Pgc-1-related coactivator, a novel, serum-inducible coactivator of nuclear respiratory factor 1-dependent transcription in mammalian cells
- PMID: 11340167
- PMCID: PMC87014
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.11.3738-3749.2001
Pgc-1-related coactivator, a novel, serum-inducible coactivator of nuclear respiratory factor 1-dependent transcription in mammalian cells
Abstract
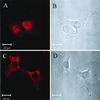
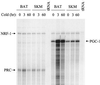
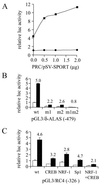
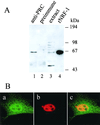
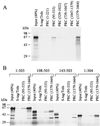
The thermogenic peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR-gamma) coactivator 1 (PGC-1) has previously been shown to activate mitochondrial biogenesis in part through a direct interaction with nuclear respiratory factor 1 (NRF-1). In order to identify related coactivators that act through NRF-1, we searched the databases for sequences with similarities to PGC-1. Here, we describe the first characterization of a 177-kDa transcriptional coactivator, designated PGC-1-related coactivator (PRC). PRC is ubiquitously expressed in murine and human tissues and cell lines; but unlike PGC-1, PRC was not dramatically up-regulated during thermogenesis in brown fat. However, its expression was down-regulated in quiescent BALB/3T3 cells and was rapidly induced by reintroduction of serum, conditions where PGC-1 was not detected. PRC activated NRF-1-dependent promoters in a manner similar to that observed for PGC-1. Moreover, NRF-1 was immunoprecipitated from cell extracts by antibodies directed against PRC, and both proteins were colocalized to the nucleoplasm by confocal laser scanning microscopy. PRC interacts in vitro with the NRF-1 DNA binding domain through two distinct recognition motifs that are separated by an unstructured proline-rich region. PRC also contains a potent transcriptional activation domain in its amino terminus adjacent to an LXXLL motif. The spatial arrangement of these functional domains coincides with those found in PGC-1, supporting the conclusion that PRC and PGC-1 are structurally and functionally related. We conclude that PRC is a functional relative of PGC-1 that operates through NRF-1 and possibly other activators in response to proliferative signals.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Control of mitochondrial transcription specificity factors (TFB1M and TFB2M) by nuclear respiratory factors (NRF-1 and NRF-2) and PGC-1 family coactivators.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Feb;25(4):1354-66. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.4.1354-1366.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15684387 Free PMC article.
-
PGC-1-related coactivator: immediate early expression and characterization of a CREB/NRF-1 binding domain associated with cytochrome c promoter occupancy and respiratory growth.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Oct;26(20):7409-19. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00585-06. Epub 2006 Aug 14. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16908542 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional activators and coactivators in the nuclear control of mitochondrial function in mammalian cells.Gene. 2002 Mar 6;286(1):81-9. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(01)00809-5. Gene. 2002. PMID: 11943463
-
Nuclear control of respiratory chain expression by nuclear respiratory factors and PGC-1-related coactivator.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008 Dec;1147:321-34. doi: 10.1196/annals.1427.006. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008. PMID: 19076454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of PPAR gamma co-activator-1, nuclear respiratory factors 1 and 2, and PPAR alpha in the adaptive response to endurance exercise.Proc Nutr Soc. 2004 May;63(2):269-73. doi: 10.1079/PNS2004334. Proc Nutr Soc. 2004. PMID: 15294042 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptional regulation of insulin-degrading enzyme modulates mitochondrial amyloid β (Aβ) peptide catabolism and functionality.J Biol Chem. 2013 May 3;288(18):12920-31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.424820. Epub 2013 Mar 22. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23525105 Free PMC article.
-
The hitchhiker's guide to PGC-1α isoform structure and biological functions.Diabetologia. 2015 Sep;58(9):1969-77. doi: 10.1007/s00125-015-3671-z. Epub 2015 Jun 25. Diabetologia. 2015. PMID: 26109214 Review.
-
PPRC1, but not PGC-1α, levels directly correlate with expression of mitochondrial proteins in human dermal fibroblasts.Genet Mol Biol. 2020 Jul 3;43(1 suppl. 1):e20190083. doi: 10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2019-0083. Genet Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32639509 Free PMC article.
-
Co-activator candidate interactions for orphan nuclear receptor NR2E1.BMC Genomics. 2016 Oct 26;17(1):832. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3173-5. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27782803 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial energy metabolism in heart failure: a question of balance.J Clin Invest. 2005 Mar;115(3):547-55. doi: 10.1172/JCI24405. J Clin Invest. 2005. PMID: 15765136 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ausubel F M, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D D, Seidman J G, Smith J A, Struhl K. Current protocols in molecular biology. New York, N.Y: John Wiley and Sons; 1990.
-
- Becker T S, Burgess S M, Amsterdam A H, Allende M L, Hopkins N. not really finished is crucial for development of the zebrafish outer retina and encodes a transcription factor highly homologous to human nuclear respiratory factor 1 and avian initiation binding repressor. Development. 1998;124:4369–4378. - PubMed
-
- Braidotti G, Borthwick I A, May B K. Identification of regulatory sequences in the gene for 5-aminolevulinate synthase from rat. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:1109–1117. - PubMed
-
- Chau C A, Evans M J, Scarpulla R C. Nuclear respiratory factor 1 activation sites in genes encoding the gamma-subunit of ATP synthase, eukaryotic initiation factor 2α, and tyrosine aminotransferase. Specific interaction of purified NRF-1 with multiple target genes. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:6999–7006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
