Identification of a novel transcriptional repressor encoded by human cytomegalovirus
- PMID: 11390608
- PMCID: PMC114322
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.13.6062-6069.2001
Identification of a novel transcriptional repressor encoded by human cytomegalovirus
Abstract
The expression of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) genes during viral replication is precisely regulated, with the interactions of both transcriptional activators and repressors determining the level of gene expression. One gene of HCMV, the US3 gene, is transcriptionally repressed early in infection. Repression of US3 expression requires viral infection and protein synthesis and is mediated through a DNA sequence, the transcriptional repressive element. In this report, we identify the protein that represses US3 transcription as the product of the HCMV UL34 open reading frame. The protein encoded by UL34 (pUL34) binds to the US3 transcriptional repressive element in yeast and in vitro. pUL34 localizes to the nucleus and alone is sufficient for repression of US3 expression. The data presented here, along with earlier data (B. J. Biegalke, J. Virol. 72:5457-5463, 1998), suggests that pUL34 binding of the transcriptional repressive element prevents transcription initiation complex formation.
Figures


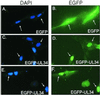
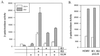
Similar articles
-
Identification of the functional domains of the essential human cytomegalovirus UL34 proteins.Virology. 2006 Sep 15;353(1):27-34. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.05.019. Epub 2006 Jun 19. Virology. 2006. PMID: 16784766
-
Characterization of the transcriptional repressive element of the human cytomegalovirus immediate-early US3 gene.J Virol. 1998 Jul;72(7):5457-63. doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.7.5457-5463.1998. J Virol. 1998. PMID: 9621001 Free PMC article.
-
IE2 protein is insufficient for transcriptional repression of the human cytomegalovirus US3 promoter.J Virol. 1997 Oct;71(10):8056-60. doi: 10.1128/JVI.71.10.8056-8060.1997. J Virol. 1997. PMID: 9311904 Free PMC article.
-
Functional roles of immediate early proteins encoded by the human cytomegalovirus UL36-38, UL115-119, TRS1/IRS1 and US3 loci.Intervirology. 1996;39(5-6):350-60. doi: 10.1159/000150506. Intervirology. 1996. PMID: 9130045 Review.
-
Inhibition of the MHC class II antigen presentation pathway by human cytomegalovirus.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2002;269:101-15. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-59421-2_7. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12224504 Review.
Cited by
-
Mouse Cytomegalovirus M34 Encodes a Non-essential, Nuclear, Early-Late Expressed Protein Required for Efficient Viral Replication.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 May 5;10:171. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00171. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32432049 Free PMC article.
-
pUL34 binding near the human cytomegalovirus origin of lytic replication enhances DNA replication and viral growth.Virology. 2018 May;518:414-422. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2018.03.017. Epub 2018 Apr 5. Virology. 2018. PMID: 29626748 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the human cytomegalovirus UL34 gene.J Virol. 2004 Sep;78(17):9579-83. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.17.9579-9583.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15308752 Free PMC article.
-
Human cytomegalovirus UL34 binds to multiple sites within the viral genome.J Virol. 2013 Mar;87(6):3587-91. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03309-12. Epub 2013 Jan 2. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23283944 Free PMC article.
-
UL34 Deletion Restricts Human Cytomegalovirus Capsid Formation and Maturation.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 21;23(10):5773. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105773. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628580 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

