217257
-
Unexpected Functional Divergence of Bat Influenza Virus NS1 Proteins.J Virol. 2018 Feb 12;92(5):e02097-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02097-17. Print 2018 Mar 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29237829 Free PMC article.
-
High-yield reassortant influenza vaccine production virus has a mutation at an HLA-A 2.1-restricted CD8+ CTL epitope on the NS1 protein.Virology. 1999 Jun 20;259(1):135-40. doi: 10.1006/viro.1999.9719. Virology. 1999. PMID: 10364497
-
Effects of influenza A virus NS1 protein on protein expression: the NS1 protein enhances translation and is not required for shutoff of host protein synthesis.J Virol. 2002 Feb;76(3):1206-12. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.3.1206-1212.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11773396 Free PMC article.
-
The role of nuclear NS1 protein in highly pathogenic H5N1 influenza viruses.Microbes Infect. 2017 Dec;19(12):587-596. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2017.08.011. Epub 2017 Sep 10. Microbes Infect. 2017. PMID: 28903072
Cited by
-
Caspase 3 activation is essential for efficient influenza virus propagation.EMBO J. 2003 Jun 2;22(11):2717-28. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg279. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12773387 Free PMC article.
-
139D in NS1 Contributes to the Virulence of H5N6 Influenza Virus in Mice.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Jan 21;8:808234. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.808234. eCollection 2021. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35127884 Free PMC article.
-
Newcastle disease virus V protein is a determinant of host range restriction.J Virol. 2003 Sep;77(17):9522-32. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.17.9522-9532.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12915566 Free PMC article.
-
The ER-Mitochondria Interface as a Dynamic Hub for T Cell Efficacy in Solid Tumors.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Apr 27;10:867341. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.867341. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35573704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomics reveals important host factors involved in the high pathogenicity of the H5N1 avian influenza virus in mice.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2017 Apr;206(2):125-147. doi: 10.1007/s00430-016-0489-3. Epub 2016 Dec 20. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28000052
References
-
- Albert M L, Sauter B, Bhardwaj N. Dendritic cells acquire antigen from apoptotic cells and induce class I- restricted CTLs. Nature. 1998;392:86–89. - PubMed
-
- Alonso-Caplen F V, Nemeroff M E, Qiu Y, Krug R M. Nucleocytoplasmic transport: the influenza virus NS1 protein regulates the transport of spliced NS2 mRNA and its precursor NS1 mRNA. Genes Dev. 1992;6:255–267. - PubMed
-
- Chien C Y, Tejero R, Huang Y, Zimmerman D E, Rios C B, Krug R M, Montelione G T. A novel RNA-binding motif in influenza A virus non-structural protein 1. Nat Struct Biol. 1997;4:891–895. - PubMed
-
- Collins M. Potential roles of apoptosis in viral pathogenesis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995;152:S20–S24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

