An important role of an inducible RNA-dependent RNA polymerase in plant antiviral defense
- PMID: 11353867
- PMCID: PMC33500
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.111440998
An important role of an inducible RNA-dependent RNA polymerase in plant antiviral defense
Abstract
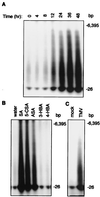
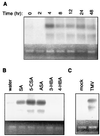
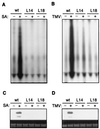
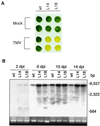
Plants contain RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP) activities that synthesize short cRNAs by using cellular or viral RNAs as templates. During studies of salicylic acid (SA)-induced resistance to viral pathogens, we recently found that the activity of a tobacco RdRP was increased in virus-infected or SA-treated plants. Biologically active SA analogs capable of activating plant defense response also induced the RdRP activity, whereas biologically inactive analogs did not. A tobacco RdRP gene, NtRDRP1, was isolated and found to be induced both by virus infection and by treatment with SA or its biologically active analogs. Tobacco lines deficient in the inducible RDRP activity were obtained by expressing antisense RNA for the NtRDRP1 gene in transgenic plants. When infected by tobacco mosaic virus, these transgenic plants accumulated significantly higher levels of viral RNA and developed more severe disease symptoms than wild-type plants. After infection by a strain of potato virus X that does not spread in wild-type tobacco plants, the transgenic NtRDRP1 antisense plants accumulated virus and developed symptoms not only locally in inoculated leaves but also systemically in upper uninoculated leaves. These results strongly suggest that inducible RdRP activity plays an important role in plant antiviral defense.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Analysis of the involvement of an inducible Arabidopsis RNA-dependent RNA polymerase in antiviral defense.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2003 Mar;16(3):206-16. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2003.16.3.206. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2003. PMID: 12650452
-
Salicylic acid treatment and expression of an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase 1 transgene inhibit lethal symptoms and meristem invasion during tobacco mosaic virus infection in Nicotiana benthamiana.BMC Plant Biol. 2016 Jan 13;16:15. doi: 10.1186/s12870-016-0705-8. BMC Plant Biol. 2016. PMID: 26757721 Free PMC article.
-
RNA silencing-related genes contribute to tolerance of infection with potato virus X and Y in a susceptible tomato plant.Virol J. 2020 Oct 8;17(1):149. doi: 10.1186/s12985-020-01414-x. Virol J. 2020. PMID: 33032637 Free PMC article.
-
Salicylic acid-mediated and RNA-silencing defense mechanisms cooperate in the restriction of systemic spread of plum pox virus in tobacco.Plant J. 2006 Oct;48(2):217-27. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02861.x. Plant J. 2006. PMID: 17018032
-
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase 1 in potato (Solanum tuberosum) and its relationship to other plant RNA-dependent RNA polymerases.Sci Rep. 2016 Mar 16;6:23082. doi: 10.1038/srep23082. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26979928 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Molecular cloning and characterization of an inducible RNA-dependent RNA polymerase gene, GhRdRP, from cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.).Mol Biol Rep. 2009 Jan;36(1):47-56. doi: 10.1007/s11033-007-9150-y. Epub 2007 Oct 11. Mol Biol Rep. 2009. PMID: 17929195
-
RNA Interference: A Natural Immune System of Plants to Counteract Biotic Stressors.Cells. 2019 Jan 10;8(1):38. doi: 10.3390/cells8010038. Cells. 2019. PMID: 30634662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural resistance of tomato plants to Tomato yellow leaf curl virus.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Dec 19;13:1081549. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1081549. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36600922 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CaRDR1, an RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Plays a Positive Role in Pepper Resistance against TMV.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Jun 28;8:1068. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01068. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28702034 Free PMC article.
-
Long-distance movement, virulence, and RNA silencing suppression controlled by a single protein in hordei- and potyviruses: complementary functions between virus families.J Virol. 2002 Dec;76(24):12981-91. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.24.12981-12991.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12438624 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Astier-Manifacier S, Cornuet P. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1978;287:1043–1046. - PubMed
-
- Astier-Manifacier S, Cornuet P. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971;232:484–493. - PubMed
-
- Boege F. Biosci Rep. 1982;2:379–389. - PubMed
-
- Boege F, Rohde W, Sanger H L. Biosci Rep. 1982;2:185–194. - PubMed
-
- Dorssers L, Zabel P, van der Meer J, van Kammen A. Virology. 1982;116:236–249. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

