A new focal adhesion protein that interacts with integrin-linked kinase and regulates cell adhesion and spreading
- PMID: 11331308
- PMCID: PMC2190577
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.153.3.585
A new focal adhesion protein that interacts with integrin-linked kinase and regulates cell adhesion and spreading
Abstract
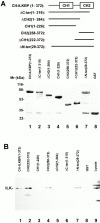
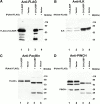
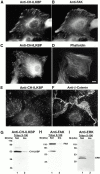
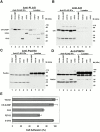
Integrin-linked kinase (ILK) is a multidomain focal adhesion (FA) protein that functions as an important regulator of integrin-mediated processes. We report here the identification and characterization of a new calponin homology (CH) domain-containing ILK-binding protein (CH-ILKBP). CH-ILKBP is widely expressed and highly conserved among different organisms from nematodes to human. CH-ILKBP interacts with ILK in vitro and in vivo, and the ILK COOH-terminal domain and the CH-ILKBP CH2 domain mediate the interaction. CH-ILKBP, ILK, and PINCH, a FA protein that binds the NH(2)-terminal domain of ILK, form a complex in cells. Using multiple approaches (epitope-tagged CH-ILKBP, monoclonal anti-CH-ILKBP antibodies, and green fluorescent protein-CH-ILKBP), we demonstrate that CH-ILKBP localizes to FAs and associates with the cytoskeleton. Deletion of the ILK-binding CH2 domain abolished the ability of CH-ILKBP to localize to FAs. Furthermore, the CH2 domain alone is sufficient for FA targeting, and a point mutation that inhibits the ILK-binding impaired the FA localization of CH-ILKBP. Thus, the CH2 domain, through its interaction with ILK, mediates the FA localization of CH-ILKBP. Finally, we show that overexpression of the ILK-binding CH2 fragment or the ILK-binding defective point mutant inhibited cell adhesion and spreading. These findings reveal a novel CH-ILKBP-ILK-PINCH complex and provide important evidence for a crucial role of this complex in the regulation of cell adhesion and cytoskeleton organization.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Assembly of the PINCH-ILK-CH-ILKBP complex precedes and is essential for localization of each component to cell-matrix adhesion sites.J Cell Sci. 2002 Dec 15;115(Pt 24):4777-86. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00166. J Cell Sci. 2002. PMID: 12432066
-
Regulation of fibronectin matrix deposition and cell proliferation by the PINCH-ILK-CH-ILKBP complex.FASEB J. 2002 Aug;16(10):1298-300. doi: 10.1096/fj.02-0089fje. Epub 2002 Jun 7. FASEB J. 2002. PMID: 12060675
-
Characterization of PINCH-2, a new focal adhesion protein that regulates the PINCH-1-ILK interaction, cell spreading, and migration.J Biol Chem. 2002 Oct 11;277(41):38328-38. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M205576200. Epub 2002 Aug 6. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12167643
-
The PINCH-ILK-parvin complexes: assembly, functions and regulation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Jul 5;1692(2-3):55-62. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2004.01.006. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 15246679 Review.
-
Integrin-linked kinase and associated proteins (review).Int J Mol Med. 1999 Jun;3(6):563-72. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.3.6.563. Int J Mol Med. 1999. PMID: 10341284 Review.
Cited by
-
Interlaboratory reproducibility of large-scale human protein-complex analysis by standardized AP-MS.Nat Methods. 2013 Apr;10(4):307-14. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2400. Epub 2013 Mar 3. Nat Methods. 2013. PMID: 23455922
-
Integrin-Linked Kinase: It's Role in the Vascular System.Int J Biomed Sci. 2007 Mar;3(1):1-8. Int J Biomed Sci. 2007. PMID: 23675014 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin-linked kinase regulates chondrocyte shape and proliferation.EMBO Rep. 2003 Apr;4(4):432-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.embor801. EMBO Rep. 2003. PMID: 12671688 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of Novel Methylation-Driven Gene Model and Investigation of PARVB Function in Glioblastoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Sep 10;11:705547. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.705547. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34568031 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional characterization of two alternative splicing variants of mouse Endothelial Cell-Specific Chemotaxis Regulator (ECSCR).Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(4):4920-4936. doi: 10.3390/ijms13044920. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22606020 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burridge K., Chrzanowska-Wodnicka M. Focal adhesions, contractility, and signaling. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1996;12:463–518. - PubMed
-
- Calderwood D.A., Shattil S.J., Ginsberg M.H. Integrins and actin filamentsreciprocal regulation of cell adhesion and signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:22607–22610. - PubMed
-
- Clark E.A., Brugge J.S. Integrins and signal transduction pathwaysthe road taken. Science. 1995;268:233–239. - PubMed
-
- Dedhar S., Hannigan G.E. Integrin cytoplasmic interactions and bidirectional transmembrane signalling. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1996;8:657–669. - PubMed
-
- Dedhar S., Williams B., Hannigan G. Integrin linked kinase (ILK)a regulator of integrin and growth-factor signaling. Trends Cell Biol. 1999;9:319–323. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

