Stat3-mediated Myc expression is required for Src transformation and PDGF-induced mitogenesis
- PMID: 11404481
- PMCID: PMC34666
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.131568898
Stat3-mediated Myc expression is required for Src transformation and PDGF-induced mitogenesis
Abstract
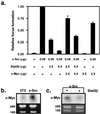
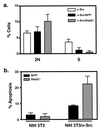
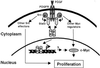
Signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) proteins perform key roles in mediating signaling by cytokines and growth factors, including platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF). In addition, Src family kinases activate STAT signaling and are required for PDGF-induced mitogenesis in normal cells. One STAT family member, Stat3, has been shown to have an essential role in cell transformation by the Src oncoprotein. However, the mechanisms by which STAT-signaling pathways contribute to mitogenesis and transformation are not fully defined. We show here that disruption of Stat3 signaling by using dominant-negative Stat3beta protein in NIH 3T3 fibroblasts suppresses c-Myc expression concomitant with inhibition of v-Src-induced transformation. Ectopic expression of c-Myc is able to partially reverse this inhibition, suggesting that c-Myc is a downstream effector of Stat3 signaling in v-Src transformation. Furthermore, c-myc gene knockout fibroblasts are refractory to transformation by v-Src, consistent with a requirement for c-Myc protein in v-Src transformation. In normal NIH 3T3 cells, disruption of Stat3 signaling with dominant-negative Stat3beta protein inhibits PDGF-induced mitogenesis in a manner that is reversed by ectopic c-Myc expression. Moreover, inhibition of Src family kinases with the pharmacologic agent, SU6656, blocks Stat3 activation by PDGF. These findings, combined together, delineate the signaling pathway, PDGF --> Src --> Stat3 --> Myc, that is important in normal PDGF-induced mitogenesis and subverted in Src transformation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Stat3 activation by Src induces specific gene regulation and is required for cell transformation.Mol Cell Biol. 1998 May;18(5):2545-52. doi: 10.1128/MCB.18.5.2545. Mol Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9566874 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the JAK-STAT pathway in PDGF-stimulated proliferation of human airway smooth muscle cells.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2002 Jun;282(6):L1296-304. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00315.2001. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12003786
-
The Src and signal transducers and activators of transcription pathways as specific targets for low molecular weight phosphotyrosine-protein phosphatase in platelet-derived growth factor signaling.J Biol Chem. 1998 Mar 20;273(12):6776-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.12.6776. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9506979
-
Activation of Stat3 in v-Src-transformed fibroblasts requires cooperation of Jak1 kinase activity.J Biol Chem. 2000 Aug 11;275(32):24935-44. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M002383200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10823829
-
G protein coupled receptor signaling through the Src and Stat3 pathway: role in proliferation and transformation.Oncogene. 2001 Mar 26;20(13):1601-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204186. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11313907 Review.
Cited by
-
PTTG acts as a STAT3 target gene for colorectal cancer cell growth and motility.Oncogene. 2014 Feb 13;33(7):851-61. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.16. Epub 2013 Feb 18. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 23416975 Free PMC article.
-
Oligonucleotide-Based Therapeutics for STAT3 Targeting in Cancer-Drug Carriers Matter.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Nov 29;15(23):5647. doi: 10.3390/cancers15235647. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38067351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thymidine phosphorylase inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation via upregulation of STAT3.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Aug;1823(8):1316-23. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.05.025. Epub 2012 Jun 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22668509 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting JAK kinase in solid tumors: emerging opportunities and challenges.Oncogene. 2016 Feb 25;35(8):939-51. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.150. Epub 2015 May 18. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 25982279 Review.
-
Transcription Factors STAT3 and MYC Are Key Players of Human Platelet Lysate-Induced Cell Proliferation.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 13;23(24):15782. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415782. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555426 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Darnell J E., Jr Science. 1997;277:1630–1635. - PubMed
-
- Stark G R, Kerr I M, Williams B R, Silverman R H, Schreiber R D. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:227–264. - PubMed
-
- Bromberg J, Darnell J E., Jr Oncogene. 2000;19:2468–2473. - PubMed
-
- Silvennoinen O, Schindler C, Schlessinger J, Levy D E. Science. 1993;261:1736–1739. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

