The multisubstrate adapter Gab1 regulates hepatocyte growth factor (scatter factor)-c-Met signaling for cell survival and DNA repair
- PMID: 11438654
- PMCID: PMC87224
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.15.4968-4984.2001
The multisubstrate adapter Gab1 regulates hepatocyte growth factor (scatter factor)-c-Met signaling for cell survival and DNA repair
Abstract
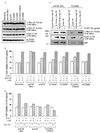
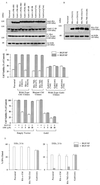
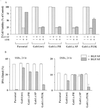
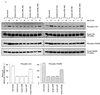
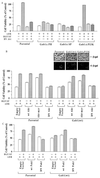
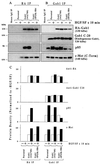
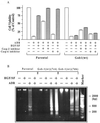
Hepatocyte growth factor (scatter factor) (HGF/SF) is a pleiotrophic mediator of epithelial cell motility, morphogenesis, angiogenesis, and tumorigenesis. HGF/SF protects cells against DNA damage by a pathway from its receptor c-Met to phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) to c-Akt, resulting in enhanced DNA repair and decreased apoptosis. We now show that protection against the DNA-damaging agent adriamycin (ADR; topoisomerase IIalpha inhibitor) requires the Grb2-binding site of c-Met, and overexpression of the Grb2-associated binder Gab1 (a multisubstrate adapter required for epithelial morphogenesis) inhibits the ability of HGF/SF to protect MDCK epithelial cells against ADR. In contrast to Gab1 and its homolog Gab2, overexpression of c-Cb1, another multisubstrate adapter that associates with c-Met, did not affect protection. Gab1 blocked the ability of HGF/SF to cause the sustained activation of c-Akt and c-Akt signaling (FKHR phosphorylation). The Gab1 inhibition of sustained c-Akt activation and of cell protection did not require the Gab1 pleckstrin homology or SHP2 phosphatase-binding domain but did require the PI3K-binding domain. HGF/SF protection of parental MDCK cells was blocked by wortmannin, expression of PTEN, and dominant negative mutants of p85 (regulatory subunit of PI3K), Akt, and Pak1; the protection of cells overexpressing Gab1 was restored by wild-type or activated mutants of p85, Akt, and Pak1. These findings suggest that the adapter Gab1 may redirect c-Met signaling through PI3K away from a c-Akt/Pak1 cell survival pathway.
Figures

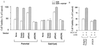

Similar articles
-
Suppression of adriamycin-induced apoptosis by sustained activation of the phosphatidylinositol-3'-OH kinase-Akt pathway.J Biol Chem. 2004 Jan 9;279(2):892-900. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M306615200. Epub 2003 Oct 21. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14570904
-
Role of NF-kappaB signaling in hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor-mediated cell protection.Oncogene. 2005 Mar 3;24(10):1749-66. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208327. Oncogene. 2005. PMID: 15688034
-
Anti-apoptotic role of caspase-cleaved GAB1 adaptor protein in hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor-MET receptor protein signaling.J Biol Chem. 2012 Oct 12;287(42):35382-35396. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.409797. Epub 2012 Aug 22. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22915589 Free PMC article.
-
Met receptor tyrosine kinase: enhanced signaling through adapter proteins.Oncogene. 2000 Nov 20;19(49):5582-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203859. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 11114738 Review.
-
Identification of functional domains in the hepatocyte growth factor and its receptor by molecular engineering.J Biotechnol. 1994 Sep 30;37(2):109-22. doi: 10.1016/0168-1656(94)90002-7. J Biotechnol. 1994. PMID: 7765452 Review.
Cited by
-
The Molecular Crosstalk between the MET Receptor Tyrosine Kinase and the DNA Damage Response-Biological and Clinical Aspects.Cancers (Basel). 2013 Dec 19;6(1):1-27. doi: 10.3390/cancers6010001. Cancers (Basel). 2013. PMID: 24378750 Free PMC article.
-
MET receptor tyrosine kinase as an autism genetic risk factor.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2013;113:135-65. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-418700-9.00005-8. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 24290385 Free PMC article. Review.
-
C-Met inhibitor MK-8003 radiosensitizes c-Met-expressing non-small-cell lung cancer cells with radiation-induced c-Met-expression.J Thorac Oncol. 2012 Aug;7(8):1211-7. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e318257cc89. J Thorac Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22617250 Free PMC article.
-
Combined EGFR/MET or EGFR/HSP90 inhibition is effective in the treatment of lung cancers codriven by mutant EGFR containing T790M and MET.Cancer Res. 2012 Jul 1;72(13):3302-11. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3720. Epub 2012 May 2. Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22552292 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of PI3K in Met Driven Cancer: A Recap.Front Mol Biosci. 2018 Oct 24;5:86. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2018.00086. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Biosci. 2018. PMID: 30406111 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adam L, Vadlamudi R, Mandal M, Chernoff J, Kumar R. Regulation of microfilament reorganization and invasiveness of breast cancer cells by kinase dead p21-activated kinase-1. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:12041–12950. - PubMed
-
- Albanese C, Johnson J, Watanabe G, Eklund N, Vu D, Arnold A, Pestell R G. Transforming p21ras mutants and c-Ets-2 activate the cyclin D promoter through distinguishable regions. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:23589–23597. - PubMed
-
- Alley M C, Scudieco D A, Monks A, Hursey M L, Czerwinski M J, Fine D L, Abbott B J, Mayo J G, Shoemaker R H, Boyd M R. Feasibility of drug screening with panels of human tumor cell lines using a microculture tetrazolium assay. Cancer Res. 1988;48:589–601. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
