Nup2p dynamically associates with the distal regions of the yeast nuclear pore complex
- PMID: 11425876
- PMCID: PMC2150724
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.153.7.1465
Nup2p dynamically associates with the distal regions of the yeast nuclear pore complex
Abstract
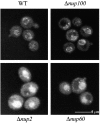
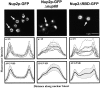
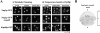
Nucleocytoplasmic transport is mediated by the interplay between soluble transport factors and nucleoporins resident within the nuclear pore complex (NPC). Understanding this process demands knowledge of components of both the soluble and stationary phases and the interface between them. Here, we provide evidence that Nup2p, previously considered to be a typical yeast nucleoporin that binds import- and export-bound karyopherins, dynamically associates with the NPC in a Ran-facilitated manner. When bound to the NPC, Nup2p associates with regions corresponding to the nuclear basket and cytoplasmic fibrils. On the nucleoplasmic face, where the Ran--GTP levels are predicted to be high, Nup2p binds to Nup60p. Deletion of NUP60 renders Nup2p nucleoplasmic and compromises Nup2p-mediated recycling of Kap60p/Srp1p. Depletion of Ran--GTP by metabolic poisoning, disruption of the Ran cycle, or in vitro by cell lysis, results in a shift of Nup2p from the nucleoplasm to the cytoplasmic face of the NPC. This mobility of Nup2p was also detected using heterokaryons where, unlike nucleoporins, Nup2p was observed to move from one nucleus to the other. Together, our data support a model in which Nup2p movement facilitates the transition between the import and export phases of nucleocytoplasmic transport.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The nucleoporin Nup60p functions as a Gsp1p-GTP-sensitive tether for Nup2p at the nuclear pore complex.J Cell Biol. 2001 Sep 3;154(5):937-50. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200101007. J Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11535617 Free PMC article.
-
Nup2p, a yeast nucleoporin, functions in bidirectional transport of importin alpha.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Nov;20(22):8468-79. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.22.8468-8479.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11046143 Free PMC article.
-
Nup2p is located on the nuclear side of the nuclear pore complex and coordinates Srp1p/importin-alpha export.J Cell Sci. 2000 Apr;113 ( Pt 8):1471-80. doi: 10.1242/jcs.113.8.1471. J Cell Sci. 2000. PMID: 10725229
-
Structural biology of nucleocytoplasmic transport.Annu Rev Biochem. 2007;76:647-71. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.76.052705.161529. Annu Rev Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17506639 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of nuclear protein transport.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1997;7(1-2):61-72. doi: 10.1615/critreveukargeneexpr.v7.i1-2.40. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1997. PMID: 9034715 Review.
Cited by
-
Nucleoporin Nup50 stabilizes closed conformation of armadillo repeat 10 in importin α5.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jan 13;287(3):2022-31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.315838. Epub 2011 Nov 30. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22130666 Free PMC article.
-
Assembly principle of a membrane-anchored nuclear pore basket scaffold.Sci Adv. 2022 Feb 11;8(6):eabl6863. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abl6863. Epub 2022 Feb 11. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 35148185 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear pore complexes and regulation of gene expression.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2017 Jun;46:26-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2016.12.006. Epub 2017 Jan 11. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28088069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selective autophagy degrades nuclear pore complexes.Nat Cell Biol. 2020 Feb;22(2):159-166. doi: 10.1038/s41556-019-0459-2. Epub 2020 Feb 6. Nat Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32029894
-
The Ccr4-Not complex interacts with the mRNA export machinery.PLoS One. 2011 Mar 28;6(3):e18302. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018302. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21464899 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aitchison J.D., Rout M.P., Marelli M., Blobel G., Wozniak R.W. Two novel related yeast nucleoporins Nup170p and Nup157pcomplementation with the vertebrate homologue Nup155p and functional interactions with the yeast nuclear pore-membrane protein Pom152p J. Cell Biol 131 1995. 1133 1148b - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aitchison J.D., Blobel G., Rout M.P. Kap104pa karyopherin involved in the nuclear transport of messenger RNA binding proteins. Science. 1996;274:624–627. - PubMed
-
- Akey C.W. Structural plasticity of the nuclear pore complex. J. Mol. Biol. 1995;248:273–293. - PubMed
-
- Allen T.D., Cronshaw J.M., Bagley S., Kiseleva E., Goldberg M.W. The nuclear pore complexmediator of translocation between nucleus and cytoplasm. J. Cell Sci. 2000;113:1651–1659. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

