Ergosterol is required for the Sec18/ATP-dependent priming step of homotypic vacuole fusion
- PMID: 11483507
- PMCID: PMC149151
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.15.4035
Ergosterol is required for the Sec18/ATP-dependent priming step of homotypic vacuole fusion
Abstract
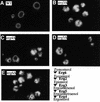
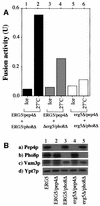
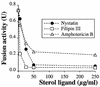
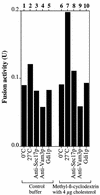
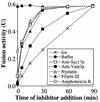
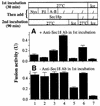
In vitro homotypic fusion of yeast vacuoles occurs in three stages: priming, the Sec18 (NSF)-mediated changes that precede vacuole association; docking, the Ypt7 and SNARE-mediated pairing of vacuoles; and fusion, mediated by calmodulin/V0/t-SNARE interactions. Defects in catalysts of each stage result in fragmented (unfused) vacuoles. Strains with deletions in any of ERG genes 3-6, lacking normal ergosterol biosynthesis, have fragmented vacuoles. The ergosterol ligands filipin, nystatin and amphotericin B block the in vitro fusion of vacuoles from wild-type cells. Each of these inhibitors acts at the priming stage to inhibit Sec17p release from vacuoles. A reversible delay in Sec18p action prevents vacuoles from acquiring resistance to any of these three drugs, confirming that their action is on the normal fusion pathway. Ergosterol or cholesterol delivery to wild-type vacuoles stimulates their in vitro fusion, and the in vitro fusion of ergDelta vacuoles requires added sterol. The need for ergosterol for vacuole priming underscores the role of lipids in organizing the membrane elements of this complex reaction.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Yeast vacuoles and membrane fusion pathways.EMBO J. 2002 Mar 15;21(6):1241-7. doi: 10.1093/emboj/21.6.1241. EMBO J. 2002. PMID: 11889030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vac8p release from the SNARE complex and its palmitoylation are coupled and essential for vacuole fusion.EMBO J. 2001 Jun 15;20(12):3145-55. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.12.3145. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11406591 Free PMC article.
-
A soluble SNARE drives rapid docking, bypassing ATP and Sec17/18p for vacuole fusion.EMBO J. 2004 Jul 21;23(14):2765-76. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600286. Epub 2004 Jul 8. EMBO J. 2004. PMID: 15241469 Free PMC article.
-
The Vtc proteins in vacuole fusion: coupling NSF activity to V(0) trans-complex formation.EMBO J. 2002 Feb 1;21(3):259-69. doi: 10.1093/emboj/21.3.259. EMBO J. 2002. PMID: 11823419 Free PMC article.
-
Yeast homotypic vacuole fusion: a window on organelle trafficking mechanisms.Annu Rev Biochem. 2000;69:247-75. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.69.1.247. Annu Rev Biochem. 2000. PMID: 10966459 Review.
Cited by
-
Direct imaging reveals stable, micrometer-scale lipid domains that segregate proteins in live cells.J Cell Biol. 2013 Jul 8;202(1):35-44. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201301039. J Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23836928 Free PMC article.
-
Nontoxic antimicrobials that evade drug resistance.Nat Chem Biol. 2015 Jul;11(7):481-7. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1821. Epub 2015 Jun 1. Nat Chem Biol. 2015. PMID: 26030729 Free PMC article.
-
Lipidome analysis reveals antifungal polyphenol curcumin affects membrane lipid homeostasis.Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2012 Jan 1;4(4):1195-209. doi: 10.2741/451. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2012. PMID: 22201946 Free PMC article.
-
Mot3 is a transcriptional repressor of ergosterol biosynthetic genes and is required for normal vacuolar function in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.EMBO J. 2002 Aug 1;21(15):4114-24. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdf415. EMBO J. 2002. PMID: 12145211 Free PMC article.
-
Yeast vacuoles and membrane fusion pathways.EMBO J. 2002 Mar 15;21(6):1241-7. doi: 10.1093/emboj/21.6.1241. EMBO J. 2002. PMID: 11889030 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bennett M.K. (1997) Ca2+ and the regulation of neurotransmitter secretion. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol., 7, 316–322. - PubMed
-
- Burd C.G. and Emr,S.D. (1998) Phosphatidylinositol (3)-phosphate signaling mediated by specific binding to RING FYVE domains. Mol. Cell, 2, 157–162. - PubMed
-
- Chavrier P. and Goud,B. (1999) The role of ARF and Rab GTPases in membrane transport. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 11, 466–475. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

