Synaptic regulation of protein synthesis and the fragile X protein
- PMID: 11416194
- PMCID: PMC34629
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.141145998
Synaptic regulation of protein synthesis and the fragile X protein
Abstract
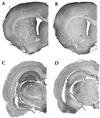
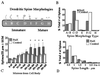
Protein synthesis occurs in neuronal dendrites, often near synapses. Polyribosomal aggregates often appear in dendritic spines, particularly during development. Polyribosomal aggregates in spines increase during experience-dependent synaptogenesis, e.g., in rats in a complex environment. Some protein synthesis appears to be regulated directly by synaptic activity. We use "synaptoneurosomes," a preparation highly enriched in pinched-off, resealed presynaptic processes attached to resealed postsynaptic processes that retain normal functions of neurotransmitter release, receptor activation, and various postsynaptic responses including signaling pathways and protein synthesis. We have found that, when synaptoneurosomes are stimulated with glutamate or group I metabotropic glutamate receptor agonists such as dihydroxyphenylglycine, mRNA is rapidly taken up into polyribosomal aggregates, and labeled methionine is incorporated into protein. One of the proteins synthesized is FMRP, the protein that is reduced or absent in fragile X mental retardation syndrome. FMRP has three RNA-binding domains and reportedly binds to a significant number of mRNAs. We have found that dihydroxyphenylglycine-activated protein synthesis in synaptoneurosomes is dramatically reduced in a knockout mouse model of fragile X syndrome, which cannot produce full-length FMRP, suggesting that FMRP is involved in or required for this process. Studies of autopsy samples from patients with fragile X syndrome have indicated that dendritic spines may fail to assume a normal mature size and shape and that there are more spines per unit dendrite length in the patient samples. Similar findings on spine size and shape have come from studies of the knockout mouse. Study of the development of the somatosensory cortical region containing the barrel-like cell arrangements that process whisker information suggests that normal dendritic regression is impaired in the knockout mouse. This finding suggests that FMRP may be required for the normal processes of maturation and elimination to occur in cerebral cortical development.
Figures
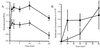

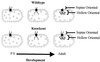
Similar articles
-
Fragile X mental retardation protein is translated near synapses in response to neurotransmitter activation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 May 13;94(10):5395-400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.10.5395. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997. PMID: 9144248 Free PMC article.
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptor activation regulates fragile x mental retardation protein and FMR1 mRNA localization differentially in dendrites and at synapses.J Neurosci. 2004 Mar 17;24(11):2648-55. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0099-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15028757 Free PMC article.
-
Dendritic spine structural anomalies in fragile-X mental retardation syndrome.Cereb Cortex. 2000 Oct;10(10):1038-44. doi: 10.1093/cercor/10.10.1038. Cereb Cortex. 2000. PMID: 11007554 Review.
-
The fragile X mental retardation protein and group I metabotropic glutamate receptors regulate levels of mRNA granules in brain.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Feb 8;102(6):2180-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0409803102. Epub 2005 Jan 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15684045 Free PMC article.
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptors and fragile x mental retardation protein: partners in translational regulation at the synapse.Sci Signal. 2008 Feb 5;1(5):pe6. doi: 10.1126/stke.15pe6. Sci Signal. 2008. PMID: 18272470 Review.
Cited by
-
The germ cell-specific RNA binding protein RBM46 is essential for spermatogonial differentiation in mice.PLoS Genet. 2022 Sep 21;18(9):e1010416. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010416. eCollection 2022 Sep. PLoS Genet. 2022. PMID: 36129965 Free PMC article.
-
Animal models of human cerebellar ataxias: a cornerstone for the therapies of the twenty-first century.Cerebellum. 2009 Sep;8(3):137-54. doi: 10.1007/s12311-009-0127-3. Cerebellum. 2009. PMID: 19669387
-
Distance delivery of a parent-implemented language intervention for young boys with fragile X syndrome.Autism Dev Lang Impair. 2017 Jan-Dec;2:10.1177/2396941517728690. doi: 10.1177/2396941517728690. Epub 2017 Sep 4. Autism Dev Lang Impair. 2017. PMID: 30417116 Free PMC article.
-
Whole genome microarray analysis of gene expression in subjects with fragile X syndrome.Genet Med. 2007 Jul;9(7):464-72. doi: 10.1097/gim.0b013e3180ca9a9a. Genet Med. 2007. PMID: 17666893 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Altered mRNA transport, docking, and protein translation in neurons lacking fragile X mental retardation protein.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Aug 31;107(35):15601-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1010564107. Epub 2010 Aug 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20713728 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

