Vac8p release from the SNARE complex and its palmitoylation are coupled and essential for vacuole fusion
- PMID: 11406591
- PMCID: PMC150195
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.12.3145
Vac8p release from the SNARE complex and its palmitoylation are coupled and essential for vacuole fusion
Abstract
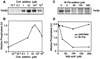
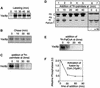
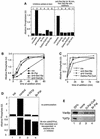
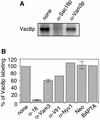
Activated fatty acids stimulate budding and fusion in several cell-free assays for vesicular transport. This stimulation is thought to be due to protein palmitoylation, but relevant substrates have not yet been identified. We now report that Vac8p, a protein known to be required for vacuole inheritance, becomes palmitoylated when isolated yeast vacuoles are incubated under conditions that allow membrane fusion. Similar requirements for Vac8p palmitoylation and vacuole fusion, the inhibition of vacuole fusion by antibodies to Vac8p and the strongly reduced fusion of vacuoles lacking Vac8p suggest that palmitoylated Vac8p is essential for homotypic vacuole fusion. Strikingly, palmitoylation of Vac8p is blocked by the addition of antibodies to Sec18p (yeast NSF) only. Consistent with this, a portion of Vac8p is associated with the SNARE complex on vacuoles, which is lost during Sec18p- and ATP-dependent priming. During or after SNARE complex disassembly, palmitoylation occurs and anchors Vac8p to the vacuolar membrane. We propose that palmitoylation of Vac8p is regulated by the same machinery that controls membrane fusion.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fusion of docked membranes requires the armadillo repeat protein Vac8p.J Biol Chem. 2001 Sep 14;276(37):35133-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M103937200. Epub 2001 Jul 5. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11441010
-
The Vtc proteins in vacuole fusion: coupling NSF activity to V(0) trans-complex formation.EMBO J. 2002 Feb 1;21(3):259-69. doi: 10.1093/emboj/21.3.259. EMBO J. 2002. PMID: 11823419 Free PMC article.
-
Ergosterol is required for the Sec18/ATP-dependent priming step of homotypic vacuole fusion.EMBO J. 2001 Aug 1;20(15):4035-40. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.15.4035. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11483507 Free PMC article.
-
Novel pathways, membrane coats and PI kinase regulation in yeast lysosomal trafficking.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 1998 Oct;9(5):527-33. doi: 10.1006/scdb.1998.0255. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 1998. PMID: 9835640 Review.
-
Probing protein palmitoylation at the yeast vacuole.Methods. 2006 Oct;40(2):171-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2006.06.020. Methods. 2006. PMID: 17012029 Review.
Cited by
-
Saccharomyces cerevisiae Env7 is a novel serine/threonine kinase 16-related protein kinase and negatively regulates organelle fusion at the lysosomal vacuole.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Feb;33(3):526-42. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01303-12. Epub 2012 Nov 19. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23166297 Free PMC article.
-
The vacuolar DHHC-CRD protein Pfa3p is a protein acyltransferase for Vac8p.J Cell Biol. 2005 Sep 26;170(7):1091-9. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200507048. J Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16186255 Free PMC article.
-
A cycle of Vam7p release from and PtdIns 3-P-dependent rebinding to the yeast vacuole is required for homotypic vacuole fusion.J Cell Biol. 2002 Apr 1;157(1):79-89. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200112098. Epub 2002 Mar 26. J Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11916982 Free PMC article.
-
Vac8 Controls Vacuolar Membrane Dynamics during Different Autophagy Pathways in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Cells. 2019 Jun 30;8(7):661. doi: 10.3390/cells8070661. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31262095 Free PMC article.
-
Yeast vacuoles and membrane fusion pathways.EMBO J. 2002 Mar 15;21(6):1241-7. doi: 10.1093/emboj/21.6.1241. EMBO J. 2002. PMID: 11889030 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Berthiaume L. and Resh,M.D. (1995) Biochemical characterization of a palmitoyl acyltransferase activity that palmitoylates myristoylated proteins. J. Biol. Chem., 270, 22399–22405. - PubMed
-
- Choi J.Y. and Martin,C.E. (1999) The Saccharomyces cerevisiae FAT1 gene encodes an acyl-CoA synthetase that is required for maintenance of very long chain fatty acid levels. J. Biol. Chem., 274, 4671–4683. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

